Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (22): 3242-3248.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.22.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Extended posterior screw rod fixation for youth thoracolumbar simple flexion compression fracture: improvement in orthopedic reduction efficiency
Zou Shou-ping, Tan Xiao-yun, Huang Qiang, Lu Dao-yun
- Department of Orthopedics, 413 Hospital of Chinese PLA, Zhoushan 316000, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Revised:2016-04-18Online:2016-05-27Published:2016-05-27 -
Contact:Tan Xiao-yun, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, 413 Hospital of Chinese PLA, Zhoushan 316000, Zhejiang Province, China -
About author:Zou Shou-ping, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, 413 Hospital of Chinese PLA, Zhoushan 316000, Zhejiang Province, China -
Supported by:the PLA General Logistics Medical Scientific Research, No. CWS11J261
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zou Shou-ping, Tan Xiao-yun, Huang Qiang, Lu Dao-yun. Extended posterior screw rod fixation for youth thoracolumbar simple flexion compression fracture: improvement in orthopedic reduction efficiency[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(22): 3242-3248.
share this article
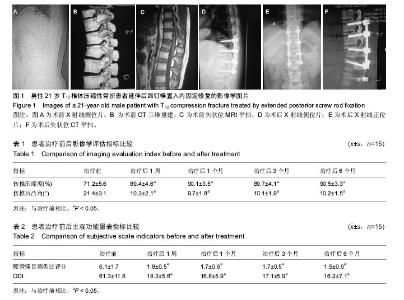
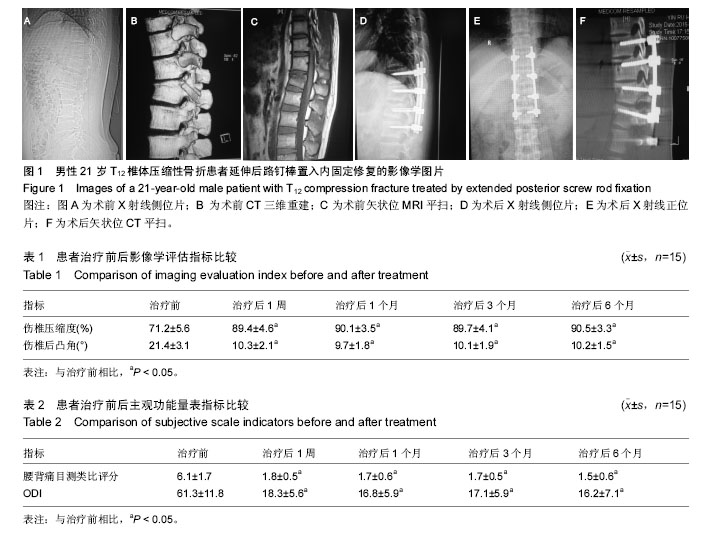
2.1 参与者数量分析 按意向性处理,纳入青年型胸腰椎单纯屈曲压缩性骨折患者15例,全部进入结果分析,均完成至少半年以上随访,无病例脱落。 2.2 病例随访情况 入选的15例患者出院前做好相关随访教育工作,对患者进行治疗前影像学评估以及治疗后1周、1个月、3个月、6个月影像学数据采集及评估工作,并且记录患者的各种主观功能数据。15例患者均顺利完成至少半年的随访。 2.3 围手术期资料 15例患者均顺利完成手术,手术时间90-150 min,平均115 min;出血量为70-150 mL,平均93 mL;住院时间为7-11 d,平均8.5 d。 2.4 影像学随访指标 所有患者治疗前、治疗后及随访期间进行脊柱损伤节段X射线、CT检查,主要测量矢状位上的伤椎高度压缩度及伤椎上下终板形成的脊柱胸腰椎后凸Cobb角。具体结果详见表1,可见治疗后及随访期均有效矫形并长期保持,治疗后和治疗前相比,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);治疗后不同时间点之间相比,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.5 主观功能量表随访指标 治疗前及治疗后不同时间点对患者进行量表测量,主要记录腰背痛目测类比评分及ODI。具体结果详见表2,可见治疗后及随访期间与治疗前相比具有良好的缓解效果,并能长期保持。治疗后和治疗前相比,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);治疗后不同时间点之间相比,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.6 并发症及不良事件 患者均顺利完成手术,切口一期愈合,未出现伤口感染、肺部感染、泌尿系统感染等并发症。所有患者均未发生神经损伤并发症,无手术操作脑脊液漏现象。 2.7 典型病例 男性患者,21岁,高处坠落致T12椎体压缩性骨折,采用延伸后路钉棒置入内固定方案治疗(固定T10-L1节段),术后矫形满意,见图1。随访1年,无不良反应。"
| [1] Ghobrial GM, Jallo J.Thoracolumbar spine trauma: review of the evidence.J Neurosurg Sci. 2013;57(2): 115-122.[2] Papanastassiou ID, Gerochristou M, Aghayev K, et al.Defining the indications, types and biomaterials of corpectomy cages in the thoracolumbar spine.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2013 ;10(2):269-279.[3] Ma X, Xing D, Ma J, et al.Risk factors for new vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty: qualitative evidence synthesized from a systematic review.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(12):E713-722.[4] Pneumaticos SG, Triantafyllopoulos GK, Giannoudis PV.Advances made in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: current trends and future directions.Injury. 2013;44(6):703-712.[5] Xing D, Chen Y, Ma JX, et al.A methodological systematic review of early versus late stabilization of thoracolumbar spine fractures.Eur Spine J. 2013; 22(10): 2157-2166.[6] Zhang Z, Fan J, Ding Q, et al.Risk factors for new osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures after vertebroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(4):E150-157.[7] Dudko S, Kusz D, Ziaja D, et al.Laceration of abdominal aorta by a fragment of fractured L2 vertebral body after a low-energy injury: a case report and review of literature.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012; 37(22):E1406-1409. [8] Joaquim AF, Patel AA.Relationships between the Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Osteosynthesefragen Spine System and the Thoracolumbar Injury Classification System: an analysis of the literature.J Spinal Cord Med. 2013;36(6):586-590.[9] Xu GJ, Li ZJ, Ma JX, et al.Anterior versus posterior approach for treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures: a meta-analysis.Eur Spine J. 2013;22(10):2176-2183.