Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (35): 7589-7600.doi: 10.12307/2025.752
Previous Articles Next Articles
Roles of SOX5 in bone metabolism and prevention of bone diseases and the relationship with exercise#br#
#br#
Li Zhipeng, Xing Rongxin, Hu Lianghong
- Guangxi Normal University for Nationalities, Chongzuo 532200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-09-07Accepted:2024-10-26Online:2025-12-18Published:2025-05-07 -
Contact:Hu Lianghong, MS, Lecturer, Guangxi Normal University for Nationalities, Chongzuo 532200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Li Zhipeng, MS, Lecturer, Guangxi Normal University for Nationalities, Chongzuo 532200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Key Project of Science and Technology Program of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education, No. GJJ170627; Key Project of Guangxi Vocational Education Teaching Reform Research Project, No. GXGZJG2024A028
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zhipeng, Xing Rongxin, Hu Lianghong. Roles of SOX5 in bone metabolism and prevention of bone diseases and the relationship with exercise#br#
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

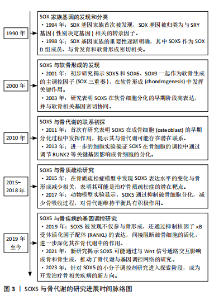
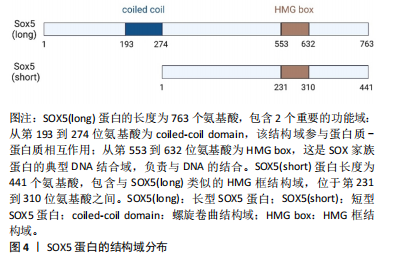
2.1 转录因子SOX5的结构与分泌 SOX基因广泛存在于动物中,少量分布于无脊椎动物中,而在人类及大多数哺乳动物中共有20种SOX基因。SOX基因的定义来自其保守的HMG盒,该结构最初发现于Y染色体上参与性别决定的SRY基因中[4]。HMG结构域识别C[A/T]TTG[A/T][A/T]序列并与DNA螺旋小沟中的AT对接触,由于SOX蛋白与DNA的结合空间上与其他蛋白的结合相容,因此它具有独特的L形构象,使DNA弯曲约75°[5]。 SOX5是SOX基因家族的一员,该家族基因根据HMG蛋白盒内外的序列同源性分为A-H共8组。SOX5属于SOX D组,其分子质量为48-89 kD,是最大的SOX蛋白之一。SOX5包含2个高度保守的功能域,其中家族特异性的HMG盒DNA结合域位于蛋白质的C端一半,具有87%的同源性,而与其他SOX蛋白的相同性不到60%。SOX5的最早研究表明其转录本长度为2 kb,编码43 kD的蛋白质[6]。随着研究的深入,发现SOX5的cDNA长度为3.9 kb,编码75 kD的蛋白质,并包含额外的N端序列,这种长形式的SOX5被命名为L-SOX5。L-SOX5的开放阅读框为2 037 bp,编码679个氨基酸,其中287个氨基酸位于SOX5蛋白质序列的N端,并且包含5'非翻译序列及终止密码子。SOX5和L-SOX5的成熟RNA来自初级转录物的差异剪接,其不同的启动子使用机制仍需进一步研究[7],详见图4。"
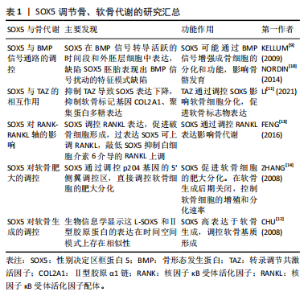
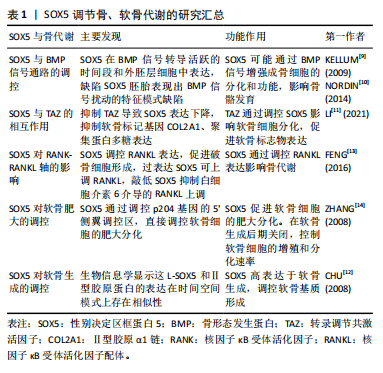
SOX5在多种细胞类型中表达,最早在小鼠胚胎的软骨形成部位中发现共表达。后续研究显示SOX5在精子细胞、神经元、少突胶质细胞及软骨细胞中均有高度表达,并与生长发育密切相关。特别地,SOX5单独在黑色素细胞和Th17细胞亚群中表达,SOX5与SOX13则在胰腺上皮细胞中共表达[8]。对于SOX5基因这些特定表达模式背后的机制,目前仍不明确,需进一步研究探索。 2.2 SOX5在骨、软骨生长和发育中的作用 2.2.1 SOX5调节骨、软骨代谢 骨代谢是指骨组织在体内的动态过程,包括骨形成和吸收,在维持骨骼健康和整体生理平衡中起着重要作用[8]。一项横断面分析欧洲人群的生物样本库(包括73 794例慢性背痛、4 883例类风湿性关节炎和7 153例骨质疏松症病例,以及242 216个跟骨密度评分)的研究发现,骨代谢异常与SOX5基因表达变化密切相关[3]。此外,一项研究表明截骨术后2周,与野生型的小鼠相比,肌肉生长抑制素敲除的小鼠骨折愈伤组织大小、三点弯曲总骨组织面积和弯曲强度显著增加,SOX5和骨形态发生蛋白2表达显著上调[9]。进一步研究发现,SOX5在骨形态发生蛋白信号转导活跃的时间段和外胚层细胞中表达,缺陷SOX5胚胎表现出骨形态发生蛋白信号扰动的特征模式缺陷[10],提示SOX5可能通过骨形态发生蛋白2从而在正常和病理状态下的骨代谢中发挥重要作用,尤其是在促进成骨方面。早期研究通过RNA原位杂交实验手段发现,SOX5在小鼠胚胎的软骨生成过程中高水平表达,具体过程包括软骨前凝结、软骨细胞分化、增殖软骨细胞、肥大前软骨细胞、肥大软骨细胞等阶段。一项细胞实验进一步证明,抑制转录调节共激活因子会导致SOX5基因表达下调,下游软骨细胞标记基因的表达和稳定性异常[11]。此外,L-SOX5 和Ⅱ型胶原A1均在软骨母细胞前细胞和母细胞中表达,生物信息学显示这两个因子的表达在时间、空间模式上存在相似性[12],这可能表明SOX5在软骨生成和分化中扮演重要角色,且可能通过多种编码RNA和蛋白质调节这一过程。进一步通过结构学方法探测到,SOX5在软骨前凝结阶段激活,在肥大前软骨细胞阶段关闭。为确认SOX5在体内软骨形成中的作用,研究者敲除小鼠的SOX5基因,发现SOX5-/-小鼠出生时患有轻度骨骼缺陷,并伴有次级腭裂、短肋骨和小软骨颅,这直接证明SOX5直接调节软骨发育和分化。 机制方面,以往研究显示核因子κB受体激活因子(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB,RANK)与核因子κB受体活化因子配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κb ligand,RANKL)结合后,激活下游的核因子κB信号通路,进而启动一系列基因表达,促进软骨细胞的分化和成熟,这些基因包括促软骨基质合成的基因(如Ⅱ型胶原A1和聚集蛋白聚糖)。研究显示SOX5过表达显著提高肿瘤坏死因子家族成员RANKL水平,而敲低SOX5则减少MH7A细胞中白细胞介素6介导的RANKL上调;ChIP分析显示,与未处理的细胞相比,白细胞介素6处理MH7A细胞中抗SOX5和RANKL特异性DNA的富集增加了约3倍;局部沉默SOX5基因减少胶原诱导关节炎模型小鼠RANKL阳性细胞,这表明SOX5通过调节炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6进而调节软骨分化和发育[13]。此外,荧光素酶实验显示SOX5在其共有结合元件处与加速软骨细胞肥大基因-p204基因的5’侧翼调节区结合,进而直接调控p204的表达[14]。而有研究显示p204是炎症因子Toll样受体4表达所必需的,再次提示SOX5调节软骨分化可能依赖于炎症因子[14]。 综上,SOX5基因在骨代谢和骨愈合中发挥着至关重要的作用,它参与骨形态发生蛋白信号通路和软骨细胞分化来维持骨骼的正常功能,见表1,但目前更多聚焦于软骨,且对机制了解并不清楚。未来应该使用条件敲除技术和组学技术,对小鼠的成骨和破骨细胞特异性敲除SOX5后,使用转录组学结合生物信息学技术确定具体变化机制,通过揭示SOX5与其他关键基因及信号通路的交互作用,为个性化治疗方案的制定提供依据。可以探索SOX5在骨修复与再生中的调节机制,评估其在创伤治疗和骨愈合中的治疗应用。"
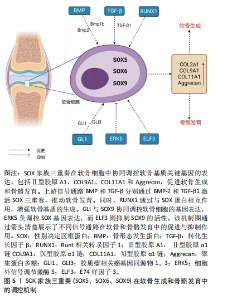
