Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (26): 4229-4235.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.26.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
Relationship between lumbar spinal stenosis and inflammatory factors in the vein serum of lumbar spinal canal
Zhang Yan, Meng Yang, Zhao Wei-dong, Huang Yu-feng, Shen Bin, Wu De-sheng
- Department of Spine Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University, Shanghai 200120, China
-
Online:2014-06-25Published:2014-06-25 -
Contact:Wu De-sheng, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Spine Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University, Shanghai 200120, China -
About author:Zhang Yan, M.D., Physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University, Shanghai 200120, China -
Supported by:the Pudong New District Health Bureau Project of Shanghai City, No. PW2011A-5
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Yan, Meng Yang, Zhao Wei-dong, Huang Yu-feng, Shen Bin, Wu De-sheng. Relationship between lumbar spinal stenosis and inflammatory factors in the vein serum of lumbar spinal canal[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(26): 4229-4235.
share this article
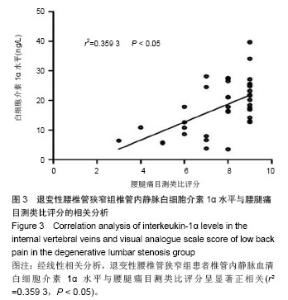
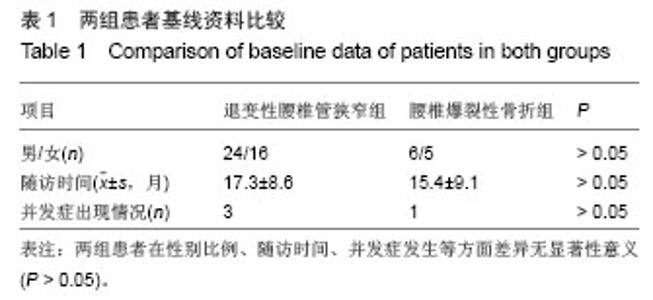
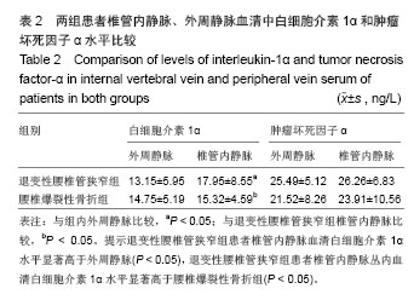
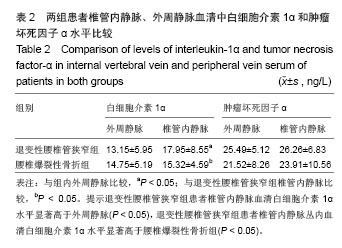
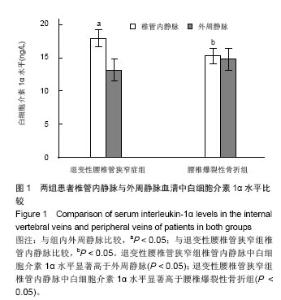
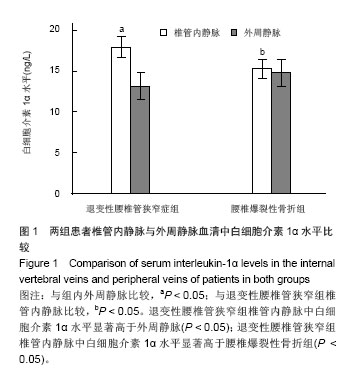
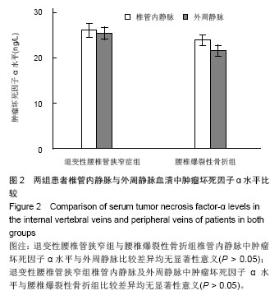
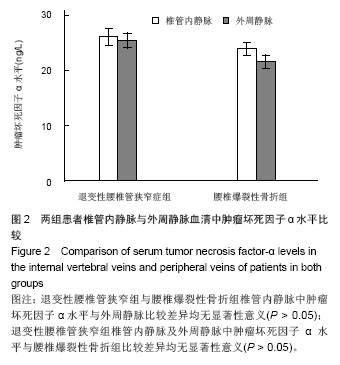
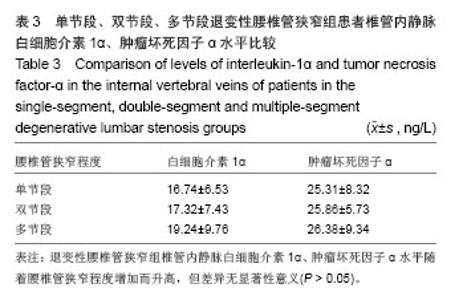
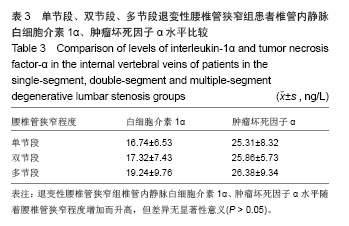
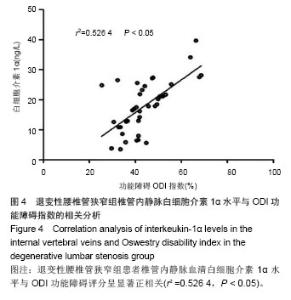
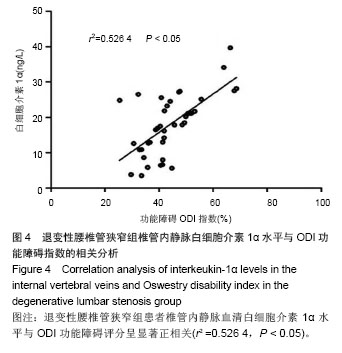
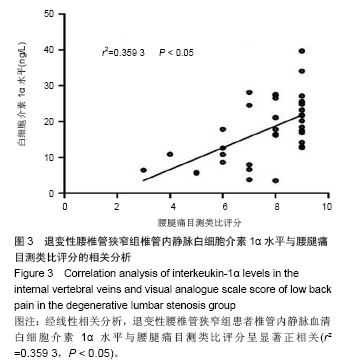
退变性腰椎管狭窄组患者椎管内静脉血清白细胞介素1α水平单节段、双节段、多节段比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);椎管内静脉血清肿瘤坏死因子α水平单节段、双节段、多节段比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.5 退变性腰椎管狭窄组椎管内静脉白细胞介素1α、肿瘤坏死因子α水平与腰腿痛及功能障碍评分相关性分析 退变性腰椎管狭窄组患者腰腿痛目测类比评分为(7.4±2.8)分,下肢痛目测类比评分为(8.3±3.1)分,ODI功能障碍评分为(17.3±4.5)分。 经线性相关分析,退变性腰椎管狭窄组患者椎管内静脉血清白细胞介素1α水平与腰腿痛目测类比评分呈显著正相关:直线回归方程:y(椎管内静脉血清白细胞介素1α水平)= 0.195 2x(腰腿痛目测类比评分)+ 7.092 1,r2=0.359 3,P < 0.05(图3)。"
