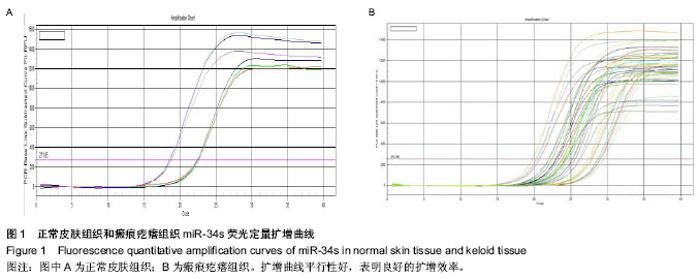
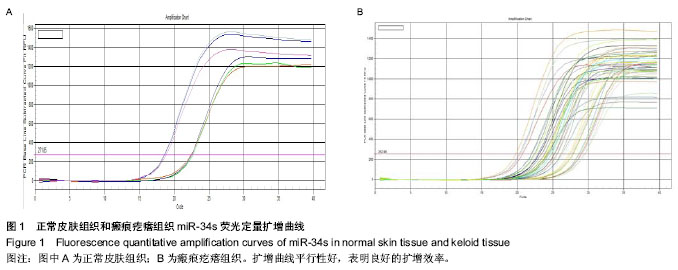
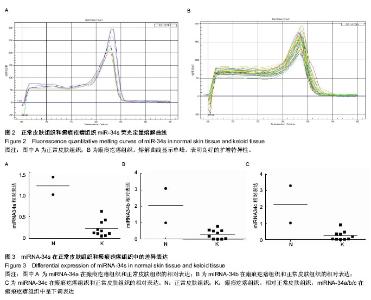
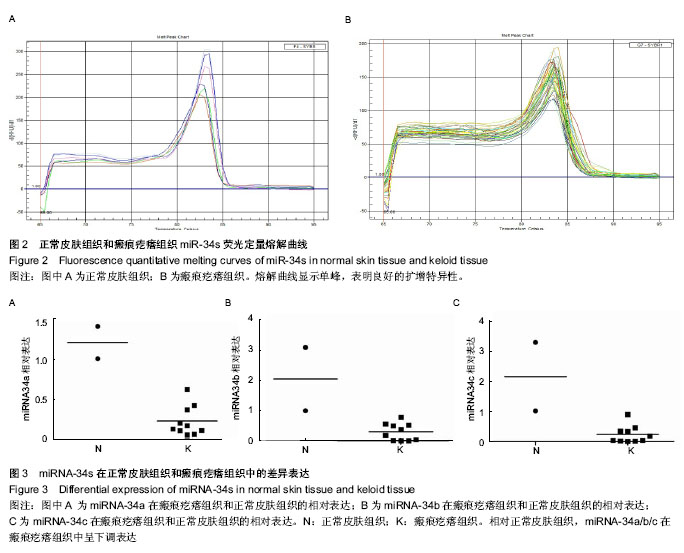
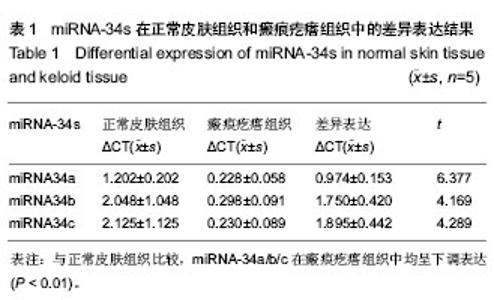
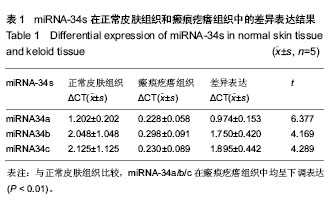
| [1] 朱学骏,王宝玺,孙建芳,等译.皮肤病学[M].2版.北京:北京大学医学出版社,2010:1835-1840.[2] 王春虎,黄渭清.瘢痕疙瘩的治疗研究进展[J].中国美容医学, 2008,17(4): 610 -613.[3] 钟珊,梅雪岭,赵俊英.不同脉宽595 nm染料激光治疗增生性瘢痕和瘢痕疙瘩的疗效[J].2013, 34(5):759-765.[4] Al-Attar A, Mess S, Thomassen JM, et al.Keloid pathogenesis and treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg.2006;117:286-300.[5] Nouri K,EIsaie ML,Vejjabhinanta V,et al.comparison of the effects of short-and long-pulse durations when using a 585-nm pulsed dye laser in the treatment of new surgical scars .Lasers Med Sci.2010;25(1):121-126.[6] Manuskiatti W, Wanitphakdeedecha R, Fitzpatrick RE.Effect of pulse width of a 595-nm flashlamp-pumped pulsed dye laser on the treatment response of keloidal and hypertrophic sternotomy scars.DermatolSurg.2007;33(2):152-161. [7] O'Hara SP,Mott JL,Splinter PL,et al.MicroRNAs: Key modulators of post transcriptional gene expression. Gastroenterology.2009;136:17-25.[8] Karres JS, Hilgers V, Carrera I,et al.The conserved microRNA miR28 tunes atrophin levels to prevent neurodegeneration in Drosophila.Cell.2007;131(1):136-145.[9] Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer.2006;6: 857-866.[10] Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res.2008;18: 997-1006.[11] Resnick KE, Alder H, Hagan JP, et al. The detection of differentially expressed microRNAs from the serum of ovarian cancer patients using a novel real-time PCR platform. Gynecol Oncol.2009;112(1): 55-59.[12] Lawrie CH,Gal S,Dunlop HM,et al.Detection of elevated levels of tumour-associated microRNAs in serum of patients with diffuse large B2cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol.2008;141(5): 672-675.[13] Gilad S, Meiri E, Yogev Y, et al. Serum microRNAs are p romising novel biomarkers. PLoS One, 2008,3(9):e3148.[14] 郭晓瑞,吴志远,黄海华,等.MicroRNA的基础与临床研究进展[J].中国实用医药,2011,6(15):256-258.[15] Satish L, Lyons-Weiler J, Hebda PA, et al. Gene expression patterns in isolated keloid fibroblasts. Wound Repair Regen. 2006;14 (4):463-470.[16] Lu M, Zhang Q, Deng M, et al.An analysis of human microRNA and diseas associations. Plos One, 2008; 3(10): e3420.[17] 娄文加,陈青,刘立,等.miR-34家族-肿瘤抑制蛋白P53基因高度相关的microRNA[J]. 遗传,2010,32(5): 423-430.[18] Ohtsuru A,Yoshimoto H,Ishihara H,et al.Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I)/IGF-I receptor axis and increased invasion activity of fibroblasts in keloid. Endocr J. 2000;47:41-44.[19] 王炜. 整形外科学(上册)[M]. 杭州:浙江科学技术出版社, 1999: 430-431.[20] Shih B,Bayat A.Genetics of keloid scaring.Arch Dermatol Res.2010;302(5):3l9-339.[21] 宗宪磊,姜笃银,蔡景龙,等.瘢痕疙瘩的肿瘤特性研究进展[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2007,8(5):393-397.[22] Wang R, Ma J, Wu Q, et al.Functional role of miR-34 family in human cancer.Curr Drug Targets.2013;14(10):1185-1191.[23] 郭晓瑞,梁杰,黄如林,等.MicroRNAs在瘢痕疙瘩中的差异表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(50):9370-9375.