2.2.2 SOX5与SOX6联合调节骨、软骨代谢 由HMG的DNA 结合结构域命名的 SOX(Sry型HMG盒)转录因子组分为6个亚家族。SOX5和SOX6属于D组的亚家族。为确认SOX5与同组源基因SOX6在软骨中的作用,进行基因敲除后发现,SOX5和SOX6单缺失小鼠出生时均具有轻度骨骼异常,而SOX5和SOX6 双敲除胎儿则死于严重的全身性软骨发育不良,伴随软骨母细胞分化不良,软骨细胞外基质成分基因消失,软骨生长板和软骨内骨的形成遭到破坏[15-16]。这表明SOX5和SOX6虽然功能相似,但并不完全作用于同一条信号通路,两者可能有着不同机制。LIU等[17]的研究表明,在SOX5/SOX6部分突变体中,软骨细胞虽然分化,但软骨生长板发育不良,它们在柱状区缓慢增殖,过早进入肥大前期,直接跳过肥大进入终末成熟。另一项研究显示SOX5和SOX6干预能够促进长骨的骨骺和干骺端之间的软骨母细胞库发育,保持软骨母细胞增殖和延迟软骨细胞肥大,并通过延迟骨化前沿诱导的软骨细胞末端分化来允许形成肥大前区和肥大区[18]。 因此,SOX5和SOX6不仅在早期分化阶段,而且在成软骨细胞的特定功能的发挥中,均扮演重要角色。 后续研究证明L-SOX5与 SOX6两者共同表达并相互作用,D组SOX基因表现出差异表达模式的长转录本和短转录本[19]。生物信息学显示L-SOX5和SOX6是SOX D亚家族的2个高度相同的蛋白质,它们具有典型的Sry相关HMG盒DNA结合结构域和独特的卷曲螺旋结构域,可介导蛋白质二聚化,从而与DNA识别位点对进行高亲和力结合,还可能作为组织蛋白质-DNA增强体复合物的结构分子,同时也可能作为其他转录因子的锚定蛋白[20]。L-SOX5和SOX6通过促进成软骨细胞的软骨构建功能(即几乎所有软骨细胞外基质基因的表达和细胞增殖),在成软骨细胞分化的独特步骤中发挥作用,使这些细胞能够最佳地发挥其特定功能,这对于形成真正的软骨初级骨骼、确保软骨生长板中的成软骨细胞及时和空间组织的成熟以及确保软骨内骨化的正确发生至关重要[21-22]。值得注意的是,关节细胞和软骨细胞中的SOX5/6特异性失活会导致关节形态发生阻滞,但生长分化因子5和无翅型MMTV整合位点家族成员9A(wingless type MMTV integration site family member 9A,Wnt9a)在关节祖细胞中的表达准时,表明未来关于转化生长因子β家族和Wnt信号通路与SOX5和SOX6在时间上和空间上的具体的关系值得进一步探索[18]。 SOX5和SOX6作为D组SOX转录因子家族的成员,在软骨生成、骨骼发育和关节形成中发挥关键作用,它们通过共同调控成软骨细胞的分化与增殖,确保软骨生长板的正常发育,并在软骨内骨化过程中发挥重要功能。双基因敲除实验进一步证明了它们在胚胎发育期中不可或缺的地位,缺失SOX5和SOX6会导致严重的软骨发育不良和影响关节发育。未来需要探讨SOX5和SOX6在不同骨细胞中的具体功能,特别是在关节形成与修复中的作用。而未来将会聚焦于阐明SOX5/SOX6与其他发育因子(如Wnt和骨形态发生蛋白信号)的交互作用机制,以推动对骨骼与软骨发育的进一步理解。 2.2.3 SOX家族三重奏 沉默SOX9后,发现成熟和肥厚的软骨细胞的发育受抑制,证实SOX9是软骨形成所必需[23]。近年来,随着高通量测序方法的发展,微阵列检测人间充质干细胞数据分析确定SOX9和SOX5是调节成骨和成脂分化的重要指标[24]。促红细胞生成素处理下,软骨细胞的增殖速率和蛋白多糖的生物合成增加,SOX9、SOX5、SOX6、Ⅱ型胶原A1和聚集蛋白聚糖等软骨形成标志基因上调[25]。沉默软骨形成因子——波形蛋白 mRNA会导致细胞外基质中SOX5、SOX6和 SOX9的mRNA和蛋白下调[26],这表明SOX9可能与SOX5和6共同调控软骨代谢。此外,AKIYAMA等[27]的研究报告指出,SOX9转基因小鼠在肢芽间充质中异位表达,从而形成异位软骨,这与SOX5和SOX6的异位表达相关;另一项研究显示SOX9的2个顺式作用增强子元件位于软骨连接蛋白(hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 1,CRTL1)的5’-非翻译区,且其与转录共激活因子L-SOX5和SOX6对CRTL1的激活为细胞类型依赖性[28]。表明SOX9基因发挥作用可能依赖于SOX5和SOX6 发挥作用[27]。因SOX5、SOX6与SOX9在软骨细胞生成中扮演着关键角色,所以将这三者称为“软骨生成三重奏”[27]。 在骨髓间充质干细胞中,H19的激活可诱导软骨生成分化。在脂肪间充质干细胞中,单独激活H19未能引起明显的软骨生成,与单独激活SOX5/SOX6/SOX9或H19相比,脂肪间充质干细胞中H19/SOX5/SOX6的共激活引发更有效的软骨生成分化;SOX5和SOX6的过表达可以显著增强SOX9的软骨生成作用,并且在软骨特异性SOX9缺陷的小鼠中未观察到SOX5和SOX6的表达;此外,分子实验显示RUNX1和RUNX2诱导SOX5和SOX6的表达,原位杂交分析表明,Prx1 DKO RUNX1和RUNX2双突变小鼠前瞻性胸骨中Ⅱ型胶原A1、SOX5和SOX6的表达严重减弱,而SOX9表达保持不变[29],这可能表明SOX5和SOX6在SOX9的下游起作用。支持这一观点的是,SOX9的过表达已被证明能够上调SOX5和SOX6的表达。与SOX9相比,L-SOX5和SOX6缺乏反式激活结构域,因此它们可能在功能性蛋白质增强子复合物的形成中发挥促进结构性和蛋白质相互作用的功能。在软骨细胞排列成纵向柱时,SOX5和SOX6继续确保细胞外基质的产生,它们在这些柱状结构中表达增加,可能延迟细胞增殖的停止和肥大前分化发生。在非肥厚软骨细胞中,三者结合数百个与软骨特异性基因相关的增强子和超级增强子(增强子簇)。SOX5/SOX6优先结合靠近SOX9的SOX样基序串联对,从而增强SOX9与DNA和基因反式激活的结合。软骨成熟的标准组织学和分子特征是软骨细胞肥大、软骨形成标志物SOX9和Ⅱ型胶原A1下调以及Col10a1上调[30]。SOX三联结合增强子还富含叉头、RUNT结构域、NFAT、锌指和AP1家族成员的识别基序[31]。 有趣的是,SOX9+/-小鼠胚胎干细胞表现出连续减少的分化成熟软骨细胞,但SOX5和SOX6的早期软骨形成缩合的形成未受到抑制[26],这与前面结论似乎相反。老年垂体腺苷酸环化酶激活多肽基因缺陷小鼠中膝关节的软骨厚度显著增加,且SOX5、SOX9和CREB 的表达在年轻基因缺陷小鼠中均降低,但SOX6、Ⅱ型胶原A1和聚集蛋白聚糖表达却比年轻小鼠高[32]。此外,骨平台期小梁骨、髂嵴骨髓和沃顿胶脐带的人类间充质干细胞矿物基质沉积的表达水平存在差异,组学结果揭示SLUG可能是重点参与控制骨软骨生成器分化程序。沉默SLUG后细胞的SOX9和SOX5 mRNA增加,SOX6和 STAT1的mRNA表达降低[33],这提示SOX家族三重奏表达趋势并不一致,其具体功能也并不一致。胫软骨CRTL1是软骨细胞外基质的关键成分。通过原位杂交在小鼠下颌髁软骨形成开始研究发现SOX9 mRNA从胚胎区到新形成的软骨连续表达,但SOX5 mRNA仅在新形成的软骨中表达[34],转化生长因子β驱动的软骨形成刺激下调间充质祖细胞中的SOX9蛋白,而不是像间充质干细胞那样增加水平[35],这表明不同的组织,SOX家族三重奏的具体表达时间和空间都需要进一步探索,才能揭示其中的情况。 研究表明,SOX9与SOX5、SOX6协同调控软骨细胞的增殖、分化和成熟,且在不同的发育阶段和组织中发挥不同的作用。SOX9的过表达能够上调SOX5和SOX6的表达,而SOX5和SOX6则通过增强SOX9与基因序列的结合,促进软骨细胞外基质的生成。此外,研究还指出SOX5和SOX6可能位于SOX9的下游,共同调控软骨特异性基因的表达。然而,SOX家族基因的表达模式在不同组织和条件下并不完全一致,例如在小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞和胎盘祖细胞中的表现差异,提示这些基因的功能与其具体的时空表达模式密切相关。未来需要进一步研究不同组织中SOX5、SOX6和SOX9的表达时间和空间分布,以揭示其在软骨和骨生成中的具体作用。分析SOX家族与转化生长因子β、Wnt等通路的协同作用,进一步了解其在软骨和骨代谢中的功能网络。 2.2.4 SOX家族三重奏机制 SOX9是一个远缘基因,与SOX5和SOX6在软骨中同时表达,是软骨前细胞分化早期阶段软骨形成所必需的。与RUNX2-/-小鼠相比,野生型小鼠髁突成骨细胞骨形态发生蛋白2、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白和SOX9 mRNA显著表达[36]。将骨髓基质细胞放在在含有转化生长因子(TGF-β3)、地塞米松和骨形态发生蛋白6的培养基中培养后SOX5、SOX6和SOX9 mRNA持续增加[37]。腺病毒转染骨形态发生蛋白2,注射后的第4,7天,免疫组化显示Ⅱ型和Ⅹ型胶原蛋白生成激活,且与L-SOX5和SOX9表达增加有关[38]。