| [1]Smith M, Davis MA, Stano M, et al. Aging baby boomers and the rising cost of chronic back pain: Secular trend analysis of longitudinal Medical Expenditures Panel Survey data for years 2000 to 2007. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2013;36(1):2-11.
[2]William CW, Jamie B, Thomas JG, et al. Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis : an evidence-based clinical guide line for the diagnosis and treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine. 2008;2: 305-310.
[3]Kaymaz M, Borcek AO, Emmez H, et al. Effectiveness of single posterior decompressive laminectomy in symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis: a retrospective study. Turk Neurosurg. 2012;22(4):430-434.
[4]Son S, Kim WK, Lee SG, et al. A comparison of the clinical outcomes of decompression alone and fusion in elderly patients with two-level or more lumbar spinal stenosis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2013;53(1):19-25.
[5]Nakamura T, Okada T, Endo M, et al. Angiopoietin-like protein 2 induced by mechanical stress accelerates degeneration and hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e85542.
[6]Takahashi N, Kikuchi S, Shubayev VI, et al. TNF-alpha and phosphorylation of ERK in DRG and spinal cord: insights into mechanisms of sciatica. Spine. 2006;31(5):523-529.
[7]Ozaktay AC, Kallakuri S, Takebayashi T,et al. Effects of interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor on sensitivity of dorsal root ganglion and peripheral receptive fields in rats. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(10):1529-1537.
[8]Gronbald M, Virri J, Tolonen J, et al. A Controlled immunohistochemical study of inflammatory cells in disc herniation tissue. Spine. 1994;19:2744.
[9]Podichetty VK. The aging spine: the role of inflammatory mediators in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2007;53(5):4-18.
[10]李强,赵建民,张元智,等.腰椎退变黄韧带中炎性细胞因子的表达[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011, 21(1):63-66.
[11]姜世峰,申才良.腰椎Modic改变中炎性细胞因子的效应[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(17):3213-3217.
