Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (31): 6765-6771.doi: 10.12307/2025.541
Previous Articles Next Articles
Plant-derived exosome-like nanovesicles stimulate osteoblasts, inhibit osteoclasts, and promote osteogenesis
Yao Wenxin1, Wang Yi1, 2, Cai Lin2, Feng Xiaobo1
- 1Department of Pain Management, 2Department of Spine Surgery and Musculoskeletal Tumor, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2024-05-15Accepted:2024-07-26Online:2025-11-08Published:2025-02-27 -
Contact:Wang Yi, MD, Attending physician, Department of Pain Management, and Department of Spine Surgery and Musculoskeletal Tumor, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, Hubei Province, China; Corresponding author: Cai Lin, MD, Professor, Department of Spine Surgery and Musculoskeletal Tumor, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, Hubei Province, China; Corresponding author: Feng Xiaobo, MD, Chief physician, Department of Pain Management, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Yao Wenxin, Master candidate, Department of Pain Management, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:Fund for Transformation of Scientific and Technological Achievements of Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, No. LCYFMS2024002 (to FXB); Excellent Doctor Fund Project of Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, No. ZNYB2023004 (to WY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yao Wenxin, Wang Yi, Cai Lin, Feng Xiaobo. Plant-derived exosome-like nanovesicles stimulate osteoblasts, inhibit osteoclasts, and promote osteogenesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6765-6771.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
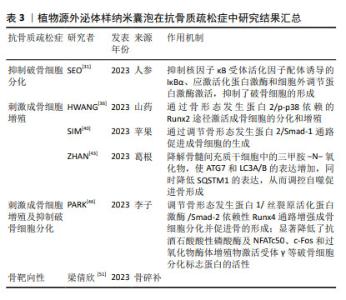
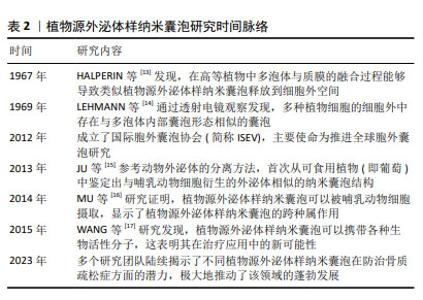
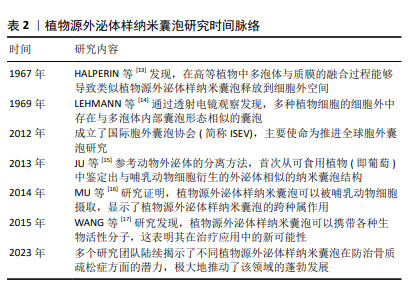
2.2 植物源外泌体样纳米囊泡概述 外泌体作为细胞间通讯的重要媒介,直径范围为30-100 nm,由多囊泡胞内体与细胞膜融合后释放到细胞外环境中[18-19]。在抗骨质疏松领域,外泌体展现出促进成骨细胞增殖、抑制破骨细胞活性及抗炎等多重功效[20-22]。然而,由于动物源外泌体的提取过程复杂、产量低、成本高等问题,寻找它的替代品成为了备受关注的热点研究方向。在此背景下,植物源外泌体样纳米囊泡逐渐进入研究视野,并因其独特的优势而备受关注。值得注意的是,植物源外泌体样纳米囊泡在大小、表面电荷、形态、密度及生物发生途径等方面与动物细胞外泌体高度相似[23],并且同样富含RNA、蛋白质和脂质等生物活性分子[24]。与哺乳动物源外泌体相比,植物源外泌体样纳米囊泡获取途径广、产量高及生产成本低,同时在安全性方面,由于植物没有任何人畜共患或人类病原体,因此体内免疫风险较低、不良反应少[25]。植物源外泌体样纳米囊泡作为一种天然产物,当前的研究焦点不仅在于如何高效获取高质量的产品,更在于深入解析植物源外泌体样纳米囊泡的生物学机制,以期实现其应用价值的最大化。 2.3 植物源外泌体样纳米囊泡在骨质疏松症治疗中的作用机制 2.3.1 植物源外泌体样纳米囊泡通过抑制破骨细胞分化抗骨质疏松症 人参是五加科植物人参属的干燥根及根茎,应用历史悠久,是回阳救逆、益气生津、补肾养血、安神明目之要药,更是现代临床用药的主要原料之一[26]。据报道,人参对心血管疾病、神经元疾病和癌症具有多种药理学特性。此外研究还发现,人参在缓解压力和神经系统疾病等方面具有巨大潜力[27-28]。人参的神奇之处不仅限于其整体提取物的应用,其内部蕴含的微观世界——如人参来源外泌体样纳米囊泡,正逐渐成为研究的新热点。在人参根中,可通过差速离心法与蔗糖梯度离心法分离提取天然纳米囊泡,通过透射电子显微镜观察到其形态呈茶托状,具有完整的双层膜结构。目前已有多项研究证明了人参源外泌体样纳米囊泡的生物学功能,例如:KIM等[27]发现人参源外泌体样纳米囊泡可通过穿透血脑屏障和调节肿瘤微环境,发挥抗神经胶质瘤作用;CAO等[29]发现,人参源外泌体样纳米囊泡通过改变巨噬细胞极化以抑制黑色素瘤生长;HAN等[30]证明人参源外泌体样纳米囊泡通过重编程冷肿瘤微环境来增强免疫检查点抗体的功效。 近来有研究证明,人参来源外泌体样纳米囊泡同样可在抗骨质疏松症方面发挥作用。