此外,多项研究显示骨形态发生蛋白2能够刺激SOX三重奏的表达和SOX9 启动子活性[39-40],表明骨形态发生蛋白2可以通过SOX蛋白介导软骨发育。其他实验显示,虽然软骨中缺乏1型受体BMPr1a或1b 的小鼠能够形成完整的软骨元件,但双突变体会发展为严重的全身性软骨发育不良,分子实验验证显示这可能是由于缺乏SOX9、L-SOX5和SOX6表达[41]。进一步研究显示转化生长因子β1诱导的趾间手指实验中,SOX8和SOX9是肢体软骨最早熟的标志物,它们的诱导是独立的,并且在骨形态发生蛋白信号激活之前;L-SOX5和SOX6分别在软骨前形成聚集体中表达 Bmpr1b 的同时和之后被诱导,它们的激活与分化软骨中Ⅱ 型胶原蛋白和聚集蛋白聚糖基因的诱导相关;Bmpr1b 的表达先于软骨前形成聚集体形态变化的出现,并建立一个标志,从该标志开始,所有SOX基因表达的维持和软骨分化的进行都依赖于骨形态发生蛋白[42]。在复制骨领形成的跖骨器官培养物中,骨形态发生蛋白诱导的软骨形成分化,Gli1的表达抑制SOX5、SOX6和SOX9表达以及SOX9的反式激活[43]。生长板通过控制骨骼的增长发挥关键作用,其中SOX9和Gli是调控软骨细胞增殖、分化与肥大的重要因子。生物信息学分析显示,SOX9和GLI的结合位点在增殖和肥大前软骨细胞中优先表达的基因中富集,提示SOX9和GLI蛋白之间可能存在协同作用。对转录组、SOX9、GLI1和GLI3的ChIP-seq数据集的整合分析进一步揭示SOX9-GLI共同调节许多基因的机制,包括Trps1、SOX9、SOX5、SOX6、Ⅱ型胶原A1、Ptch1、Gli1和Gli2等[44]。 此外,免疫共沉淀测定证实RUNX1与SOX5、SOX6和SOX9蛋白之间的蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用。敲除RUNX1能够增加小鼠关节软骨和初级软骨细胞中Co10a和软骨分化抑制因子Bapx1表达的降低,RUNX1诱导的肥厚分化抑制作用可通过Bapx1的siRNA沉默而减弱,同时软骨生成标志物的表达未发生显著变化[45]。因此,RUNX1通过与SOX蛋白合作增强基质的产生,并通过Bapx1至少部分抑制软骨分化,从而有助于维持关节软骨的完整性。ELF3的过表达则会显著降低启动子的转录活性,从而下调SOX9驱动的启动子活性,这表明ELF3与SOX9直接相互作用。进一步研究发现,ELF3与SOX9的HMG结构域直接相互作用[46]。高水平的ERK5磷酸化与低水平的间充质祖细胞软骨形成相关,磷酸化 ERK1/2水平与间充质祖细胞软骨形成的进展平行。siRNA介导的ERK5通路成分MEK5和ERK5敲低导致软骨特征标记基因SOX9、Ⅱ型胶原A1、AGC、L-SOX5和SOX6的间充质祖细胞沉淀mRNA转录水平增加,以及SOX9蛋白、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和阿尔新蓝染色蛋白多糖的积累增强[47]。在体外实验中,L-SOX5、SOX6和SOX9结合并协同激活Ⅱ型胶原A1基因的软骨特异性增强子,这些基因编码细胞外基质大分子(例如Ⅱ型、Ⅸ型和Ⅺ型胶原、聚集聚糖和链接蛋白)、基质的调节因子(如软骨素4-磺基转移酶11)以及关键的信号通路成分(如成纤维细胞生长因子受体3)。RACE 分析确定SOX6 的人胚胎增强子,并确定46 bp 的核心增强子区域(CES6)。以CES6为诱饵进行酵母单杂交测定以筛选其他软骨形成因子,并鉴定出锌指蛋白 ZNF449,生物信息学显示ZNF449是SOX6、SOX9 和Ⅱ型胶原A1的反式激活增强子或启动子[48]。干扰素γ抑制Ⅱ型胶原A1和聚集蛋白聚糖的mRNA水平,但不抑制SOX9、L-SOX5和SOX6 的mRNA水平[49]。 综上所述,SOX5、SOX6和SOX9作为“软骨生成三重奏”,在软骨形成和分化过程中扮演关键角色,它们通过调控软骨细胞的增殖和分化,确保软骨基质的产生及生长板的正常发育。在骨形态发生蛋白信号通路的参与下,SOX蛋白三重奏的表达被激活,促进了软骨形成的标志基因表达。RUNX1、GLI等因子与SOX蛋白的相互作用也揭示了更复杂的调控网络,详见图5。未来将进一步研究SOX5、SOX6、SOX9在软骨生成中的精细调控机制,尤其是在不同发育阶段及不同组织环境下的作用差异,探讨这些转录因子与其他关键调控因子的交互作用,特别是在骨和软骨疾病中的潜在治疗靶点。"


2.3 SOX5与疾病 2.3.1 SOX5与骨肉瘤 尤文肉瘤是青少年第二常见的骨骼(骨和软骨)癌,其特征是异常嵌合融合基因 EWSA/FLI1表达,免疫共沉淀显示Ewsa与SOX9 相互作用。与野生斑马鱼胚胎相比,EWSA胚胎中SOX9靶基因SOX5下调[50],提示SOX家族三重奏可能是调节骨肉瘤的重要因子。以往研究表明,BRY基因在软骨和骨骼发育过程中起到了诱导中胚层分化的作用,而SOX5则进一步引导这些细胞分化为软骨细胞[51],两者可能在不同的发育阶段或时间点互为补充。然而,最新的研究发现BRY基因在癌症中扮演了关键角色。体外和体内实验显示,BRY驱动上皮-间充质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT),并促进乳腺癌骨转移。染色质免疫沉淀分析结果表明,SOX5是BRY的直接下游靶基因,提示SOX5可能是在癌细胞向骨组织的转移中起到促进作用[52]。在其他类型的癌症中,SOX5在骨肉瘤(osteosarcoma)组织和细胞系中显著上调,并且发现过表达SOX5会促进骨肉瘤细胞和EMT细胞的迁移和侵袭[53]。Si-SOX5瞬时转染骨肉瘤细胞MG63干扰组的迁移细胞数为较对照组的显著减少,siSOX5-3干扰组的侵袭细胞数为较对照组的显著减少。蛋白结果显示siSOX5干扰组的侵袭相关蛋白(基质金属蛋白酶2,9、Twist1和Snail1)的表达均较对照组显著降低[54]。 在机制层面,骨肉瘤组织中SOX5 mRNA表达水平显著性高于邻近匹配的正常组织。与对照组hFOB1.19细胞系相比,SOX5 mRNA和蛋白水平在4种具有转移潜能的骨肉瘤细胞系中的表达都是相对升高的;增强SOX5表达后,骨肉瘤细胞体外迁移和侵袭的能力都显著性增强,骨肉瘤细胞中上皮特异性标志物E-钙黏蛋白表达水平下调,而间质特异性标志物神经钙黏蛋白和波形蛋白表达水平上调,同时促EMT转录子Snail表达上调,且丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶1(serine/threonine kinase,Raf1)的表达上调;而沉默SOX5表达后逆转,并通过蛋白抑制剂U0126证实SOX5促进EMT依赖于Raf1/ERK1/2信号通路的活化,这提示SOX5高表达是提示骨肉瘤易发生转移的一个分子标志。此外,SOX5通过活化Raf1-ERK信号通路来调节Snail表达而诱导EMT过程发生,从而调节骨肉瘤的侵袭和转移[55]。骨肉瘤组织和细胞中circ_0007534和SOX5的水平升高,而miR-219a-5p水平则降低;研究表明,沉默circ_0007534能够抑制骨肉瘤细胞的增殖、集落形成、迁移和侵袭;生物信息学分析显示circ_0007534靶向miR-219a-5p,而miR-219a-5p则与SOX5相互作用[56]。此外,ILF3-AS1在骨肉瘤组织和细胞系中的表达显著上调,临床分析表明ILF3-AS1的高表达与晚期临床分期、远处转移和较短的总生存期密切相关;功能研究显示,敲低ILF3-AS1能够抑制骨肉瘤细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭,并促进细胞凋亡;荧光素酶报告实验进一步证实ILF3-AS1通过靶向SOX5的3’-UTR区域调控其表达[57]。 综上,研发调节骨肉瘤中SOX5表达的技术可能是治疗疾病的关键,但目前少见过表达或敲除SOX5在癌症转移中的作用,以及SOX5是否会成为癌症的主要诱因还有待探究。未来关于SOX三重奏在其中的作用值得进一步探索,通过基因和蛋白的表达来验证可能是关键的一步。 2.3.2 SOX5与骨质疏松症 骨质疏松症是一种以骨密度降低和骨强度下降为特征的疾病。SCEA 分析观察到卡斯钦-贝克病(Kaschin-Bek disease)患者的骨质疏松症与尺骨和桡骨骨密度之间存在显著多效性效应,全基因组关联Meta分析确定多效性效应的候选基因为SOX5[58]。研究表明,骨质疏松症患者由于骨密度低、骨强度弱,股骨头容易受损,增加发生缺血性坏死的风险。此外,骨质疏松症患者骨折风险增加,尤其是髋部骨折,髋部骨折可能导致股骨头的血液供应受损,从而增加股骨头缺血性坏死的发生风险。因此,骨质疏松症被认为是股骨头缺血性坏死的一个重要危险因素。在股骨头缺血性坏死患者的软骨组织中,miR-21-5p的表达显著下调[59]。研究表明,人脐带间充质干细胞通过分泌外泌体将miR-21-5p递送至hFOB1.19细胞和人脐静脉内皮细胞,增强人脐静脉内皮细胞的血管生成能力和hFOB1.19细胞的成骨能力,表现为碱性磷酸酶活性和钙沉积的增加以及成骨相关标志物骨钙素、RUNX2和Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的表达上调;SOX5的异位表达则可以抵消外泌体miR-21-5p的作用。