Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (9): 1953-1962.doi: 10.12307/2025.161
Previous Articles Next Articles
Causal relationship between modifiable factors and joint sports injuries
Dong Tingting, Chen Tianxin, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei
- Forth Department of Bone and Joint, Wangjing Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100102, China
-
Received:2024-02-27Accepted:2024-04-13Online:2025-03-28Published:2024-10-11 -
Contact:Zhang Lei, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Forth Department of Bone and Joint, Wangjing Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100102, China -
About author:Dong Tingting, MD candidate, Forth Department of Bone and Joint, Wangjing Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100102, China -
Supported by:Fundamental Research Funds for Central Public Welfare Research Institutes, No. ZZ15-XY-CT-10 (to ZL); Innovation Fund-Major Research Project of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, No. CI2021A02009 (to ZL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dong Tingting, Chen Tianxin, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei. Causal relationship between modifiable factors and joint sports injuries[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1953-1962.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
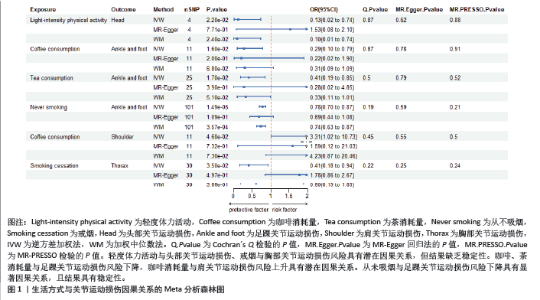
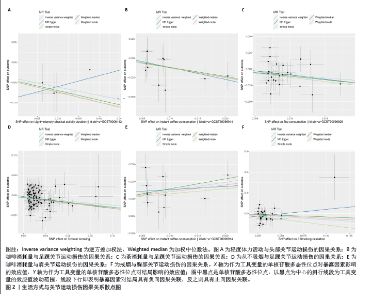
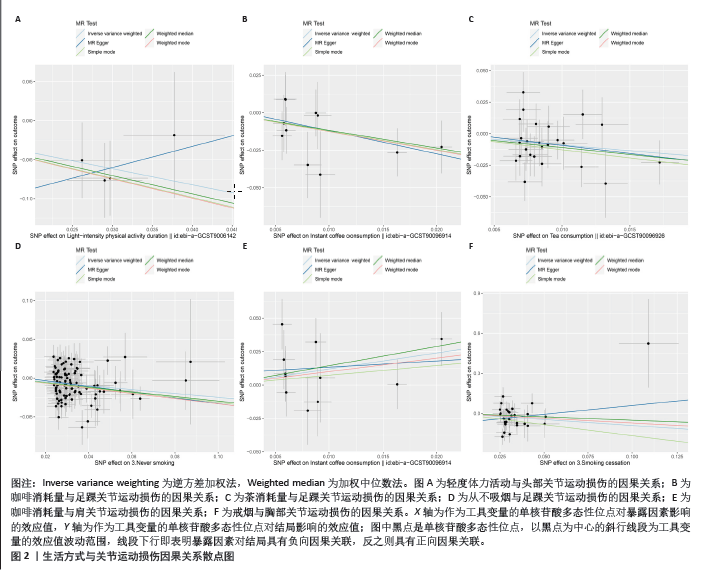
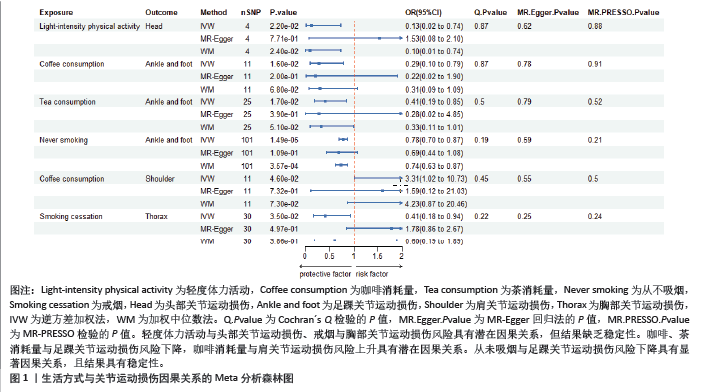
2.1 工具变量筛选结果 根据工具变量筛选的显著性阈值和去除连锁不平衡条件,得到符合条件的工具变量。在生活方式方面,得到4-113个工具变量,F值范围为10.30-615.92;在代谢特征方面,得到4-343个工具变量,F值范围为20.12-16 907.95;在营养摄入方面,得到6-19个工具变量,F值范围为20.84-34.10。此研究各暴露的F值均> 10,提示受弱工具变量影响的可能性较小,见表1。 2.2 MR分析结果 2.2.1 生活方式与关节运动损伤的因果关系 运用逆方差加权法评估生活方式与关节运动损伤的因果关系。结果显示,轻度体力活动与头部关节运动损伤风险下降,咖啡和茶消耗量与足踝关节运动损伤风险下降,咖啡消耗量与肩关节运动损伤风险上升,戒烟与胸部关节运动损伤风险下降均具有潜在因果关系(P < 0.05)。此外,从未吸烟与足踝关节运动损伤风险下降具有显著因果关系(P < 5×10-3)。加权中位数法和MR-Egger法显示轻度活动与头部关节运动损伤、戒烟与胸部关节运动损伤风险下降的Beta值方向不一致,其余因果关系Beta值方向均一致,具体见图1,2。"
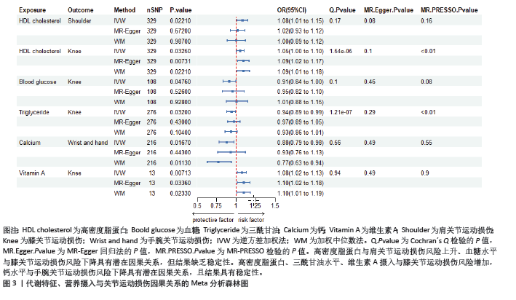
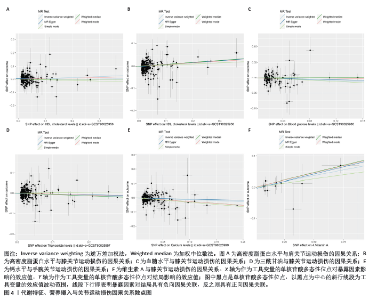
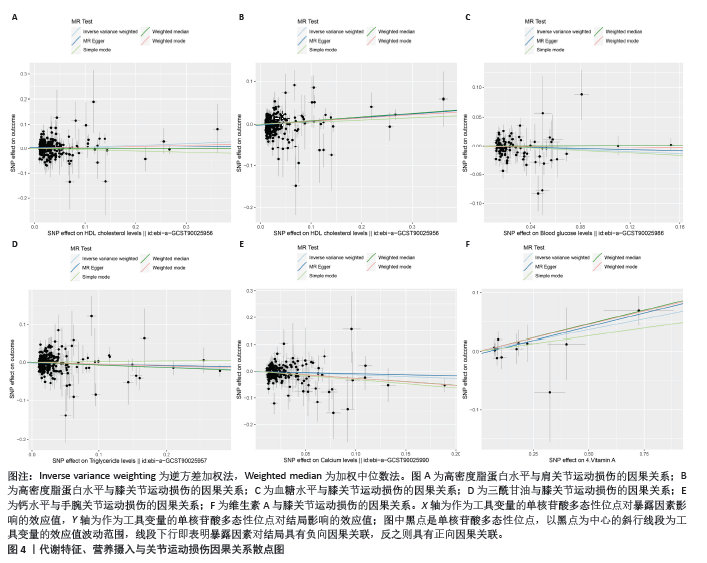
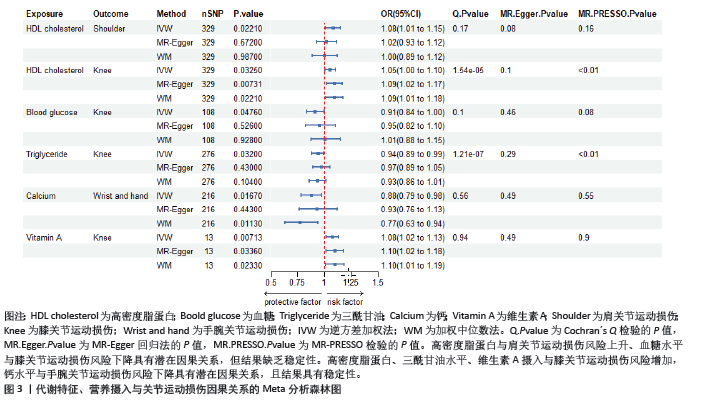
2.2.2 代谢特征与关节运动损伤的因果关系 运用逆方差加权法评估代谢特征与关节运动损伤的因果关系。结果显示高密度脂蛋白水平与肩关节运动损伤风险增加具有潜在因果关系(P < 0.05);高密度脂蛋白、血糖、三酰甘油水平与膝关节运动损伤风险增加具有潜在因果关系(P < 0.05);钙水平与手腕关节运动损伤风险下降具有潜在因果关系(P < 0.05)。加权中位数法和MR-Egger法显示高密度脂蛋白与肩关节运动损伤、血糖水平与膝关节运动损伤因果关系的Beta值方向不一致,其余结果Beta值方向一致,具体见图3,4。 2.2.3 营养摄入与关节运动损伤的因果关系 运用逆方差加权法评估营养摄入与关节运动损伤的因果关系。结果显示维生素A摄入与膝关节运动损伤风险增加具有潜在因果关系(P < 0.05)。加权中位数法和MR-Egger法显示上述结果Beta值方向一致,具体见图3,4。"