SEO等[31]通过蛋白质印迹法鉴定破骨细胞分化相关的信号通路发现,人参来源外泌体样纳米囊泡实质上抑制了核因子κB受体活化因子配体诱导的IκBα、应激活化蛋白激酶和细胞外调节蛋白激酶激活,通过扩展抑制了破骨细胞的形成。多项研究已经证明,人参皂苷可通过调节芳烃受体/PRELP/核因子κB轴和激活β-catenin和Runx参与的Wnt通路等方法来抑制破骨细胞,从而预防及治疗骨质疏松症[8,32]。然而,SEO等[31]通过抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶染色比较了人参皂苷中抑制能力最强的Rb1与外泌体对破骨细胞分化的抑制作用,结果显示外泌体组中检测到的破骨细胞更少,证明了人参来源外泌体样纳米囊泡在抑制破骨细胞分化方面的功效显著高于人参皂苷。人参来源外泌体样纳米囊泡通过调控 核因子κB受体活化因子/核因子κB受体活化因子配体/骨保护素信号通路及深度干预破骨细胞分化,在骨质疏松症防治中展现巨大潜力,为治疗这一代谢性骨病提供了新方向。 2.3.2 植物源外泌体样纳米囊泡通过刺激成骨细胞增殖抗骨质疏松症 山药来源外泌体样纳米囊泡:山药属于薯蓣科薯蓣属植物,富含多种营养成分,如维生素、黏多糖、薯蓣皂苷、矿物质等,具有补脾养胃、生津益肺、补肾涩精的功效[33]。随着科学研究的深入,山药中的活性成分在治疗骨质疏松症方面的潜力逐渐显现。ZHANG等[34]从山药中分离提取了多肽和蛋白质,发现了山药肽和蛋白质具有多种药理活性,包括雌激素刺激及促进成骨等,证明山药肽和蛋白质具有对骨质疏松症的治疗潜力。WONG等[35]从山药中分离出一种名为DOI的新型蛋白,发现其可增加骨密度、骨体积分数和骨小梁数量,同时由于DOI可刺激雌二醇生物合成及孕酮分泌,认为DOI可以在体内产生抗骨质疏松症作用。这些发现不但为开发新的抗骨质疏松药物提供了新的可能性,也进一步证明了山药中活性物质的药理作用和潜力。HWANG等[36]研究发现,山药来源外泌体样纳米囊泡通过骨形态发生蛋白2/p-p38依赖的Runx2途径激活成骨细胞的分化和增殖,而后将山药来源外泌体样纳米囊泡应用于卵巢切除术诱导的绝经后骨质疏松症小鼠模型中,发现骨生成显著增强。早有研究证明,山药中薯蓣皂苷可增强成骨MC3T3-E1细胞的增殖、分化和矿化[37-38]。新的研究发现,少量外泌体可诱导更高的成骨细胞增殖、矿化和mRNA与蛋白质表达,同时通过对口服纳米囊泡的小鼠进行示踪以及分析其心、脑、肝、肾等重要器官,证明了山药来源外泌体样纳米囊泡的生物相容性及安全性[35]。综上所述,山药来源外泌体样纳米囊泡能够通过信号通路途径有效促进成骨细胞的增殖,进而显著促进骨形成;同时因其具有出色的生物安全性和相容性,可以作为治疗骨质疏松症的潜在治疗剂。 苹果来源外泌体样纳米囊泡:苹果属蔷薇科苹果属落叶乔木植物,《滇南本草》记载“苹果生津、润肺、解暑、开胃、醒酒,可治筋骨疼痛等。”苹果含有多种多酚化合物,如儿茶素、表儿茶素、根皮苷、原花青素、绿原酸、羟基肉桂酸盐、芦丁和槲皮素。研究表明,多酚可显著增加骨保护素与核因子κB配体受体激活剂的比率,预防肥胖引起的骨量流失[39]。多酚对骨骼的保护作用为探究苹果中其他物质的生物活性提供了重要的方向。SIM等[40]研究发现,经苹果来源外泌体样纳米囊泡处理的成骨细胞碱性磷酸酶活性显著升高;此外,苹果来源外泌体样纳米囊泡上调了与成骨细胞生长和分化相关的基因和蛋白表达,如Runx2、碱性磷酸酶、骨桥蛋白和骨形态发生蛋白2/4等,从而进一步激活了细胞外调节蛋白激酶和JNK相关的丝裂原激活蛋白激酶信号。这些结果表明,苹果来源外泌体样纳米囊泡可能通过调节骨形态发生蛋白2/Smad-1通路促进成骨细胞的生成,从而预防骨质疏松症。苹果来源外泌体样纳米囊泡的促进作用对成骨细胞的分化产生了积极影响,这可能为骨质疏松症的治疗提供潜在的应用价值。 葛根来源外泌体样纳米囊泡:葛根为豆科葛属植物的根,是一种传统的药食两用植物,性甘、辛、凉,有解肌退热、生津止渴、升阳止泻、通经活络之效。早有研究表明,从葛根中分离得到的外泌体样纳米囊泡可以促进M1型巨噬细胞向M2型巨噬细胞转化,进而提高抗炎作用[41]。已知三甲胺-N-氧化物是肠道菌群代谢的一种小分子有机化合物,研究显示三甲胺-N-氧化物可能参与了骨质疏松症的发展和进展,例如一项研究发现,加速老化的雄性小鼠模型中三甲胺-N-氧化物的血清水平显著增加,并且与骨密度降低相关[42]。ZHAN等[43]发现葛根外泌体样纳米囊泡能够降解骨髓间充质干细胞中的三甲胺-N-氧化物,使ATG7和LC3A/B的表达增加,同时降低SQSTM1的表达,从而调控自噬促进骨形成;此外,葛根来源外泌体样纳米囊泡还能够逆转骨小梁区域骨再生标志物的减少,如骨密度、骨体积分数和骨小梁厚度等,促进成骨细胞的分化。葛根外泌体样纳米囊泡揭示了对骨质疏松症防治的潜在机制,通过降解三甲胺-N-氧化物调控自噬,促进骨形成、减少骨吸收,为骨质疏松症治疗提供了新的研究视角和策略,展现了中医药材在现代生物医学研究中的独特价值与应用前景。 然而,在肯定这些研究成果的同时也需保持批判性思维,山药活性成分的提取与纯化技术仍面临挑战,这直接影响到其作为药物或功能性食品的商业化应用。提高提取效率、降低成本并确保产品的纯度和稳定性,是未来研究的重要方向。 2.3.3 植物源外泌体样纳米囊泡通过刺激成骨细胞及抑制破骨细胞双重作用抗骨质疏松症 蔷薇科李属木本植物,《滇南本草》记载李子味甘酸,有清热、生津、利水、健胃、祛肝火的功效,主治虚劳内热、消渴、腹水、小便不利、消化不良等症。近年来的多项研究表明,李子中多种成分可在保护骨健康方面发挥作用。SMITH等[44]研究发现,李子干中的多酚和碳水化合物在介导骨形成和吸收的改变方面发挥作用,具有潜在的益生元活性,从而在雌激素缺乏症中保护骨骼。紧随其后,RENDINA等[45]研究指出,李子干可以防止骨质流失并诱导椎骨的合成代谢反应,这些结构变化与成骨细胞活性指标的局部上调和破骨细胞生成的下调相吻合;此外,李子干还可以通过增强全身谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶活性等多种机制改善骨骼健康。这些研究不仅提供了有力的证据,证明了李子在骨骼疾病预防及治疗中的重要作用,同时也为人们进一步探索李子中的新有效成分开辟了可能性。