在绝经后骨质疏松症患者的骨髓样本中,人间充质干细胞中SOX5的mRNA和蛋白表达水平上调;SOX5的过表达导致碱性磷酸酶活性和成骨细胞标记物(包括Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、Runx2和Osterix)基因表达的降低;同时,SOX5过表达还增加了Kruppel样因子4基因的表达,而SOX5沉默则产生相反效果;敲低Kruppel样因子4能够消除SOX5过表达对人间充质干细胞成骨分化的抑制作用,这提示SOX5可能是相关疾病治疗的潜在靶点[60]。 SHOX 缺乏症可导致Léri-Weill 椎骨发育不良、Langer 髓系发育不良、Turner 综合征和特发性身材矮小。分析SHOX 过表达人成纤维细胞中的差异表达基因,多个 SOX 家族成员(SOX5、SOX6、SOX8 和SOX18)显著失调[61]。进行酵母双杂交筛选,鉴定出SOX5和SOX6两种转录因子是与SHOX相互作用的蛋白质;免疫共沉淀测定证实人细胞中存在SHOX-SOX5和SHOX-SOX6相互作用,SHOX 同源结构域和 SOX6 HMG 结构域与 SHOX-SOX6 相互作用有关。此外,在软骨骨生成障碍综合征和特发性矮小患者中发现不同SHOX错义突变破坏这种相互作用。SOX三重奏的转录靶标Agc1编码软骨的主要成分之一聚集蛋白聚糖。SHOX与SOX5/SOX6和SOX9合作激活上游Agc1增强子,而SHOX突变会影响这种激活[30]。SHOX2与SHOX一样,直接调节NPPB,同时通过与SOX三重奏的合作激活ACAN。酵母-两种杂交和免疫共沉淀测定法鉴定并表征与SHOX2二聚化有关的蛋白质结构域及其与SOX5/SOX6和SHOX的相互作用。不同时间点人胎儿生长板的免疫组化表明,SHOX2与SHOX和SOX 三重奏的成员共表达[62]。 研究表明,骨质疏松症患者由于骨折风险增加,尤其是髋部骨折,进一步提高股骨头缺血性坏死的发生率,SOX5在此类病理过程中发挥重要作用,特别是在成骨分化的调控中。SOX5的过表达抑制成骨标记物的表达,并通过调控Kruppel样因子4等基因影响骨质代谢。此外,SHOX和SOX家族成员在骨骼发育中的相互作用进一步揭示了SOX基因在骨代谢调节中的复杂机制。进一步探讨SOX5在骨质疏松症和股骨头缺血性坏死中的具体分子机制,以寻找潜在的治疗靶点;深入研究SHOX与SOX家族在骨骼发育中的协同作用,特别是在调控成骨和软骨分化中的功能,结合miRNA、外泌体等新兴研究领域,探索SOX家族在骨组织修复与再生中的应用前景。 2.3.3 SOX5与骨关节炎 研究表明,炎症因子如肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1等通过激活特定信号通路(如核因子κB通路),抑制软骨细胞的增殖和分化,并导致软骨细胞的程序性死亡[63]。此外,这些炎症因子还诱导基质金属蛋白酶和去整合素和金属蛋白酶(a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs,ADAMTSs)的表达,破坏软骨基质(如Ⅱ型胶原和聚糖),从而影响软骨的正常功能[64]。特别是在关节炎等慢性炎症性疾病中,持续存在的炎症因子导致软骨组织难以有效再生[65]。对金黄色葡萄球菌周围关节感染患者和无菌性松动患者的假体周围组织进行单细胞RNA测序,通过分析36 466个细胞,在人骨-植入物界面中鉴定出8种主要细胞类型,而成纤维细胞scRNA-seq数据的荟萃分析发现SOX5参与调节关节炎患者的骨基质产生[66]。进一步研究揭示,类风湿性关节炎发病时的年龄与RANKL启动子SNP之间存在关联,该启动子通过与转录因子SOX5结合提高其活性;促炎因子干预后,类风湿性关节炎和类风湿滑膜成纤维细胞系MH7A中的SOX5和RANKL表达均上调,表明炎症因子的增加是SOX5增加的主要原因[13],这提示炎症因子可能通过SOX5调节软骨的发育和分化。在机制上,肿瘤坏死因子α刺激能够显著上调SOX5 mRNA表达[60]。另一项研究表明,肿瘤坏死因子α刺激髓核细胞后,通过上调miR-143-3p导致细胞外基质代谢异常并诱发凋亡;生物信息学分析表明,miR-143-3p的下游直接靶基因为SOX5,且实验显示miR-143-3p对SOX5的表达具有负调控作用[67]。 有趣的是,人间充质干细胞成骨细胞命运确定的早期阶段进行全面的转录组分析,鉴定出当间充质干细胞成为成骨谱系时,miR-181A1HG 被下调,并在成脂分化过程中保留,在没有成骨刺激的情况下敲除 MIR181A1HG 会阻碍细胞周期进程;RNA-seq分析表明,染色质结合miR-181A1HG的缺失会改变骨骼基因网络(例如SOX5和DLX5)表达和骨形态发生蛋白2反应性[68]。更为有趣的是,研究发现miR-194和miR-146b均能直接影响人脂肪干细胞和人骨髓来源的骨骼干细胞的软骨分化[69],生物信息学和基因实验进一步证明SOX5是这两者的下游靶点。将si-SOX5转染骨关节炎软骨细胞(OA-si SOX5),OA-si SOX5细胞中白细胞介素6和白细胞介素1β mRNA表达显著低于对照组细胞(OA-NC si-RNA);Ⅱ型胶原A1和ACAN mRNA显著高于OA-NC si-RNA细胞;OA-si SOX5细胞中基质金属蛋白酶1和基质金属蛋白酶13蛋白水平明显低于OA-NC si-RNA细胞,表明下调SOX5表达可能通过抑制基质金属蛋白酶的表达、促进细胞外基质的合成与分泌、抑制细胞凋亡和炎症反应进而缓减骨关节炎的发展[70]。 研究表明,SOX5、SOX6和SOX9等基因在炎症环境中受调控,在骨与软骨的生成、修复中扮演重要角色。尤其是SOX5,受肿瘤坏死因子α等炎症因子的刺激,表达水平上升,从而参与软骨细胞的调控。miRNA如miR-143-3p、miR-194和miR-146b对SOX5的表达具有负调控作用,提示非编码RNA可能是SOX5的重要的调控手段。未来将深入探讨炎症因子与SOX家族基因的调控网络,尤其是在骨与软骨相关疾病中的作用机制。研究miRNA与SOX基因之间的调控关系,以开发针对软骨损伤和骨关节炎的精准治疗方法。评估低氧环境和其他微环境因素对软骨再生和SOX蛋白表达的影响,推动软骨再生医学的发展。 2.3.4 SOX5与药物治疗疾病 与单层细胞相比,藻酸盐包埋的细胞COL2、COL10、聚集蛋白聚糖和SOX5、SOX6和SOX9的mRNA在第7天显著上调[71]。在单层、球体和三维培养系统各种组合中,只有 SOX5、SOX6和SOX9组合(SOX三重奏)成功地在所有测试的细胞类型(包括非软骨形成类型)中诱导软骨细胞分化[72],提示可能通过药物或者技术手段调节SOX家族三重奏进而有效促进软骨修复。 在药物干预方面,siTwist2能够增加SOX5和蛋白多糖的mRNA水平,从而促进软骨生成[73-74]。间充质干细胞C3H10T1/2细胞中,Compound-1比骨形态发生蛋白2更明显增加L-SOX5、SOX6和SOX9(SOX trio)的表达,促进软骨分化,同时抑制细胞的成脂分化[75]。功能丧失分析表明,敲低雌激素受体a会损害包括SOX9、Ⅱ型胶原A1、SOX5、SOX6、Runx2和col10a等基因表达,从而诱导咽弓软骨形成异常。重要的是,SOX9的上游区域确定雌激素受体a的结合元件,表明雌激素受体a可能直接调节 SOX9 表达[76]。用骨形态发生蛋白2(第3-10天)替换骨形态发生蛋白4则加速SOX9基因表达的增加,并提升软骨生成基因SOX5、ACAN和Ⅱ型胶原A1的表达水平[77],这种变化还增强软骨形成细胞聚集体的形成,并增加了Ⅱ型胶原蛋白的沉积量,而这一过程并未伴随肥大软骨细胞标志物COL10A1的表达。与骨形态发生蛋白4相比,骨形态发生蛋白2对人胚胎干细胞生成软骨细胞具有更高的特异性[78]。 在生物技术方面,用SOX5、SOX6和SOX9基因(SOX Trio)转染骨髓来源的间充质干细胞、脂肪来源的间充质干细胞和去分化的软骨细胞,封装在纤维蛋白水凝胶中,软骨形成基因和蛋白质在表达 SOX Trio 的细胞中比在未转染的细胞中高表达;SOX Trio表达骨髓来源间充质干细胞、脂肪来源间充质干细胞和去分化软骨细胞移植的裸鼠中,观察到软骨组织快速形成[79]。颅骨愈合具有挑战性,尤其是对于骨质疏松症患者,因为骨质疏松症患者的干细胞极易发生成脂分化。激活骨质疏松性脂肪来源间充质干细胞中的软骨诱导SOX Trio基因(SOX5、SOX6、SOX9)和抑制脂肪诱导基因(C/ebp-α、Ppar-γ)可以重编程细胞分化并改善植入后的颅骨愈合;递送到骨质疏松大鼠脂肪来源间充质干细胞后,CRISPR-BiD增强软骨形成和体外软骨形成,以及骨愈合[80]。在椎间盘退化期间,髓核和椎间盘的中央隔室发生退化。用4个因子(LDN、AGN、FGF和CHIR)混合物处理H9-人胚胎干细胞6 d成功产生脊索细胞,通过形态学、泛基因组高通量单细胞RNA测序揭示SOX5可能是重要因子[81]。