| [1] OJA L, PIKSÖÖT J. Physical activity and sports participation among adolescents: associations with sports-related knowledge and attitudes. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(10):1-8. [2] RUI P, ASHMAN JJ, AKINSEYE A. Emergency department visits for injuries sustained during sports and recreational activities by patients aged 5-24 years. 2010-2016. Natl Health Stat Report. 2019;(133):1-15. [3] MIGLIORINI F, MAFFULLI N, PINTORE A, et al. Osteoarthritis risks and sports: an evidence-based systematic review. Sports Med Arthrosc. 2022;30(3):118-140. [4] HUANG K, IHM J. Sleep and injury risk. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2021;20(6):286-290. [5] ARDELJAN A, PALMER J, DRAWBERT H, et al. Partial thickness rotator cuff tears: patient demographics and surgical trends within a large insurance database. J Orthop. 2020;17:158-161. [6] HALLIDAY TM, PETERSON NJ, THOMAS JJ, et al. Vitamin D status relative to diet, lifestyle, injury, and illness in college athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011; 43(2):335-343. [7] 陈天鑫,董婷婷,李妍,等.孟德尔随机化分析血液代谢物与肌少症相关特征的因果关系[J].中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(27):4288-4292. [8] BI W, YANG M, JIANG C. Causal effect of body mass index and physical activity on the risk of joint sports injuries: Mendelian randomization analysis in the European population. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):676. [9] WANG Y, ZHANG Y, ZHAO C, et al. Physical activity, sedentary behavior, and osteoarthritis: a two-sample mendelian randomization analysis. Iran J Public Health. 2023;52(10):2099-2108. [10] SUN Y, CAO X, CAO D, et al. Genetic estimation of correlations and causalities between multifaceted modifiable factors and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Front Nutr. 2022;9:1009122. [11] KURKI MI, KARJALAINEN J, PALTA P, et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature. 2023;613(7944):508-518. [12] JIANG L, ZHENG Z, FANG H, et al. A generalized linear mixed model association tool for biobank-scale data. Nat Genet. 2021;53(11):1616-1621. [13] BUCHWALD J, CHENOWETH MJ, PALVIAINEN T, et al. Genome-wide association meta-analysis of nicotine metabolism and cigarette consumption measures in smokers of European descent. Mol Psychiatry. 2021; 26(6):2212-2223. [14] WANG Z, EMMERICH A, PILLON NJ, et al. Genome-wide association analyses of physical activity and sedentary behavior provide insights into underlying mechanisms and roles in disease prevention. Nat Genet. 2022;54(9): 1332-1344. [15] QI G, DUTTA D, LEROUX A, et al. Genome-wide association studies of 27 accelerometry-derived physical activity measurements identified novel loci and genetic mechanisms. Genet Epidemiol. 2022;46(2):122-138. [16] DASHTI HS, JONES SE, WOOD AR, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies genetic loci for self-reported habitual sleep duration supported by accelerometer-derived estimates. Nat Commun. 2019; 10(1):1100. [17] JONES SE, LANE JM, WOOD AR, et al. Genome-wide association analyses of chronotype in 697,828 individuals provides insights into circadian rhythms. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):343. [18] SCHOELER T, SPEED D, PORCU E, et al. Participation bias in the UK Biobank distorts genetic associations and downstream analyses. Nat Hum Behav. 