Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (48): 7185-7191.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.48.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biocompatibility of anatomic porous titanium fusion cage
A Jian-cuo, Wang Xi-min, Li Zhan-yin, Xu Zhi-hua
- Qinghai Red Cross Hospital, Xining 810000, Qinghai Province, China
-
Revised:2016-09-10Online:2016-11-25Published:2016-11-25 -
About author:A Jian-cuo, Associate chief physician, Qinghai Red Cross Hospital, Xining 810000, Qinghai Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
A Jian-cuo, Wang Xi-min, Li Zhan-yin, Xu Zhi-hua. Biocompatibility of anatomic porous titanium fusion cage[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(48): 7185-7191.
share this article
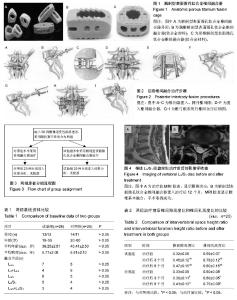
2.1 参与者数量分析 按意向性处理,50例腰椎退变性疾病患者全部进入结果分析,无脱落。 2.2 随机分组流程图 见图3。 2.3 基线资料比较 两组基线资料比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),组间具有可比性,见表1。 2.4 融合率比较 随访6-29个月,试验组23例获得融合,融合率为92.0%,显著高于对照组17例节段获得融合,融合率为68.0%,试验组融合率高于对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.5 两组椎间隙高度比和椎间孔高度比的比较 治疗前,两组椎间隙高度比和椎间孔高度比比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);试验组治疗后3,6个月的椎间隙高度比和椎间孔高度比显著高于对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表2。"

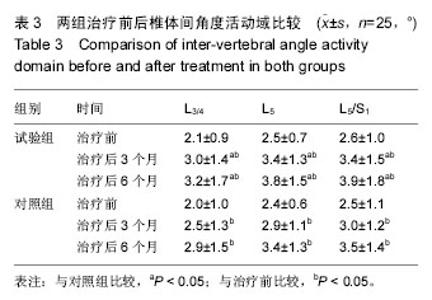
2.6 两组椎体间角度活动域的比较 治疗前,两组L3/4、L5及L5/S1椎体间角度活动域比较差异无显著性意义 (P > 0.05);试验组治疗后3,6个月的L3/4、L5及L5/S1椎体间角度活动域显著大于对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表3。 2.7 两组融合节段前凸角、腰椎前凸角、腰椎水平角及骶骨水平角的比较 治疗前,两组融合阶段前凸角、腰椎前凸角、腰椎水平角及骶骨水平角比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);试验组治疗后3,6个月的融合节段前凸角、腰椎前凸角、腰椎水平角及骶骨水平角显著大于对照组(P < 0.05),见表4。 2.8 两组融合器生物相容性比较 试验组解剖型表面微孔钛合金椎间融合器生物相容性良好,术后患者能进行正常的功能锻炼,并未出现等排斥不良反应;对照组3例出现感染、慢性脑脊液漏等后遗症,发生率为12.0%。 2.9 典型病例 40岁女性患者术前行MRI检查显示L5/S1间盘突出,中央偏左,行解剖型表面微孔钛合金椎间融合器置入治疗,治疗后效果理想,见图4。 "

| [1] 吴海挺,蒋国强,卢斌,等.Dynesys 动态稳定系统治疗多节段腰椎退变性疾病的中远期临床疗效观察[J].中国骨伤,2015,28(11):1000-1005.[2] 陈喜君,范顺武.动态中和固定系统治疗腰椎退行性疾病的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2013,26(6):526-529.[3] Jiang YQ,Che W,Wang HR,et al.Minimum 5 year follow up of multi segmental lumbar degenerative disease treated with discecto-my and the Wallis interspinous device.J Clin Neurosci.2015;22(7): 1144-1149.[4] 伍骥,张新和.棘突间动态稳定系统在保留脊柱运动功能中的作用与思考[J].中国骨伤,2011,24(4):269-272.[5] Maserati MB,Tormenti MJ,Panczykowski DM,et al.The use of a hybrid dynamic stabilization and fusion system in the lumbar spine:preliminary experience.Neurosurg Focus.2010;28(6):E2.[6] Kim CH,Chung CK,Jahng TA.Comparisons of outcomes after single or multilevel dynamic stabilization:effects on adjacent segment.J Spinal Disord Tech.2011;24(1):60-67.[7] Yu SW,Yen CY,Wu CH,et al.Radiographic and clinical results of posterior dynamic stabilization for the treatment of multisegment degenerative disc disease with a minimum follow up of 3 years.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2012;132(5):583-589.[8] Kim MK,Lee SH,Kim ES,et al.The impact of sagittal balance on clinical results after posterior interbody fusion for patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis: a pilot study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2011;12:69.