椎间盘疾病是常见的脊柱疾病,在存在或不存在潜在的神经系统疾病时会导致颈部或背部疼痛,可能利用正常人真皮成纤维细胞诱导分化为髓核细胞。使用三维培养系统证明 MYC、Kruppel样因子4、NOTO、SOX5、SOX6和SOX9在正常人真皮成纤维细胞中的异位表达产生髓核样细胞;定量 PCR、微阵列分析和荧光激活细胞分选显示,诱导的髓核细胞表现出完全分化表型[82]。此外,脊索能够形成椎间盘的髓核,并在脊柱形成中起主要作用。在 SOX5(-/-)/SOX6(-/-)胚胎中,脊索形成典型的杆状结构,未被细胞外基质鞘包围,同时内环和椎体的发育受到严重损害,并且没有髓核,这与细胞外基质基因-脊索细胞和推定的内环和椎体的周围软骨细胞中的胶原蛋白2、聚集蛋白聚糖和珀莱斯红糖基因的下调有关[15]。 髌下脂肪垫的干细胞是修复关节软骨缺损的干细胞的潜在来源。缺氧已被证明可以改善成体干细胞的软骨形成。在缺氧条件下,髌下脂肪垫干细胞聚集体显示软骨形成反应蛋白多糖的基质积累增加,关键转录因子SOX5、SOX6和SOX9 的表达,聚集蛋白聚糖和胶原蛋白 Ⅱ、Ⅸ、Ⅹ和Ⅺ表达增加[83]。软骨细胞在骨关节炎期间不能有效地自我再生并失去其表型,这个过程称为去分化,也发生在自体软骨细胞植入的第一个扩增步骤中,为确保自体软骨细胞植入治疗成功,软骨细胞必须分化并能够合成透明软骨基质分子。在骨形态发生蛋白2 处理下,重分化和代谢活跃的软骨细胞合成一种透明样软骨基质,这可能是由于Ⅱ型胶原A1基因表达的特异性增加涉及Ⅱ型胶原A1的特异性增强子区域,该区域结合反式激活剂SOX9/L-SOX5/SOX6和Sp1[84]。骨关节炎中软骨暴露一直是一个巨大的挑战。微阵列基因表达比较小鼠软骨下骨和软骨之间的组织特异性转录物,进一步的组合方法确定两种均包含 SOX9 和SOX5的3-TF组合,这种组合的功能可以将软骨细胞引导至浅表区或深层区域表型,从而有效改善软骨暴露[85]。此外,骨关节炎患者的髌下脂肪垫含有干细胞,可以通过低侵入性方法分离,分离后,软骨细胞提取物诱导SOX9、L-SOX5、SOX6和Ⅱ型胶原A1等软骨形成基因的mRNA表达增加,进而促进软骨细胞、髌下脂肪垫来源干细胞和转分化髌下脂肪垫来源干细胞能够在3D PLGA支架上生长、扩增和产生细胞外基质[86]。 通过不同的培养系统和药物干预,SOX三重奏在多种细胞类型中成功诱导了软骨细胞的生成,尤其是在纳米多乙醇酸支架或纤维蛋白水凝胶封装中,它们显著增强软骨组织的形成。此外,骨形态发生蛋白、转化生长因子β等生长因子以及cAMP依赖性蛋白激酶通路也被证明参与了SOX三重奏的调控过程。未来应该聚焦于探索不同生长因子组合对SOX三重奏调控软骨生成的影响,尤其是在特定疾病环境下的应用。研究SOX三重奏在成骨和软骨分化抑制中的潜在机制,以开发新的骨与软骨疾病治疗策略。评估CRISPR技术与SOX三重奏的结合在骨缺损修复和再生医学中的应用潜力,特别是对于骨质疏松症患者的颅骨愈合。 2.4 SOX5与运动 目前,关于运动与SOX5的直接研究较为有限。仅有一项研究表明,SOX5是9个与运动期间心率急剧增加和恢复相关的基因之一[87]。然而,运动对与SOX家族其他成员,如SOX9的影响已有较多报道。小鼠运动前后进行的PCR阵列分析显示,SOX9、Ⅱ型胶原A1和COMP基因的表达显著增强;在另一项组学研究中,RUNX1、SOX9和PAX3转录因子的结合位点在耐力训练中高度表达,组学结果提示运动可能通过调节SOX家族进而诱导软骨细胞分化[88]。不同动物和细胞实验进一步验证了这一点,与正常对照组相比,兔创伤性骨关节炎模型中,关节牵引后软骨中Ⅱ型胶原、聚集蛋白聚糖、SOX9和滑液超氧化物歧化酶的表达均上调[89];进一步发现特别是运动组软骨再生基因的表达量最高,包括Ⅱ型胶原蛋白、聚集蛋白聚糖和SOX9[90-91]。并且有氧运动显著提高骨关节炎大鼠软骨组织中SOX9和HIF1的表达[92]。从健康或关节受损小鼠中分离的关节软骨细胞包埋在琼脂糖凝胶中,动态加压负荷后,SOX9表达水平显著增加[93]。 而不同的运动,对SOX家族的调节具体作用可能也并不完全相同。一项研究显示相比于小强度游泳组,大强度游泳组SOX6上升幅度更为显著[94]。此外,振动训练组中SOX9 mRNA和蛋白的表达显著升高;与高频振动相比,低频振动训练不仅降了Mankin评分、JNK和NF-κB p65的表达,还显著提高SOX9 mRNA和蛋白的表达,这表明低频振动训练在软骨修复方面优于高频振动[95]。后续研究也表明,通过对不同强度、频率和持续时间的对比,低强度和低频率运动后,软骨细胞通过长时间内改变SOX9的mRNA表达,表现出最显著的合成代谢反应[96]。此外,在急性运动中,与对照组、16 m/min和24 m/min组相比,8 m/min组表现出最高的SOX5表达量。与对照组相比,慢性运动显示8 m/min和12 m/min组的关节软骨厚度增加[97]。然而,8%的拉伸增加了非肌腱细胞相关基因LPL、SOX9和RUNX-2的表达,而4%的拉伸对这些基因的表达影响最小[98]。ITR小鼠表现出异常软骨形成分化升高以及非肌腱细胞相关基因LPL、RUNX-2和SOX9的基因表达增加[99]。因此,未来还需要进一步验证。 在其他组织中,SOX9 mRNA在对照组髓核样品中表达较弱,但在运动组中表达显著增强;与对照组相比,运动大鼠在椎间盘的髓核和纤维环区域中,Ⅱ型胶原A1、聚集蛋白聚糖和SOX9蛋白的表达均有增加,有趣的是该研究显示SOX6蛋白本身没有变化[96]。此外,运动还通过区域依赖性机制重塑星形胶质细胞。在已知被运动激活的大脑区域中,qRT-PCR分析显示运动诱导的SOX9表达显著升高。此外,半程马拉松表现后,循环祖细胞中SOX9、Ⅱ型胶原A1和COMP的表达也显著增加[100]。机制方面,与跑步机跑步相比,运动降低miR-124和miR-132的表达[101],同时增加它们的靶基因糖皮质激素受体(GR)、SOX9和GTP活化蛋白P250的表达[102]。此外,miRNA谱分析表明,靶向RUNX1、SOX9和PAX3的多个miRNA在耐力训练后表达下调,这提示运动可能通过调节miRNA的表达有效调控SOX9的活性[103-104]。跑步机训练还提高了机械生长因子的表达,增强了肌腱干细胞在髌腱和跟腱中的增殖潜力。尽管如此,跑步机训练虽然上调了腱细胞相关基因如Ⅰ型胶原和肌腱调节素,但并未显著影响非腱细胞相关基因如SOX9的表达,这部分内容仍有待进一步研究[104-105]。 研究表明,运动可通过增加SOX9、Ⅱ型胶原A1、COMP等基因的表达,促进软骨细胞的分化和修复。此外,不同强度、频率的运动对SOX家族成员的调控作用各不相同。振动训练、跑步等运动形式对SOX9的表达也有显著影响,但效果最好的运动形式仍存在争议,未来的研究可以进一步探讨运动对SOX5及其家族的具体调控机制,尤其是在不同类型、强度和持续时间的运动对SOX家族成员的作用差异。此外,深入研究SOX5及其家族在不同组织中的调控机制,尤其是在非软骨组织,如星形胶质细胞、椎间盘和肌腱中的功能,也将为运动医学和软骨修复提供新的见解。"

| [1] BALASUBRAMANIAN R, CROWLEY WF, JR. Isolated Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) Deficiency//ADAM MP, FELDMAN J, MIRZAA GM, et al. GeneReviews(®). Seattle (WA); University of Washington, Seattle Copyright © 1993-2024, University of Washington, Seattle. GeneReviews is a registered trademark of the University of Washington, Seattle. All rights reserved. 1993. [2] NGUYEN NTK, LEE SS, CHEN PH, et al. Enhanced Calvarial Bone Repair Using ASCs Engineered with RNA-Guided Split dCas12a System that Co-Activates Sox 5, Sox6, and Long Non-Coding RNA H19. Small. 2024; 20(21):e2306612. [3] KASHER M, WILLIAMS FMK, FREIDIN MB, et al. Insights into the pleiotropic relationships between chronic back pain and inflammation-related musculoskeletal conditions: rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporotic abnormalities. Pain. 2023;164(3):e122-e134. [4] XUE JD, XIANG WF, CAI MQ, et al. Biological functions and therapeutic potential of SRY related high mobility group box 5 in human cancer. Front Oncol. 