PARK等[46]成功在李子中分离提取了外泌体样纳米囊泡,通过对成骨细胞分化标志蛋白碱性磷酸酶、骨桥蛋白、Runx2和Osterix表达水平的检测表明,成骨细胞的分化和矿化受到外泌体的调节;进一步实验发现,李子来源外泌体样纳米囊泡可以调节骨形态发生蛋白1/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶/Smad-2依赖性Runx4通路增强成骨细胞分化并促进骨的形成;李子来源外泌体样纳米囊泡显著降低了抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶及NFATc50、c-Fos和过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ等破骨细胞分化标志蛋白的活性,表明它可能通过影响这些蛋白质的表达来减少破骨细胞的分化。李子来源外泌体样纳米囊泡在抗骨质疏松症方面的作用主要表现在刺激成骨细胞分化和减少破骨细胞分化2个方面,有望成为一种新型的抗骨质疏松症药物,具有广阔的研究和应用前景。为了实现这一目标,需要进一步验证来源外泌体样纳米囊泡在抗骨质疏松症方面的效果和安全性及作用机制,以便更好地理解其在骨骼健康维护中的作用。 2.3.4 植物源外泌体样纳米囊泡具有骨靶向性 骨碎补是一种具有悠久临床应用历史的中药材,历版《中国药典》均有记载,其来源于水龙骨科植物槲蕨的干燥根茎,性味辛、苦,温,归肾、肝经,具有疗伤止痛、补肾强骨的功效,常用于肾虚腰痛、耳鸣耳聋、牙齿松动、跌扑闪挫及骨折等病症的治疗[47]。近年来,许多研究者对骨碎补的抗骨质疏松作用进行了深入的研究。骨碎补中的总黄酮等活性成分可通过调控多种骨代谢途径发挥抗骨质疏松的作用。SHI等[48]研究发现,总黄酮可通过抑制组织蛋白酶K保护骨基质的稳定性对骨质疏松症有明显的治疗作用,这意味着总黄酮可以减少骨基质的降解,从而维持骨结构的完整性,达到抗骨质疏松症的效果。SHI等[48-50]研究证明了骨碎补总黄酮可通过提高卵巢切除术后大鼠胫骨中Wnt/低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5/β-catenin通路中关键蛋白表达,调控成骨细胞的分化和骨形成,从而发挥抗骨质疏松症作用。这些研究结果进一步揭示了中药材骨碎补在治疗骨质疏松症方面的潜在价值。骨碎补抗骨质疏松症的作用机制既包括直接抑制骨基质的降解,也包括通过调节骨代谢关键信号通路的活化来促进骨形成。不仅如此,梁倩欣[51]研究还发现骨碎补来源外泌体样纳米囊泡通过不同给药途径注入小鼠体内后,在心脏、肝脏、肾脏、脾脏、肺脏等均未检测到相关信号,然而在不同时间点都在骨内检测到了骨碎补来源外泌体样纳米囊泡信号,这表明其具有一定的骨靶向性。这一特性使得植物源外泌体样纳米囊泡在骨质疏松症治疗中具有独特优势,为今后治疗骨质疏松症提供了一个新的思路,但目前关于此领域研究的报道较少,其骨靶向作用机制的具体细节和作用效果尚不完全清楚,这限制了人们对植物源外泌体样纳米囊泡在骨骼健康中作用的全面理解。 植物源外泌体样纳米囊泡在抗骨质疏松症中的研究结果汇总,见表3。 "

| [1] LORENTZON M. Treating osteoporosis to prevent fractures: current concepts and future developments. J Intern Med. 2019;285(4): 381-394. [2] RAISZ LG. Pathogenesis of osteoporosis: concepts, conflicts, and prospects. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(12):3318-3325. [3] REGINSTER JY, BURLET N. Osteoporosis: A still increasing prevalence. Bone. 2006;38(2, Supplement 1):4-9. [4] 杨成,吴斗,刘强.骨质疏松症流行病学、影响因素及其相关机制研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2023,12(4):306-310. [5] 邱晓萍,刘铠婕,林宇慧,等.骨质疏松症的流行病学、管理与防治研究进展[J].山东医药,2023,63(21):107-111. [6] CUMMINGS SR, MELTON LJ. Epidemiology and outcomes of osteoporotic fractures. Lancet. 2002;359(9319):1761-1767. [7] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会,章振林.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(14):1671-1691. [8] YANG N, ZHANG X, LI L, et al. Ginsenoside Rc Promotes Bone Formation in Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis In Vivo and Osteogenic Differentiation In Vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11): 6187. [9] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977. [10] 高文静,侯敏,王攀,等.外泌体作为中药新活性成分的研究进展[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2019,21(9):1869-1876. [11] ZHUANG X, DENG ZB, MU J, et al. Ginger-derived nanoparticles protect against alcohol-induced liver damage. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:28713. [12] LI Z, WANG H, YIN H, et al. Arrowtail RNA for Ligand Display on Ginger Exosome-like Nanovesicles to Systemic Deliver siRNA for Cancer Suppression . Sci Rep-Uk. 2018;8(1):14644. [13] HALPERIN W, JENSEN WA. Ultrastructural changes during growth and embryogenesis in carrot cell cultures. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967;18(3): 428-443. [14] LEHMANN H, SCHULZ D. [Electron microscopical studies of differentiating processes in mosses : II. Formation of cell plate and cell wall]. Planta. 1969;85(4):313-325. [15] JU S, MU J, DOKLAND T, et al. Grape exosome-like nanoparticles induce intestinal stem cells and protect mice from DSS-induced colitis. Mol Ther. 2013;21(7):1345-1357. [16] MU J, ZHUANG X, WANG Q, et al. Interspecies communication between plant and mouse gut host cells through edible plant derived exosome-like nanoparticles. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2014;58(7):1561-1573. [17] WANG Q, REN Y, MU J, et al. Grapefruit-Derived Nanovectors Use an Activated Leukocyte Trafficking Pathway to Deliver Therapeutic Agents to Inflammatory Tumor Sites. Cancer Res. 2015;75(12):2520-2529. [18] MURPHY DE, DE JONG OG, BROUWER M, et al. Extracellular vesicle-based therapeutics: natural versus engineered targeting and trafficking. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(3):1-12. [19] VAN NIEL G, D’ANGELO G, RAPOSO G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(4):213-228. [20] REN L, ZENG F, DENG J, et al. Inflammatory osteoclasts-derived exosomes promote bone formation by selectively transferring lncRNA LIOCE into osteoblasts to interact with and stabilize Osterix. Faseb J. 2022;36(2):e22115. [21] COSENZA S, TOUPET K, MAUMUS M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes are more immunosuppressive than microparticles in inflammatory arthritis. Theranostics. 2018;8(5):1399-1410. [22] DENG L, WANG Y, PENG Y, et al. Osteoblast-derived microvesicles: A novel mechanism for communication between osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Bone. 2015;79:37-42. [23] KIM J, LI S, ZHANG S, et al. Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles and their therapeutic activities. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022;17(1):53-69. [24] TENG Y, REN Y, SAYED M, et al. Plant-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Shape the Gut Microbiota. Cell Host Microbe. 2018;24(5):637-652.e8. [25] XU XH, YUAN TJ, DAD HA, et al. Plant Exosomes As Novel Nanoplatforms for MicroRNA Transfer Stimulate Neural Differentiation of Stem Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Nano Lett. 2021;21(19):8151-8159. [26] 刘伟,刘永博,王梓,等.人参的化学成分与转化机理研究进展[J].吉林农业大学学报,2023,45(6):664-673. [27] KIM HJ, JUNG SW, KIM SY, et al. Panax ginseng as an adjuvant treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. J Ginseng Res. 2018;42(4):401-411. [28] KANG S, MIN H. Ginseng, the ‘Immunity Boost’: The Effects of Panax ginseng on Immune System. J Ginseng Res. 2012;36(4):354-368. [29] CAO M, YAN H, HAN X, et al. Ginseng-derived nanoparticles alter macrophage polarization to inhibit melanoma growth. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):326. [30] HAN X, WEI Q, LV Y, et al. Ginseng-derived nanoparticles potentiate immune checkpoint antibody efficacy by reprogramming the cold tumor microenvironment. Mol Ther. 2022;30(1):327-340. [31] SEO K, YOO JH, KIM J, et al. Ginseng-derived exosome-like nanovesicles extracted by sucrose gradient ultracentrifugation to inhibit osteoclast differentiation. Nanoscale. 2023;15(12):5798-5808. [32] ZHANG D, DU J, YU M, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 prevents osteoporosis via the AHR/PRELP/NF-κB signaling axis. Phytomedicine. 2022;104:154205. [33] 毕嘉谣,田湾湾,张翼,等.经典名方中山药的本草考证[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2021,23(8):159-162. [34] ZHANG L, NG TB, LAM J KW, et al. Research and Development of Proteins and Peptides with Therapeutic Potential from Yam Tubers. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2019;20(3):277-284. [35] WONG KL, LAI YM, LI KW, et al. A Novel, Stable, Estradiol-Stimulating, Osteogenic Yam Protein with Potential for the Treatment of Menopausal Syndrome. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10179. [36] HWANG JH, PARK YS, KIM HS, et al. Yam-derived exosome-like nanovesicles stimulate osteoblast formation and prevent osteoporosis in mice. J Control Release. 2023;355:184-198. [37] ZHANG C, PENG J, WU S, et al. Dioscin promotes osteoblastic proliferation and differentiation via Lrp5 and ER pathway in mouse and human osteoblast-like cell lines. J Biomed Sci. 2014;21(1):30. [38] ALCANTARA EH, SHIN MY, SOHN HY, et al. Diosgenin stimulates osteogenic activity by increasing bone matrix protein synthesis and bone-specific transcription factor Runx2 in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. J Nutr Biochem. 2011;22(11):1055-1063. [39] MENG X, WANG X, HAN Y, et al. Protective effects of apple polyphenols on bone loss in mice with high fat diet-induced obesity. Food Funct. 2022;13(15):8047-8055. [40] SIM Y, SEO HJ, KIM DH, et al. The Effect of Apple-Derived Nanovesicles on the Osteoblastogenesis of Osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 Cells. J Med Food. 2023;26(1):49-58. [41] WU J, MA X, LU Y, et al. Edible Pueraria lobata-Derived Exosomes Promote M2 Macrophage Polarization. Molecules. 2022;27(23): 8184. [42] LI L, CHEN B, ZHU R, et al. Fructus Ligustri Lucidi preserves bone quality through the regulation of gut microbiota diversity, oxidative stress, TMAO and Sirt6 levels in aging mice. Aging (Albany NY). 2019; 11(21):9348-9368. [43] ZHAN W, DENG M, HUANG X, et al. Pueraria lobata-derived exosome-like nanovesicles alleviate osteoporosis by enhacning autophagy. J Control Release. 