[24] 吴志远,卢玲,郭晓瑞,等.瘢痕疙瘩microRNA表达谱的筛选及miR-199a-5p生物功能的初步研究[J].中华整形外科杂志,2013, 29(4):279-284.[25] Liu Y, Yang D, Xiao Z,et al. miRNA expression profiles in keloid tissue and corresponding normal skin tissue.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2012 ;36(1):193-201. [26] Bai Y, Liu H, Zuo X,et al. Comparative study of microRNA profiling in keloid fibroblast and annotation of differential expressed microRNAs.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin.2013; 45(8):692-699. [27] Yamazaki H,Chijiwa T,Inoue Y,et al.Over expression of the miR-34 family suppresses invasive growth of malignant melanoma with the wild-type p53 gene.Exp Ther Med. 2012; 3(5):793-796.[28] Tanaka N,Toyooka S,Soh J,et al. Frequent methylation and oncogenic role of microRNA-34b/c in small-cell lung Cancer. Lung Cancer.2012:76(1):32-38.[29] Garofalo M,Jeon YJ,Nuovo GJ,et al.MiR-34a/c-Dependent PDGFR-α/β Down regulation Inhibits Tumorigenesis and Enhances TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Lung Cancer.PLoS One.2013;8(6):e67581. [30] Tanaka N, Toyooka S, Soh J, et al.Down regulation of microRNA-34 induces cell proliferation and invasion of human mesothelial cells. Oncol Rep. 2013;29(6):2169-2174.[31] Javeri A, Ghaffarpour M, Taha MF,et al.Down regulation of miR-34a in breast tumors is not associated with either p53 mutations or promoter hypermethylation while it correlates with metastasis.Med Oncol. 2013;30(1):413.[32] Hermeking H. The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis.Cell Death Differ.2010;17:193-199.[33] Siemens H, Jackstadt R, Kaller M,et al.Repression of c-Kit by p53 is mediated by miR-34 and is associated with reduced chemoresistance, migration and stemness. Oncotarget.2013; 4(9):1399-1415.[34] Concepcion CP,Han YC, Mu P,et al.Intact p53-dependent responses in miR-34-deficient mice.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(7): e1002797.[35] Douglas R,Hurst,Mick D,et al.Metastamir:The Field of Metastasis - Regulatory microRNA Is Spreading.Cancer Res 2009;69:7495-7498.[36] Hau A, Ceppi P, Peter ME.CD95 is part of a let-7/p53/miR-34 regulatory network.PLoS One.2012;7(11):e49636.[37] Tamura M, Uyama M, Sugiyama Y, et al.Canonical Wnt signaling activates miR-34 expression during osteoblastic differentiation.Mol Med Rep. 2013;8(6):1807-1811.[38] Dickson JR, Kruse C, Montagna DR,et al.Alternative polyadenylation and miR-34 family members regulate tau expression.J Neurochem.2013;127(6):739-749.[39] Iqbal N, Mei J, Liu J, et al.miR-34a is essential for p19Arf-driven cell cycle arrest.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(5). [Epub ahead of print][40] Jin K, Xiang Y, Tang J, et al.miR-34 is associated with poor prognosis of patients with gallbladder cancer through regulating telomere length in tumor stem cells.Tumour Biol. 2013. [Epub ahead of print][41] Hahn S, Jackstadt R, Siemens H,et al.SNAIL and miR-34a feed-forward regulation of ZNF281/ZBP99 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition.EMBO J. 2013;32(23): 3079-3095. |