[9] Xavier F,Goldwyn E,Hayes W,et al. A comparison of the compressive strength of various distal locking screw options in the treatment of tibia fractures with intramedullary nails.J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2011; 21(3):185-192.[10] 张国栋,毛文玉,廖维靖,等.基于三维重建技术及有限元分析的脊柱骨密度测量及其意义解剖型表面微孔钛合金椎间融合器置入治疗[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2010, 28(1):78-84.[11] Rollinghoff M,Zarghooni K,Dargel J,et al.The present role of verteb roplasty and kyphoplasty in the treatment of fresh vertebral compression fractures. Minerva Chir.2010;65(4):429-437.[12] Li XH,Song YM,Duan H.Preparation and in vitro biomechanical analysis of PDLLA Cage following implantation into a goat cervical spine model. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu.2009;13(52):10211-10217.[13] 徐惠,李春雷,张斯凡,等.微孔纳米羟基磷灰石的水热合成与结构表征[J].化学研究与应用,2008,20(11): 1405-1409.[14] 吴刚强,刘进,郎中敏,等.羟基磷灰石纳米粉体的制备及表征[J].无机盐工业,2009,41(10):32-34.[15] 石袁嫒,刘昌胜.溶胶-凝胶法制备纳米羟基磷灰石[J].中国医学科学学报,2002,24(2):129-133.[16] 嵇伟平,韩培,蒋垚,等.纳米骨植入材料表面结构及作用机制研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2007,28(2): 125-127.[17] Abd El-Fattah H,Helmy Y,El-Kholy B,et al.In vivo animal histomorphometric study for evaluating biocompatibility and osteointegration of nano-hydroxyapatite as biomaterials intissue engineering.J Egypat Natl Canc Iust.2010;22(4): 241-250.[18] 李鸿,李玉宝,严永刚,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66多孔材料制备和生物安全性初步评价[J].生物医学工程杂志,2008,25(5):1126-1129.[19] Wang L,Song Y,Pei F,et al.Application of nano-hydroxyapatite/ polyamide 66 cage in reconstruction of spinal stability after resection of spinal tumor.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2011;25(8):941-945.[20] Huang D,Zuo Y,Li J,et al.Bioactive composite gradient coatings of nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide66 fabricated on polyamide66 substrates.J R Soc Interface. 2012;9(72):1450-1457.[21] Xu Q,Lu H,Zhang J,et al.Tissue engineering scaffold material of porous nanohydroxyapatite/polyamide 66.Int J Nanomedicine.2010;5:331-335.[22] Huang D,Zuo Y,Zou Q,et al.Reinforced nanohydroxyapatite/polyamide66 scaffolds by chitosan coating for bone tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2012;100(1):51-57.[23] 周立伟,魏世成,李玉宝,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合人工骨修复颅骨缺损的动物实验研究[J].口腔医学,2009,29(11):561-585.[24] 肖进飞,张阳,李放,等.Dynesys动态内固定与融合术治疗L4/5单节段退变疾病的疗效对比[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2014,24(10):873-878.[25] 胡炜,吴彦生,张斌,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合生物活性材料构建的人工椎体治疗脊柱疾病[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(38):7177-7180.[26] Macheras GA,Papageloppoulos PJ,Kateros K,et al.Radiological evaluation of the metal-bone interface of a porous tantalum monoblock acetabular component.J Bone Joint Sung(Br).2006,88:304-309.[27] Jafari SM,Bender B,Coyle C,et al.Dotantalum and titanium cups show similar vesults in revision hip artroplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2010;468(2): 459-465.[28] 路荣建,刘洪臣.