[10] Wood KB, Li W, Lebl DR, et al.Management of thoracolumbar spine fractures. Spine J. 2014;14(1): 145-164.[11] Bakhsheshian J, Dahdaleh NS, Fakurnejad S, et al.Evidence-based management of traumatic thoracolumbar burst fractures: a systematic review of nonoperative management.Neurosurg Focus. 2014; 37(1):E1.[12] Chang V, Holly LT. Bracing for thoracolumbar fractures. Neurosurg Focus. 2014;37(1):E3.[13] Scheer JK, Bakhsheshian J, Fakurnejad S, et al. Evidence-Based Medicine of Traumatic Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: A Systematic Review of Operative Management across 20 Years.Global Spine J. 2015;5(1):73-82.[14] Kim BG, Dan JM, Shin DE. Treatment of thoracolumbar fracture. Asian Spine J. 2015;9(1):133-146.[15] Lopez AJ, Scheer JK, Smith ZA, et al.Management of flexion distraction injuries to the thoracolumbar spine.J Clin Neurosci. 2015;22(12):1853-1856.[16] Schroeder GD, Kepler CK, Koerner JD, et al.Can a Thoracolumbar Injury Severity Score Be Uniformly Applied from T1 to L5 or Are Modifications Necessary? Global Spine J. 2015;5(4):339-345.[17] Gamanagatti S, Rathinam D, Rangarajan K, et al.Imaging evaluation of traumatic thoracolumbar spine injuries: Radiological review. World J Radiol. 2015;7(9):253-265.[18] El Tecle NE, Abode-Iyamah KO, Hitchon PW, et al.Management of spinal fractures in patients with ankylosing spondylitis.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015; 139:177-182. [19] Hwee Weng DH, Jun HT, Chuen ST, et al.Subsequent Vertebral Fractures Post Cement Augmentation of the Thoracolumbar Spine: Does it Correlate With Level-specific Bone Mineral Density Scores? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(24):1903-1909.[20] Theologis AA, Burch S. Prevention of Acute Proximal Junctional Fractures After Long Thoracolumbar Posterior Fusions for Adult Spinal Deformity Using 2-level Cement Augmentation at the Upper Instrumented Vertebra and the Vertebra 1 Level Proximal to the Upper Instrumented Vertebra. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(19):1516-1526.[21] Sadiqi S, Oner FC, Dvorak MF, et al.The Influence of Spine Surgeons' Experience on the Classification and Intraobserver Reliability of the Novel AOSpine Thoracolumbar Spine Injury Classification System-An International Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015; 40(23): E1250-1256.[22] Jo DJ, Kim YS, Kim SM, et al.Clinical and radiological outcomes of modified posterior closing wedge osteotomy for the treatment of posttraumatic thoracolumbar kyphosis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015; 23(4):510-517.[23] Vu TT, Morishita Y, Yugue I, et al.Radiological Outcome of Short Segment Posterior Instrumentation and Fusion for Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures. Asian Spine J. 2015;9(3):427-432.[24] Khurjekar K, Hadgaonkar S, Kothari A, et al. Demographics of Thoracolumbar Fracture in Indian Population Presenting to a Tertiary Level Trauma Centre.Asian Spine J. 2015;9(3):344-351.[25] Jeon CH, Lee HD, Lee YS, et al.Is It Beneficial to Remove the Pedicle Screw Instrument After Successful Posterior Fusion of Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures?[J]Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(11): E627-633.[26] Amirjamshidi A.The long-term efficacy of pedicular screw fixation in patients suffering from thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurological deficit. Asian J Neurosurg. 2015;10(4):289-290.[27] Javadi SA, Naderi F.The long-term efficacy of pedicular screw fixation at patients suffering from thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurological deficit. Asian J Neurosurg. 2015;10(4):286-289.[28] Azimi P, Mohammadi HR, Azhari S, et al.The AOSpine thoracolumbar spine injury classification system: A reliability and agreement study. Asian J Neurosurg. 2015;10(4):282-285.[29] Nakajima H, Uchida K, Honjoh K, et al.Surgical treatment of low lumbar osteoporotic vertebral collapse: a single-institution experience. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016; 24(1):39-47.[30] Bourghli A, Boissière L, Vital JM, et al.Modified closing-opening wedge osteotomy for the treatment of sagittal malalignment in thoracolumbar fractures malunion. Spine J. 2015;15(12):2574-2582.[31] Kim BJ, Rhee Y, Kim CH, et al. Plasma periostin associates significantly with non-vertebral but not vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women: Clinical evidence for the different effects of periostin depending on the skeletal site.Bone. 2015;81:435-441.[32] Schwab F.Treatment with or without an Orthosis is Equivalent for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture without Neurologic Injury. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(16): 1374.[33] Shen J, Xu L, Zhang B, et al.Risk Factors for the Failure of Spinal Burst Fractures Treated Conservatively According to the Thoracolumbar Injury Classification and Severity Score (TLICS): A Retrospective Cohort Trial.PLoS One. 2015;10(8): e0135735.[34] Loibl M, Korsun M, Reiss J, et al.Spinal fracture reduction with a minimal-invasive transpedicular Schanz Screw system: clinical and radiological one-year follow-up. Injury. 2015;46 Suppl 4:S75-82.[35] El Tecle NE, Abode-Iyamah KO, Hitchon PW, et al.Management of spinal fractures in patients with ankylosing spondylitis.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015; 139:177-182.[36] Zhao QM, Gu XF, Yang HL, et al.Surgical outcome of posterior fixation, including fractured vertebra, for thoracolumbar fractures. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2015;20(4):362-367.[37] Schroeder GD, Kepler CK, Koerner JD, et al. Is there a regional difference in morphology interpretation of A3 and A4 fractures among different cultures? J Neurosurg Spine. 2015:1-8. [Epub ahead of print][38] Theologis AA, Tabaraee E, Toogood P, et al.Anterior corpectomy via the mini-open, extreme lateral, transpsoas approach combined with short-segment posterior fixation for single-level traumatic lumbar burst fractures: analysis of health-related quality of life outcomes and patient satisfaction. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24(1):60-68.[39] Schroeder GD, Kepler CK, Koerner JD, et al.A Worldwide Analysis of the Reliability and Perceived Importance of an Injury to the Posterior Ligamentous Complex in AO Type A Fractures.Global Spine J. 2015;5(5):378-382.[40] Chou PH, Ma HL, Liu CL, et al.Is removal of the implants needed after fixation of burst fractures of the thoracolumbar and lumbar spine without fusion? a retrospective evaluation of radiological and functional outcomes. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(1):109-116. |
| [1] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [2] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [3] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [4] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [5] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [6] | Li Jing, Yang Long, Wang Jian-ji, Liu Qin, Zou Qiang, Sun Yu, Ma Min-xian, Ye Chuan. Three-dimensional reconstruction based on DICOM data and its application for orthopedic implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1046-1051. |
| [7] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [8] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [9] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [10] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [11] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [12] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [13] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [14] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| [15] | Zhang Yun-ge, Song Ke-guan. Periprosthetic osteolysis induced by wear particles: research progress of calcineurin/activated T cell nuclear factor signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1115-1122. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||