2024;14:1332148. [5] LIAN R, WU G, XU F, et al. Clinical cases series and pathogenesis of Lamb-Shaffer syndrome in China. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024;19(1):281. [6] TENORIO-CASTANO J, GÓMEZ ÁS, CORONADO M, et al. Lamb-Shaffer syndrome: 20 Spanish patients and literature review expands the view of neurodevelopmental disorders caused by SOX5 haploinsufficiency. Clinical genetics. 2023;104(6): 637-647. [7] ZHU GQ, DONG P, LI DY, et al. Clinical characterization of Lamb-Shaffer syndrome: a case report and literature review. BMC Med Genomics. 2023;16(1):22. [8] ZHAO Y, PENG X, WANG Q, et al. Crosstalk Between the Neuroendocrine System and Bone Homeostasis. Endocr Rev. 2024;45(1):95-124. [9] KELLUM E, STARR H, AROUNLEUT P, et al. Myostatin (GDF-8) deficiency increases fracture callus size, Sox-5 expression, and callus bone volume. Bone. 2009;44(1):17-23. [10] NORDIN K, LABONNE C. Sox5 Is a DNA-binding cofactor for BMP R-Smads that directs target specificity during patterning of the early ectoderm. Dev Cell. 2014;31(3):374-382. [11] LI Y, YANG S, QIN L, et al. TAZ is required for chondrogenesis and skeletal development. Cell Discov. 2021;7(1):26. [12] CHU FT, TANG GH, HU Z, et al. Mandibular functional positioning only in vertical dimension contributes to condylar adaptation evidenced by concomitant expressions of L-Sox5 and type II collagen. Arch Oral Biol. 2008;53(6):567-574. [13] FENG X, SHI Y, XU L, et al. Modulation of IL-6 induced RANKL expression in arthritic synovium by a transcription factor SOX5. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32001. [14] ZHANG Y, KONG L, CARLSON CS, et al. Cbfa1-dependent expression of an interferon-inducible p204 protein is required for chondrocyte differentiation. Cell Death Differ. 2008;15(11):1760-1771. [15] SMITS P, LEFEBVRE V. Sox5 and Sox6 are required for notochord extracellular matrix sheath formation, notochord cell survival and development of the nucleus pulposus of intervertebral discs. Development. 2003;130(6):1135-1148. [16] DY P, SMITS P, SILVESTER A, et al. Synovial joint morphogenesis requires the chondrogenic action of Sox5 and Sox6 in growth plate and articular cartilage. Dev Biol. 2010;341(2):346-59. [17] LIU CF, LEFEBVRE V. The transcription factors SOX9 and SOX5/SOX6 cooperate genome-wide through super-enhancers to drive chondrogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(17):8183-8203. [18] SMITS P, DY P, MITRA S, et al. Sox5 and Sox6 are needed to develop and maintain source, columnar, and hypertrophic chondrocytes in the cartilage growth plate. J Cell Biol. 2004;164(5):747-758. [19] IKEDA T, ZHANG J, CHANO T, et al. Identification and characterization of the human long form of Sox5 (L-SOX5) gene. Gene. 2002;298(1):59-68. [20] MAK CCH, TO K, FEKIR K, et al. Infrapatellar fat pad adipose-derived stem cells co-cultured with articular chondrocytes from osteoarthritis patients exhibit increased chondrogenic gene expression. Cell Commun Signal. 2022;20(1):17. [21] OSSENDORFF R, WALTER SG, SCHILDBERG FA, et al. Biologic principles of minced cartilage implantation: a narrative review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(6):3259-3269. [22] MATTHEWS JR, SONNIER JH, PAUL RW, et al. A systematic review of cartilage procedures for unstable osteochondritis dissecans. Phys Sportsmed. 2023;51(6):497-505. [23] HARGUS G, KIST R, KRAMER J, et al. Loss of Sox9 function results in defective chondrocyte differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells in vitro. Int J Dev Biol. 2008;52(4):323-332. [24] YLÖSTALO J, SMITH JR, POCHAMPALLY RR, et al. Use of differentiating adult stem cells (marrow stromal cells) to identify new downstream target genes for transcription factors. Stem Cells. 2006;24(3):642-652.