[12]姜世峰,申才良,董福龙,等.退变腰椎Modic改变及分型与肿瘤坏死因子α、基质金属蛋白酶3的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(26):4847-4851.
[13]Lee JM, Song JY, J Baek M. Interleukin-1β induces angiogenesis and innervation in human intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2011;2(29):265-269.
[14]于杰,朱立国,高景华,等.腰椎间盘突出症患者血清白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α表达与其疼痛的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(2):301.
[15]李松军,梁寒洁,柯楚群,等.腰椎间盘突出物及髓核炎性因子变化与症状性疼痛的关系[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(22):4303-4307.
[16]Risbud MV, Shapiro IM. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content. Nature Review Rheumatol. 2014;10(1):44-56.
[17]Groen RJ, Grobbelaar M, Muller CJ, et al. Morphology of the human internal vertebral venous plexus: a cadaver study after latex injection in the 21-25-week fetus. Clin Anat. 2005;18(6): 397-403.
[18]Wang H, Liu H, Zheng ZM, et al. Role of death receptor, mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum pathways in different stages of degenerative human lumbar disc. Apoptosis. 2011;16(10):990-1003.
[19]Zhu GB, Jiang XR, Xia CL, et al. Association of FAS and FAS ligand polymorphisms with the susceptibility and severity of lumbar disc degeneration in Chinese Han population. Biomarkers. 2011;16(6):485-490.
[20]Schistad EI, Jacobsen LM, Røe C, et al.The Interleukin-1α Gene C>T Polymorphism rs1,800,587 is Associated with Increased Pain Intensity and Decreased Pressure Pain Thresholds in Patients with Lumbar Radicular Pain. Clin J Pain. 2013. [Epub ahead of print].
[21]Omair A, Holden M, Lie BA, et al. Treatment outcome of chronic low back pain and radiographic lumbar disc degeneration are associated with inflammatory and matrix degrading gene variants: a prospective genetic association study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:105
[22]Gruber-Schoffnegger D, Drdla-Schutting R, Hönigsperger C, et al. Induction of thermal hyperalgesia and synaptic long-term potentiation in the spinal cord lamina I by TNF-α and IL-1β is mediated by glial cells. J Neurosci. 2013;33(15): 6540-6551.
[23]Andrade P, Hoogland G, Garcia MA, et al. Elevated IL-1β and IL-6 levels in lumbar herniated discs in patients with sciatic pain. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(4):714-720.
[24]Tischer T, Aktas T, Milz S,et al. Detailed pathological changes of human lumbar facet joints L1-L5 in elderly individuals. Eur Spine J. 2006;15: 308-315.
[25]Pelletier JP, Martel-Pelletier J, Abramson SB. Osteoarthritis , an inflammatory disease : potential implication for this selection of new therapeutic targets. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44: 1237 -1247.
[26]Doita M, Kanatani T, Harada T, et al. Immunohistologic study of the ruptured intervertebral disc of the lumbar spine. Spine. 1996;15(21): 235-241.
[27]Takahashi H, Suguro T, Okazima Y, et al. Inflammatory cytokines in the herniated disc of the lumbar spine. Spine. 1996;15(21): 218-224.
[28]O'Donnell JL, O'Donnell AL. Prostaglandin E2 content in herniated lumbar disc disease. Spine. 1996;15(21): 1653-1655.
[29]Piperno M, le Graverand MPH, Reboul P, et al. Phospholipase A2 activity in herniated lumbar discs: Clinical correlations and inhibition by piroxicam. Spine. 1997;15(22): 2061-2065.
[30]Kawakami M, Tamaki T, Hashizume H, et al. The Role of Phospholipase A2 and Nitric Oxide in Pain‐Related Behavior Produced by an Allograft of Intervertebral Disc Material to the Sciatic Nerve of the Rat. Spine. 1997;15(22): 1074-1079.
[31]Kato T, Haro H, Komori H, et al. Sequential dynamics of inflammatory cytokine, angiogenesis inducing factor and matrix degrading enzymes during spontaneous resorption of the herniated disc. J Orthop Res. 2004;4(22):895-900.
[32]Pimentel DC, E Abd O, Benyamin RM, et al. Anti-tumor necrosis factor antagonists in the treatment of low back pain and radiculopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain Physician. 2014;17(1):E27-44.
[33]Gruber HE, Hoelscher GL, Ingram JA, et al. Production and expression of RANTES (CCL5) by human disc cells and modulation by IL-1-β and TNF-α in 3D culture. Exp Mol Pathol. 2014;96(2):133-138.