2023;7(7): 1216-1227. [19] PIRASTU N, MCDONNELL C, GRZESZKOWIAK EJ, et al. Using genetic variation to disentangle the complex relationship between food intake and health outcomes. PLoS Genet. 2022;18(6): e1010162. [20] DÖNERTAS HM, FABIAN DK, VALENZUELA MF, et al. Common genetic associations between age-related diseases. Nat Aging. 2021;1(4):400-412. [21] BARTON AR, SHERMAN MA, MUKAMEL RE, et al. Whole-exome imputation within UK Biobank powers rare coding variant association and fine-mapping analyses. Nat Genet. 2021;53(8):1260-1269. [22] MBATCHOU J, BARNARD L, BACKMAN J, et al. Computationally efficient whole-genome regression for quantitative and binary traits. Nat Genet. 2021;53(7): 1097-1103. [23] EMDIN CA, KHERA AV, KATHIRESAN S. Mendelian randomization. JAMA. 2017; 318(19):1925-1926. [24] YU N, QI H, GUO Y, et al. Associations between rheumatoid arthritis and skin cancer: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90(1):198-200. [25] DUAN L, XIAO R, LIU S, et al. Causality between cognitive performance and cardiovascular disease: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Gene. 2024;891:147822. [26] MOUNIER N, KUTALIK Z. Bias correction for inverse variance weighting Mendelian randomization. Genet Epidemiol. 2023;7(4): 314-331. [27] BOWDEN J, SMITH GD, HAYCOCK PC, et al. Consistent estimation in mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016;40(4): 304-314. [28] CURTIN F, SCHULZ P. Multiple correlations and Bonferroni’s correction. Biol Psychiatry. 1998;44(8):775-777. [29] STEPHENSON SD, KOCAN JW, VINOD AV, et al. A comprehensive summary of systematic reviews on sports injury prevention strategies. Orthop J Sports Med. 2021;9(10): 23259671211035776. [30] STATTIN K, MICHAËLSSON K, LARSSON SC, et al. Leisure-time physical activity and risk of fracture: a cohort study of 66,940 men and women. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32(8): 1599-1606. [31] SOLIGARD T, PALMER D, STEFFEN K, et al. Sports injury and illness incidence in the PyeongChang 2018 Olympic Winter Games: a prospective study of 2914 athletes from 92 countries. Br J Sports Med. 2019;53(17):1085-1092. [32] MASON L, CONNOLLY J, DEVENNEY LE, et al. Sleep, nutrition, and injury risk in adolescent athletes: a narrative review. Nutrients. 2023;15(24):1-16. [33] CHENNAOUI M, VANNEAU T, TRIGNOL A, et al. How does sleep help recovery from exercise-induced muscle injuries? J Sci Med Sport. 2021;24(10):982-987. [34] SIROTKIN AV, KOLESÁROVÁ A. The anti-obesity and health-promoting effects of tea and coffee. Physiol Res. 2021;70(2):161-168. [35] HODGSON AB, RANDELL RK, JEUKENDRUP AE. The metabolic and performance effects of caffeine compared to coffee during endurance exercise. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e59561. [36] MOON HS, CHUNG CS, LEE HG, et al. Inhibitory effect of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on lipid accumulation of 3T3-L1 cells. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2007;15(11): 2571-2582. [37] HIBI M, TAKASE H, IWASAKI M, et al. Efficacy of tea catechin-rich beverages to reduce abdominal adiposity and metabolic syndrome risks in obese and overweight subjects: a pooled analysis of 6 human trials. Nutr Res. 2018;55:1-10. [38] VUURBERG G, ALTINK N, RAJAI M, et al. Weight, BMI and stability are risk factors associated with lateral ankle sprains and chronic ankle instability: a meta-analysis. J ISAKOS. 2019;4(6):313-327. [39] CHUNG CM, SHIN S, LEE Y, et al. Determination of the Predictors with the Greatest Influence on Walking in the Elderly. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022; 58(11):1-13. [40] ŐSZ BE, JÎTCĂ G, ȘTEFĂNESCU RE, et al. Caffeine and its antioxidant properties-it is all about dose and source. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(21):1-21. [41] CHEN YH, CHOU YH, YANG TY, et al. The effects of frequent coffee drinking on female-dominated healthcare workers experiencing musculoskeletal pain and a lack of sleep. J Pers Med. 2022;13(1):1-13. [42] ZHAO J, LUO M, LIANG G, et al. Risk factors for supraspinatus tears: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Orthop J Sports Med. 2021;9(10):23259671211042826. [43] HOU W, CHEN S, ZHU C, et al. Associations between smoke exposure and osteoporosis or osteopenia in a US NHANES population of elderly individuals. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1074574. [44] HUEGEL J, NUSS CA, CHAN PYW, et al. Chronic nicotine exposure minimally affects rat supraspinatus tendon properties and bone microstructure. Ann Biomed Eng. 2021;49(5):1333-1341. [45] BISHOP JY, SANTIAGO-TORRES JE, RIMMKE N, et al. Smoking predisposes to rotator cuff pathology and shoulder dysfunction: a systematic review. Arthroscopy. 2015; 31(8):1598-1605. [46] AL-BASHAIREH AM, HADDAD LG, WEAVER M, et al. The effect of tobacco smoking on musculoskeletal health: a systematic review. J Environ Public Health. 2018:4184190. [47] LEE DO, EOM JS, JUNG HG. The effect of smoking on the outcomes of lateral ankle ligament reconstruction. J Orthop Sci. 2018;23(1):88-91. [48] SENORSKI EH, SVEDMAN S, SVANTESSON E, et al. Understanding limitations in sport 1 year after an Achilles tendon rupture: a multicentre analysis of 285 patients. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(1):233-244. [49] VAIDYA R, LAKE SP, ZELLERS JA. Effect of diabetes on tendon structure and function: not limited to collagen crosslinking. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2023;17(1):89-98. [50] ADAMSKA O, STOLARCZYK A, GONDEK A, et al. Ligament alteration in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Med. 2022;11(19):1-11. [51] QIAN Y, HUANG H, WAN R, et al. Progress in studying the impact of hyperlipidemia and statins on rotator cuff injury and repair. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1279118. [52] CHAPOTTE-BALDACCI CA, COGNARD C, BOIS P, et al. Handling a mature calcium signature through optogenetics improves the differentiation of primary murine myotubes. Cell Calcium. 2022;103:102546. [53] YUAN H, KURASHINA K, BRUIJN JD, et al. A preliminary study on osteoinduction of two kinds of calcium phosphate ceramics. Biomaterials.1999;20(19):1799-806. [54] CAI J, ZHANG Q, CHEN J, et al. Electrodeposition of calcium phosphate onto polyethylene terephthalate artificial ligament enhances graft-bone integration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(3): 783-793. [55] ALSHAMRANI HA, ALLOUB H, BURKE D, et al. Vitamin D intake, calcium intake and physical activity among children with wrist and ankle injuries and the association with fracture risk. Nutr Health. 2019;25(2):113-118. [56] CIPOLLETTA E, MOSCIONI E, SIROTTI S, et al. Diagnosis of calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition disease by ultrasonography: how many and which sites should be scanned? Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kead565. [57] TENFORDE AS, SAYRES LC, SAINANI KL, et al. Evaluating the relationship of calcium and vitamin D in the prevention of stress fracture injuries in the young athlete: a review of the literature. PM R. 2010;2(10):945-949. [58] CHOI JT, YOSHIDA B, JALALI O, et al. Malnutrition in orthopaedic sports medicine: a review of the current literature. Sports Health. 2021;13(1):65-70. [59] STECKER RA, HARTY PS, JAGIM AR, et al. Timing of ergogenic aids and micronutrients on muscle and exercise performance. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2019;16(1):37. [60] HEFFERNAN SM, HORNER K, VITO GD, et al. The role of mineral and trace element supplementation in exercise and athletic performance: a systematic review. Nutrients. 2019;11(3):1-32. [61] IOLASCON G, MORETTI A, PAOLETTA M, et al. Muscle regeneration and function in sports: a focus on Vitamin D. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(10):1-9. [62] RIGHI NC, SCHUCH FB, NARDI ATD, et al. Effects of vitamin C on oxidative stress, inflammation, muscle soreness, and strength following acute exercise: meta-analyses of randomized clinical trials. Eur J Nutr. 2020;59(7):2827-2839. [63] BHATTACHARYA S, SINGH A. Phasing out of the universal mega dose of vitamin-a prophylaxis to avoid toxicity. AIMS Public Health. 2017;4(1):38-46. [64] TACK C, SHORTHOUSE F, KASS L. The physiological mechanisms of effect of vitamins and amino acids on tendon and muscle healing: a systematic review. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2018;28(3): 294-311. |
| [1] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei, Zhou Jiatan. Based on Mendelian randomization, the causal relationship between 1400 metabolites and sarcopenia and the correlation analysis of cardiovascular disease were investigated [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-11. |