多孔钽作为骨植入材料的研究进展[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2013, 11(3):173-176.[29] 李海鹏,姚建华,孙天胜,等.多孔钽金属髋臼假体在初次全髋关节置换中的应用[J].解放军医药杂志,2013,25(9): 32-34.[30] Dabrowski B,Swieszkowski W,Godlinski D,et al.Highly porous titanium scaffolds for orthopaedic applications.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2010;95(1):53-61.[31] Meneghini RM,Meyer C,Buckley CA,et al.Mechanical stability of novel highly porous metal acetabular components in revision total hip arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty.2010;25(3):337-341.[32] Sagomonyants KB,Hakim-Zargar M,Jhaveri A,et al.Porous tantalum stimulates the proliferation and osteogenesis of osteoblasts from elderly female patients.J Orthop Res.2011;29(4):609-616.[33] 于晓明,谭丽丽,杨柯.医用金属表面的钽涂层制备及其临床应用趋势[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2013, 5(2): 115-119.[34] 贺瑞,张文志,尚希福,等.钽金属椎间融合器在腰椎间盘突出症减压术后复发融合术中的应用[J].颈腰痛杂志,2013, 34(5):387-390.[35] 张海宁,吕成昱,王英振,等.多孔涂层钽金属棒系统治疗成人股骨头缺血性坏死[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(38): 7053-7056.[36] Jiménez JR,Mondal A,Chamoreau LM,et al.An {Fe<sub>60</sub>} tetrahedral cage: building nanoscopic molecular assemblies through cyanometallate and alkoxo linkers.Dalton Trans. 2016;45(44):17610-17615.[37] Zheng YR,Suntharalingam K,Bruno PM,et al. Mechanistic Studies of the Anticancer Activity of An Octahedral Hexanuclear Pt(II) Cage.Inorganica Chim Acta. 2016;452:125-129.[38] Gropp C,Trapp N,Diederich F.Alleno-Acetylenic Cage (AAC) Receptors: Chiroptical Switching and Enantioselective Complexation of trans-1,2- Dimethylcyclohexane in a Diaxial Conformation. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.2016;55(46): 14444-14449. [39] Morgenstern M,von Rüden C,Callsen H,et al.The unstable thoracic cage injury: The concomitant sternal fracture indicates a severe thoracic spine fracture. Injury. 2016;47(11):2465-2472. [40] Gerig JT.Examination of Trifluoroethanol Interactions with Trp-Cage through MD Simulations and Intermolecular Nuclear Overhauser Effects.J Phys Chem B. 2016;120(43):11256-11265.[41] Chen CS,Yeh WY.An Open-Cage Fullerene That Mimics the C<sub>60</sub> H<sub>10</sub> (5,5)-Carbon Nanotube Endcap to Host Acetylene and Hydrogen Cyanide Molecules.Chemistry. 2016;22(46): 16425-16428. [42] Marx A,Beier A,Richter A,et al.Major acetabular defects treated with the Burch-Schneider antiprotrusion cage and impaction bone allograft in a large series: a 5- to 7- year follow-up study.Hip Int.2016:0.doi: 10.5301/hipint.5000388. [Epub ahead of print][43] Kandasamy R,Calsbeek JJ,Morgan MM.Analysis of inflammation-induced depression of home cage wheel running in rats reveals the difference between opioid antinociception and restoration of function.Behav Brain Res.2016;317:502-507. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [9] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [11] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [12] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [13] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [14] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [15] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||