[34]Jimbo K, Park JS, Yokosuka K, et al. Positive feedback loop of interleukin-1 beta upregulating production of inflammatory mediators in human intervertebral disc cells in vitro.J Neurosurg Spine. 2005;2(5): 589-595.
[35]Igarashi T, Kikuchi S, Shubayev V, et al. Exogenous tumor necrosis factor-alpha mimics nucleus pulposus-induced neuropathology: molecular, histologic, and behavioral comparisons in rats. Spine. 2000;1(25): 2975-2980.
[36]潘力,李忠华,马廉亭,等.椎管内静脉丛的应用解剖学研究[J].中国临床神经外科杂志,2006,11(11):664-666.
[37]Endres S. Epidural varicosis as a possible cause of radicular pain: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2011;5(1): 537-539.
[38]孟阳,吴德升,沈彬.腰椎管内静脉丛曲张的相关研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2013, 23(5): 475-477.
[39]Waters CM, Moser W, Walkinshaw G, et al. Death of neurons in the neonatal rodent and primate globus pallidus occurs by a mechanism of apoptosis. Neuroscience. 1994;6:881-894.
[40]陈海,龚凯,罗卓荆,等.退变性腰椎管狭窄中小关节源性炎性因子作用的初步探讨[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(7):543-547.
[41]Carames B, Lopez-Armada MJ, Cillero-Pastor B, et al. Differential effects of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β on cell death in human articular chond rocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16(6):715-722. |
| [1] | Yao Rubin, Wang Shiyong, Yang Kaishun. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of single-segment lumbar spinal stenosis improves lumbar-pelvic balance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1387-1392. |
| [2] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [3] | Gao Yan, Zhao Licong, Zhao Hongzeng, Zhu Yuanyuan, Li Jie, Sang Deen. Alteration of low frequency fluctuation amplitude at brain-resting state in patients with chronic discogenic low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1160-1165. |
| [4] | Tian Yang, Tang Chao, Liao Yehui, Tang Qiang, Ma Fei, Zhong Dejun. Consistency and repeatability of CT and MRI in measurement of spinal canal area in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3882-3887. |
| [5] | Young Lihjier, Ouyang Lin, Chen Dingwei, Lin Qi. A biomechanical analysis of low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5267-5271. |
| [6] | Wang Jing, Xu Shuai, Liu Haiying. Hidden blood loss during posterior lumbar interbody fusion in lumbar spinal stenosis patients with and without rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5307-5314. |
| [7] | Zhang Chunlin, Shang Lijie, Yan Xu, Cao Zhengming, Shao Chenglong, Feng Yang. Mid-long-term effect of only placed expandable interbody fusion cage in the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis with vertebral instability using micro-endoscopic discectomy system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 335-341. |
| [8] | Liu Jinyu, Ding Yu, Jiang Qiang, Cui Hongpeng, Lu Zhengcao. A finite element model of full endoscope lumbar fenestration and biomechanical characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4291-4296. |
| [9] | Wen Wangqiang, Xu Haoxiang, Zhang Zepei, Miao Jun. Related factors and biomechanical characteristics of lumbar facet joint degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3883-3889. |
| [10] | Xie Rui, Zhu Liguo, Yu Jie, Li Kaiming, Zhuang Minghui, Chang Xiaojuan, Dai Wenkang. Interpretation of American Osteopathic Association Guidelines for osteopathic manipulative treatment of nonspecific low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3401-3408. |
| [11] | Shen Canghai, Feng Yongjian, Song Yancheng, Liu Gang, Liu Zhiwei, Wang Ling, Dai Haiyang. Value of quantitative MRI T2WI parameters in predicting surgical outcome of thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2893-2899. |
| [12] | Tian Jie, Ru Jiangying. Preservation of the spinous process ligament complex in expanded decompression of lumbar spinal canal: advantages and disadvantages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1228-1234. |
| [13] | Li Peng, Yang Shuye, Zhang Kai, Jia Long, Du Gangqiang, Liu Dong, Zhang Xinjun, Zhang Degang, Wang Zhigang. Influence of different wear particles on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 894-900. |
| [14] | Chen Xiaolan, Wang Lin, Liang Xiaotian, Li Yu1, Liu Haitao, Wang Bo, He Hui, Liu Chunyu. Gait characteristics of youth with chronic non-specific low back pain: spatio-temporal and kinetic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 556-561. |
| [15] | He Da, Zhao Jingwei, Liu Bo, Tian Wei. Comparison of limited fusion and full curve fusion for mild lumbar degenerative scoliosis with stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(36): 5811-5817. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||