| [3] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [4] |
Zhao Wensheng, Li Xiaolin, Peng Changhua, Deng Jia, Sheng Hao, Chen Hongwei, Zhang Chaoju, He Chuan.
Gut microbiota and osteoporotic fractures #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1296-1304.
|
| [5] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [6] | Li Jiatong, Jin Yue, Liu Runjia, Song Bowen, Zhu Xiaoqian, Li Nianhu . Association between thyroid function levels and phenotypes associated with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1312-1320. |
| [7] | Wu Guangtao, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Fan Yidong, Li Weicai, Zhu Baogang, Cao Ying . Causal relationship between immune cells and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1081-1090. |
| [8] | Wang Xuepeng, , He Yong, . Effect of insulin-like growth factor family member levels on inflammatory arthritis: a FinnGen biobank-based analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7656-7662. |
| [9] | Wang Tao, Wang Shunpu, Min Youjiang, Wang Min, Li Le, Zhang Chen, Xiao Weiping. Causal relationship between gut microbiota and rheumatoid arthritis: data analysis in European populations based on GWAS data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7663-7668. |
| [10] | Han Jie, Pan Chengzhen, Shang Yuzhi, Zhang Chi. Identification of immunodiagnostic biomarkers and drug screening for steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7690-7700. |
| [11] | Wu Zhenhua, Zhang Xiwei, Wang Yipin, Li Qianqian. Relationship between seven serum lipid traits and osteoarthritis: a large sample analysis of European population in IEU OPEN GWAS database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 7004-7014. |
| [12] | Liu Xiaowu, Liu Jinping, Wu Ting, He Xian, Cai Jianxiong. Antioxidants from different sources and osteoarthritis: a genome-wide association analysis in European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 7015-7027. |
| [13] | Zhang Bochun, Li Wei, Li Guangzheng, Ding Haoqin, Li Gang, Liang Xuezhen, . Association between neuroimaging changes and osteonecrosis: a large sample analysis from UK Biobank and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6574-6582. |
| [14] | Luo Weidong, Pu Bin, Gu Peng, Huang Feng, Zheng Xiaohui, Chen Fuhong. Mendelian randomization study on the association between telomere length and 10 common musculoskeletal diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 654-660. |
| [15] | Chen Tianxin, , Zhang Zhilong, Zhang Shuai, Gao Yun, Zhu Yuqi, Yang Shengping. Causal relationship between immune cells and bone metabolic diseases: a Mendelian randomization analysis of European populations in international databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6326-6332. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||