[25] WAN L, ZHANG F, HE Q, et al. EPO promotes bone repair through enhanced cartilaginous callus formation and angiogenesis. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e102010. [26] BOBICK BE, TUAN RS, CHEN FH. The intermediate filament vimentin regulates chondrogenesis of adult human bone marrow-derived multipotent progenitor cells. J Cell Biochem. 2010;109(1):265-276. [27] AKIYAMA H, CHABOISSIER MC, MARTIN JF, et al. The transcription factor Sox9 has essential roles in successive steps of the chondrocyte differentiation pathway and is required for expression of Sox5 and Sox6. Genes Dev. 2002;16(21):2813-2828. [28] KOU I, IKEGAWA S. SOX9-dependent and -independent transcriptional regulation of human cartilage link protein. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(49): 50942-50948. [29] KIMURA A, INOSE H, YANO F, et al. Runx1 and Runx2 cooperate during sternal morphogenesis. Development. 2010;137(7):1159-1167. [30] AZA-CARMONA M, SHEARS DJ, YUSTE-CHECA P, et al. SHOX interacts with the chondrogenic transcription factors SOX5 and SOX6 to activate the aggrecan enhancer. Hum Mol Genet. 2011;20(8):1547-1559. [31] NAGY A, KÉNESI E, RENTSENDORJ O, et al. Evolutionarily conserved, growth plate zone-specific regulation of the matrilin-1 promoter: L-Sox5/Sox6 and Nfi factors bound near TATA finely tune activation by Sox9. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31(4):686-699. [32] SZEGECZKI V, BAUER B, JÜNGLING A, et al. Age-related alterations of articular cartilage in pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) gene-deficient mice. GeroScience. 2019;41(6):775-793. [33] TORREGGIANI E, LISIGNOLI G, MANFERDINI C, et al. Role of Slug transcription factor in human mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2012;16(4):740-751. [34] SHIBATA S, SUDA N, SUZUKI S, et al. An in situ hybridization study of Runx2, Osterix, and Sox9 at the onset of condylar cartilage formation in fetal mouse mandible. J Anat. 2006;208(2):169-177. [35] DIEDERICHS S, GABLER J, AUTENRIETH J, et al. Differential Regulation of SOX9 Protein During Chondrogenesis of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Versus Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: A Shortcoming for Cartilage Formation. Stem Cells Dev. 2016;25(8):598-609. [36] FUKUOKA H, SHIBATA S, SUDA N, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein rescues the lack of secondary cartilage in Runx2-deficient mice. J Anat. 2007;211(1):8-15. [37] SEKIYA I, VUORISTO JT, LARSON BL, et al. In vitro cartilage formation by human adult stem cells from bone marrow stroma defines the sequence of cellular and molecular events during chondrogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(7):4397-4402. [38] UUSITALO H, HILTUNEN A, AHONEN M, et al. Induction of periosteal callus formation by bone morphogenetic protein-2 employing adenovirus-mediated gene delivery. Matrix Biol. 2001;20(2):123-127. [39] OMOTEYAMA K, TAKAGI M. The effects of Sp7/Osterix gene silencing in the chondroprogenitor cell line, ATDC5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;403(2):242-246. [40] GAO L, SHEU T J, DONG Y, et al. TAK1 regulates SOX9 expression in chondrocytes and is essential for postnatal development of the growth plate and articular cartilages. J Cell Sci. 2013;126(Pt 24):5704-5713. [41] YOON BS, OVCHINNIKOV DA, YOSHII I, et al. Bmpr1a and Bmpr1b have overlapping functions and are essential for chondrogenesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(14):5062-5067. [42] CHIMAL-MONROY J, RODRIGUEZ-LEON J, MONTERO JA, et al. Analysis of the molecular cascade responsible for mesodermal limb chondrogenesis: Sox genes and BMP signaling. Dev Biol. 2003;257(2):292-301. [43] HOJO H, OHBA S, TANIGUCHI K, et al. Hedgehog-Gli activators direct osteo-chondrogenic function of bone morphogenetic protein toward osteogenesis in the perichondrium. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(14):9924-9932. [44] TAN Z, NIU B, TSANG KY, et al. Synergistic co-regulation and competition by a SOX9-GLI-FOXA phasic transcriptional network coordinate chondrocyte differentiation transitions. PLoS Genet. 2018; 14(4):e1007346. [45] YANO F, OHBA S, MURAHASHI Y, et al. Runx1 contributes to articular cartilage maintenance by enhancement of cartilage matrix production and suppression of hypertrophic differentiation. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):7666. [46] OTERO M, PENG H, HACHEM KE, et al. ELF3 modulates type II collagen gene (COL2A1) transcription in chondrocytes by inhibiting SOX9-CBP/p300-driven histone acetyltransferase activity. Connect Tissue Res. 2017;58(1):15-26. [47] BOBICK BE, MATSCHE AI, CHEN FH, et al. The ERK5 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways play opposing regulatory roles during chondrogenesis of adult human bone marrow-derived multipotent progenitor cells. J Cell Physiol. 2010;224(1):178-186. [48] OKADA K, FUKAI A, MORI D, et al. Identification of SCAN domain zinc-finger gene ZNF449 as a novel factor of chondrogenesis. PLoS One. 2014;9(12) e115169. [49] OSAKI M, TAN L, CHOY BK, et al. The TATA-containing core promoter of the type II collagen gene (COL2A1) is the target of interferon-gamma-mediated inhibition in human chondrocytes: requirement for Stat1 alpha, Jak1 and Jak2. Biochem J. 2003;369(Pt 1):103-115. [50] MERKES C, TURKALO TK, WILDER N, et al. Ewing sarcoma ewsa protein regulates chondrogenesis of Meckel’s cartilage through modulation of Sox9 in zebrafish. PLoS One. 2015;10(1):e0116627. [51] CERSOSIMO LM, WORLEY JN, BRY L. Approaching toxigenic Clostridia from a One Health perspective. Anaerobe. 2024;87:102839. [52] CHEN M, ZOU S, HE C, et al. Transactivation of SOX5 by Brachyury promotes breast cancer bone metastasis. Carcinogenesis. 2020;41(5): 551-560. [53] ZHANG D, LIU S. SOX5 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in osteosarcoma via regulation of Snail. J BUON. 2017;22(1):258-264. [54] 李景峰,陈舒振,杨阳,等. SOX5对骨肉瘤细胞迁移和侵袭能力的影响[J].骨科,2017,8(4):309-312+316. [55] 张岱阳. SOX5通过调节Snail促进骨肉瘤中上皮-间质转化的研究[D].武汉:武汉大学,2017. [56] ZHANG P, LI J. Down-regulation of circular RNA hsa_circ_0007534 suppresses cell growth by regulating miR-219a-5p/SOX5 axis in osteosarcoma. J Bone Oncol. 2021:27:100349. [57] HU XH, DAI J, SHANG HL, et al. SP1-mediated upregulation of lncRNA ILF3-AS1 functions a ceRNA for miR-212 to contribute to osteosarcoma progression via modulation of SOX5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;511(3):510-517. [58] WEN Y, GUO X, HAO J, et al. Integrative analysis of genome-wide association studies and gene expression profiles identified candidate genes for osteoporosis in Kashin-Beck disease patients. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(3):1041-1046. [59] FANG S, LIU Z, WU S, et al. Pro-angiognetic and pro-osteogenic effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-21-5p in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):226. [60] XU L, ZHENG L, WANG Z, et al. TNF-α-Induced SOX5 Upregulation Is Involved in the Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through KLF4 Signal Pathway. Mol Cells. 2018;41(6):575-581. [61] HOFFMANN S, ROETH R, DIEBOLD S, et al. Identification and Tissue-Specific Characterization of Novel SHOX-Regulated Genes in Zebrafish Highlights SOX Family Members Among Other Genes. Front Genet. 2021;12:688808. [62] AZA-CARMONA M, BARCA-TIERNO V, HISADO-OLIVA A, et al. NPPB and ACAN, two novel SHOX2 transcription targets implicated in skeletal development. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e83104. [63] DE JONG MME, CHEN L, RAAIJMAKERS M, et al. Bone marrow inflammation in haematological malignancies. Nat Rev Immunol. 2024;24(8):543-558. [64] MONJE A, PONS R, NART J, et al. Selecting biomaterials in the reconstructive therapy of peri-implantitis. Periodontology 2000. 2024; 94(1):192-212.
[65] GAO Y, ZHANG Y, LIU X. Rheumatoid arthritis: pathogenesis and therapeutic advances. MedComm. 2024;5(3):e509.