2023;364:644-653. [44] SMITH BJ, HATTER B, WASHBURN K, et al. Dried Plum’s Polyphenolic Compounds and Carbohydrates Contribute to Its Osteoprotective Effects and Exhibit Prebiotic Activity in Estrogen Deficient C57BL/6 Mice. Nutrients. 2022;14(9):1685. [45] RENDINA E, HEMBREE KD, DAVIS MR, et al. Dried plum’s unique capacity to reverse bone loss and alter bone metabolism in postmenopausal osteoporosis model. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e60569. [46] PARK YS, KIM HW, HWANG JH, et al. Plum-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles Induce Differentiation of Osteoblasts and Reduction of Osteoclast Activation. Nutrients. 2023;15(9):2107. [47] 尹子丽,谭文红,冯德强,等.骨碎补的本草考证及炮制、药用历史沿革[J].中国药房,2019,30(12):1725-1728. [48] SHI XL, LIU K, WU LG. Interventional value of total flavonoids from Rhizoma Drynariae on Cathepsin K, a potential target of osteoporosis. Chin J Integr Med. 2011;17(7):556-560. [49] 邓强,乔小万,李中锋,等.骨碎补活性成分治疗骨骼系统疾病研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2022,24(7):1-5. [50] 张莉丽,张布衣,余阳.骨碎补总黄酮上调骨质疏松症模型大鼠Wnt/LRP-5/β-catenin通路表达的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023, 29(6):807-811. [51] 梁倩欣.骨碎补源性细胞外囊泡基本特征、生物活性及靶向性研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2023. [52] KARAMANIDOU T, TSOUKNIDAS A. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Therapeutic Nanocarriers. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;23(1):191. [53] MU N, LI J, ZENG L, et al. Plant-Derived Exosome-Like Nanovesicles: Current Progress and Prospects. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18: 4987-5009. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [3] | Han Haihui, Ran Lei, Meng Xiaohui, Xin Pengfei, Xiang Zheng, Bian Yanqin, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [4] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [5] | Wang Wentao, Hou Zhenyang, Wang Yijun, Xu Yaozeng. Apelin-13 alleviates systemic inflammatory bone loss by inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1548-1555. |
| [6] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [7] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [8] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [9] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [10] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [11] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [12] | Lyu Liting, Yu Xia, Zhang Jinmei, Gao Qiaojing, Liu Renfan, Li Meng, Wang Lu. Bibliometric analysis of research process and current situation of brain aging and exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1457-1465. |
| [13] | Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [14] | Cao Yue, Ye Xinjian, Li Biyao, Zhang Yining, Feng Jianying. Effect of extracellular vesicles for diagnosis and therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1523-1530. |
| [15] | Li Yueyao, Zhang Min, Yang Jiaju. Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||