[66] YU J, WANG B, ZHANG F, et al. Single-cell transcriptome reveals Staphylococcus aureus modulating fibroblast differentiation in the bone-implant interface. Mol Med. 2023;29(1):35. [67] GAO D, HU B, DING B, et al. N6-Methyladenosine-induced miR-143-3p promotes intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating SOX5. Bone. 2022;163:116503. [68] TYE CE, GHULE PN, GORDON JAR, et al. LncMIR181A1HG is a novel chromatin-bound epigenetic suppressor of early stage osteogenic lineage commitment. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):7770. [69] BUDD E, DE ANDRÉS MC, SANCHEZ-ELSNER T, et al. MiR-146b is down-regulated during the chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow derived skeletal stem cells and up-regulated in osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2017:7:46704. [70] 张磊,宁玉辉,李国顺,等.敲低SOX5对骨关节炎软骨细胞生物学功能的影响[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2017,6(12):932-937. [71] HERLOFSEN SR, KÜCHLER AM, MELVIK JE, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in self-gelling alginate discs reveals novel chondrogenic signature gene clusters. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(7-8):1003-1013. [72] IKEDA T, KAMEKURA S, MABUCHI A, et al. The combination of SOX5, SOX6, and SOX9 (the SOX trio) provides signals sufficient for induction of permanent cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(11):3561-3573. [73] ENKHMANDAKH B, BAYARSAIHAN D. Single-cell transcriptome profiling reveals distinct expression patterns among genes in the mouse incisor dental pulp. Int J Dev Biol. 2023;67(1):19-25. [74] TAKAI H, VAN WIJNEN AJ, OGATA Y. Induction of chondrogenic or mesenchymal stem cells from human periodontal ligament cells through inhibition of Twist2 or Klf12. J Oral Sci. 2019;61(2):313-320. [75] NOGUCHI K, WATANABE Y, FUSE T, et al. A new chondrogenic differentiation initiator with the ability to up-regulate SOX trio expression. J Pharmacol Sci. 2010;112(1): 89-97. [76] KIM YI, NO LEE J, BHANDARI S, et al. Cartilage development requires the function of Estrogen-related receptor alpha that directly regulates sox9 expression in zebrafish. Sci Rep. 2015;5:18011. [77] JANG Y, JUNG H, NAM Y, et al. Centrifugal gravity-induced BMP4 induces chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells via SOX9 upregulation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):184. [78] WANG T, NIMKINGRATANA P, SMITH CA, et al. Enhanced chondrogenesis from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2019;39:101497. [79] YANG HN, PARK JS, WOO DG, et al. Chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells and dedifferentiated chondrocytes by transfection with SOX Trio genes. Biomaterials. 2011;32(30):7695-7704. [80] TRUONG VA, LIN YH, NGUYEN NTK, et al. Bi-directional gene activation and repression promote ASC differentiation and enhance bone healing in osteoporotic rats. Mol Ther. 2022;30(1):92-104. [81] DIAZ-HERNANDEZ ME, KHAN NM, TROCHEZ CM, et al. Derivation of notochordal cells from human embryonic stem cells reveals unique regulatory networks by single cell-transcriptomics. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(6):5241-5255. [82] SEKI S, IWASAKI M, MAKINO H, et al. Direct Reprogramming and Induction of Human Dermal Fibroblasts to Differentiate into iPS-Derived Nucleus Pulposus-like Cells in 3D Culture. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(7):4059. [83] KHAN WS, ADESIDA AB, HARDINGHAM TE. Hypoxic conditions increase hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 2alpha and enhance chondrogenesis in stem cells from the infrapatellar fat pad of osteoarthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(3):R55. [84] LEGENDRE F, OLLITRAULT D, HERVIEU M, et al. Enhanced hyaline cartilage matrix synthesis in collagen sponge scaffolds by using siRNA to stabilize chondrocytes phenotype cultured with bone morphogenetic protein-2 under hypoxia. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2013;19(7):550-567. [85] LI M, ZHANG L, LI J, et al. Direct Reprogramming of Mouse Subchondral Bone Osteoblasts into Chondrocyte-like Cells. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2582. [86] LÓPEZ-RUIZ E, PERÁN M, COBO-MOLINOS J, et al. Chondrocytes extract from patients with osteoarthritis induces chondrogenesis in infrapatellar fat pad-derived stem cells. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):246-258. [87] VAN DE VEGTE YJ, TEGEGNE BS, VERWEIJ N, et al. Genetics and the heart rate response to exercise. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(12):2391-2409. [88] DALLE CARBONARE L, MOTTES M, CHERI S, et al. Increased Gene Expression of RUNX2 and SOX9 in Mesenchymal Circulating Progenitors Is Associated with Autophagy during Physical Activity. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:2019:8426259. [89] KELLER P, VOLLAARD NB, GUSTAFSSON T, et al. A transcriptional map of the impact of endurance exercise training on skeletal muscle phenotype. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011;110(1):46-59. [90] LIU X, CHEN R, SONG Z, et al. Exercise following joint distraction inhibits muscle wasting and delays the progression of post-traumatic osteoarthritis in rabbits by activating PGC-1α in skeletal muscle. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):325. [91] SUN ZB, PENG H. Experimental Study on the Prevention of Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis in the Rabbit Knee Using a Hinged External Fixator in Combination with Exercises. J Invest Surg. 2019;32(6):552-559. [92] ASADI S, FARZANEGI P, AZARBAYJANI MA. Combined therapies with exercise, ozone and mesenchymal stem cells improve the expression of HIF1 and SOX9 in the cartilage tissue of rats with knee osteoarthritis. Physiol Int. 2020;107(2):231-242. [93] NOMURA M, MORIYAMA H, WAKIMOTO Y, et al. Disuse atrophy of articular cartilage can be restored by mechanical reloading in mice. Mol Biol Rep. 2024;51(1):1018. [94] SOCI UPR, FERNANDES T, BARAUNA VG, et al. Epigenetic control of exercise training-induced cardiac hypertrophy by miR-208. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016;130(22):2005-2015. [95] WANG ZB, WANG L, LIU QQ, et al. Repair impact of vibration exercise with different frequencies on articular cartilage of rats with early knee osteoarthritis and its JNK/NF-κB, SOX9 mechanisms. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2022;38(1):41-46. [96] WAKIMOTO Y, MIURA Y, INOUE S, et al. Effects of different combinations of mechanical loading intensity, duration, and frequency on the articular cartilage in mice. Mol Biol Rep. 2024;51(1):862. [97] HE C, TSUBAKI T, INOUE S, et al. Effects of aerobic exercise at different intensities on articular cartilage in mice. Physiol Int. 2024;111(3):271-286. [98] ZHANG J, WANG JH. Moderate Exercise Mitigates the Detrimental Effects of Aging on Tendon Stem Cells. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0130454. [99] ZHANG J, NIE D, WILLIAMSON K, et al. Moderate and intensive mechanical loading differentially modulate the phenotype of tendon stem/progenitor cells in vivo. PLoS One. 2020;15(12):e0242640. [100] BRISBY H, WEI AQ, MOLLOY T, et al. The effect of running exercise on intervertebral disc extracellular matrix production in a rat model. Spine. 2010;35(15):1429-1436. [101] LUNDQUIST AJ, PARIZHER J, PETZINGER GM, et al. Exercise induces region-specific remodeling of astrocyte morphology and reactive astrocyte gene expression patterns in male mice. J Neurosci Res. 2019; 97(9):1081-1094. [102] SHEN H, SCHWARTZ AG, CIVITELLI R, et al. Connexin 43 Is Necessary for Murine Tendon Enthesis Formation and Response to Loading. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(8):1494-1503. [103] DEIANA M, MALERBA G, DALLE CARBONARE L, et al. Physical Activity Prevents Cartilage Degradation: A Metabolomics Study Pinpoints the Involvement of Vitamin B6. Cells. 2019;8(11):1374. [104] MOJTAHEDI S, SHABKHIZ F, RAVASI AA, et al. Voluntary wheel running promotes improvements in biomarkers associated with neurogenic activity in adult male rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;533(4):1505-1511. [105] ZHANG J, WANG JH. The effects of mechanical loading on tendons-an in vivo and in vitro model study. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e71740. |
| [1] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [2] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [3] | Li Kaiying, Wei Xiaoge, Song Fei, Yang Nan, Zhao Zhenning, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng. Mechanism of Lijin manipulation regulating scar formation in skeletal muscle injury repair in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [4] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [5] | Wang Yuru, Li Siyuan, Xu Ye, Zhang Yumeng, Liu Yang, Hao Huiqin. Effects of wogonin on joint inflammation in collagen-induced arthritis rats via the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1026-1035. |
| [6] | Bai Jing, Zhang Xue, Ren Yan, Li Yuehui, Tian Xiaoyu. Effect of lncRNA-TNFRSF13C on hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in periodontal cells by modulation of #br# miR-1246 #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 928-935. |
| [7] | Zhi Fang, Zhu Manhua, Xiong Wei, Lin Xingzhen. Analgesic effect of acupuncture in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 936-941. |
| [8] | Yu Hui, Yang Yang, Wei Ting, Li Wenli, Luo Wenqian, Liu Bin. Gadd45b alleviates white matter damage in chronic ischemic rats by modulating astrocyte phenotype [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7797-7803. |
| [9] | Zheng Yitong, Wang Yongxin, Liu Wen, Amujite, Qin Hu. Action mechanism of intrathecal transplantation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for repair of spinal cord injury under neuroendoscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7743-7751. |
| [10] | Zhang Yixuan, Li Dongna, Liu Chunyan. Pathological processes, inflammatory responses, and related biomarkers of periodontitis: a multi-omics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7601-7610. |
| [11] | Pan Chun, Fan Zhencheng, Hong Runyang, Shi Yujie, Chen Hao. Effect and mechanism of polystyrene microplastics on prostate in male mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7353-7361. |
| [12] | Su Yongkun, Sun Hong, Liu Miao, Yang Hua, Li Qingsong. Development of novel antioxidants and antioxidant combination carried by nano-hydrogel systems in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7376-7384. |
| [13] | Wang Kairu, Fu Shizhe, Li Jiahui, Yan Ru, Ma Yuru, Shi Bo, Ye Congyan , Yan Rui, Cong Guangzhi, Jia Shaobin. Spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1 participates in vascular smooth muscle cell calcification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6836-6842. |
| [14] | Yan Laijun, Ge Haiya, Wang Zhengming, Yang Zongrui, Niu Lifeng, Zhan Hongsheng. Mechanism by which Tongdu Huoxue Decoction inhibits macrophage inflammation to delay intervertebral disc degeneration in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6851-6857. |
| [15] | Zhao Xuemei, Wang Rui, Ao · Wuliji, Bao Shuyin, Jiang Xiaohua. Effects of Agiophyllum Oligo Saccharides on inflammation and apoptosis of mouse synovial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6939-6946. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||