Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 2631-2640.doi: 10.12307/2025.374
Causal relationship between visceral adipose tissue and osteoarthritis
Sun Pengcheng1, Zhang Xiaoyun2, Li Zhengpeng1, Li Yongjin1, Gao Zhengang1, Li Kunjian1
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-04-08Accepted:2024-06-11Online:2025-04-28Published:2024-09-11 -
Contact:Zhang Xiaoyun, MD, Associate chief physician, Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Sun Pengcheng, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Special Funds for the Construction of Traditional Chinese Medicine Talent Team - Gui’s Traditional Chinese Medicine Master Cultivation Project, No. [2023]1 (to ZXY [project participant]); “Gui’s Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance and Innovation Team” (Class A) of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2022A004 (to ZXY [project participant])
How to cite this article: Sun Pc, Zhang Xy,
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Pengcheng, Zhang Xiaoyun, Li Zhengpeng, Li Yongjin, Gao Zhengang, Li Kunjian . Causal relationship between visceral adipose tissue and osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2631-2640.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
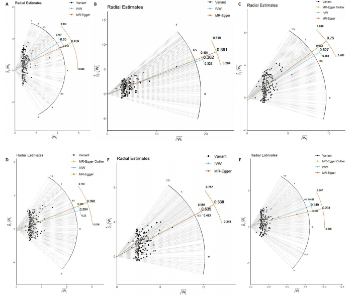
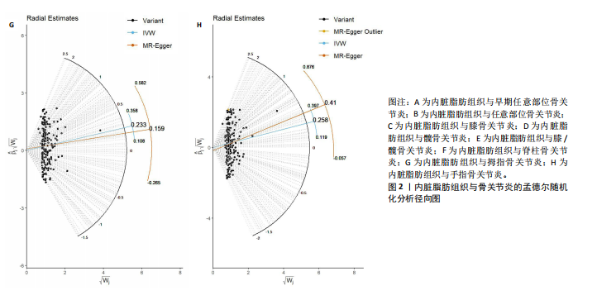
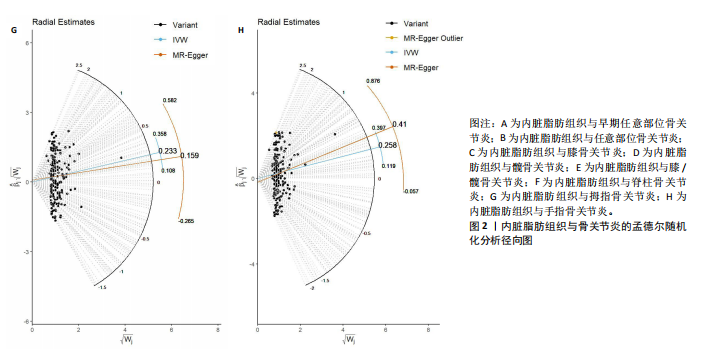
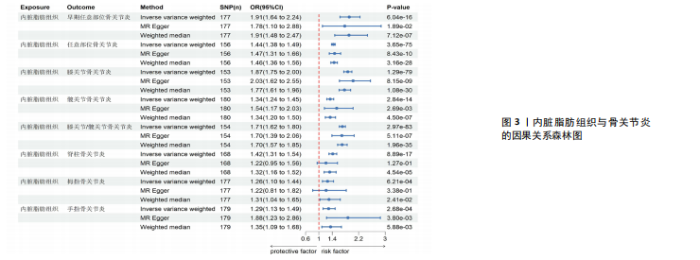
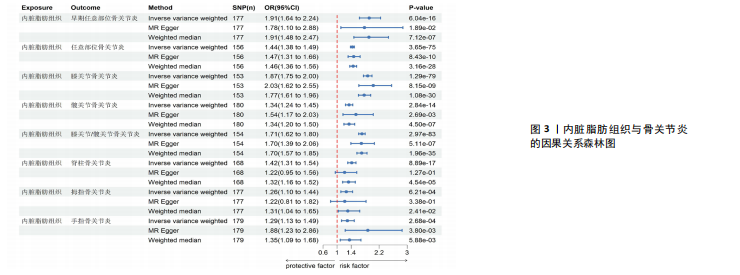
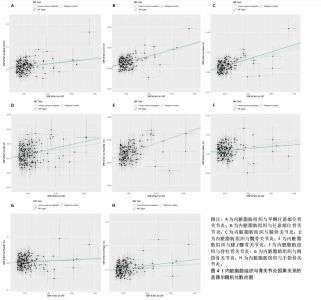
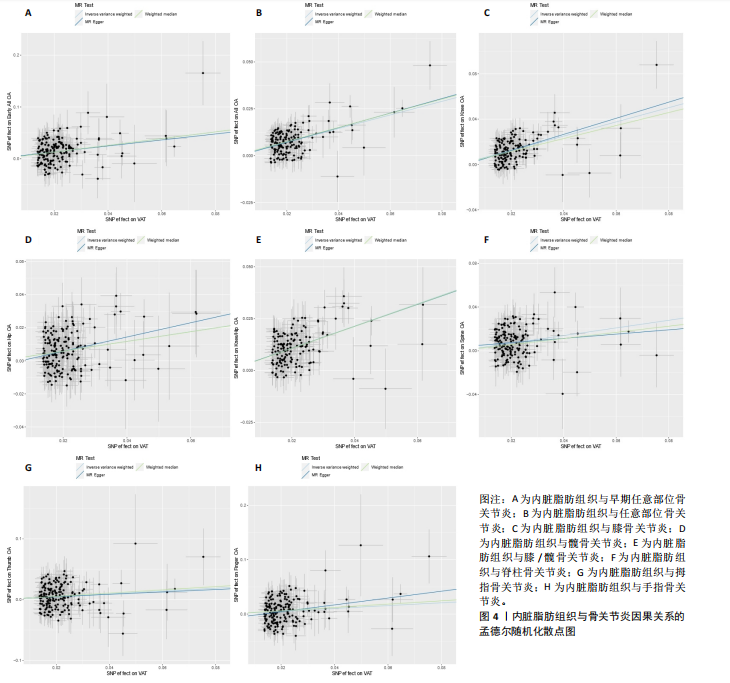
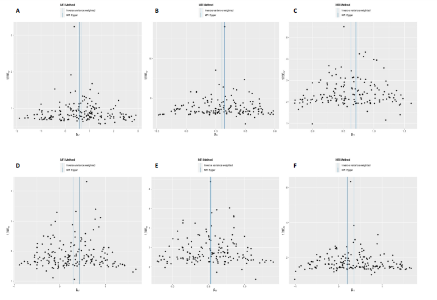
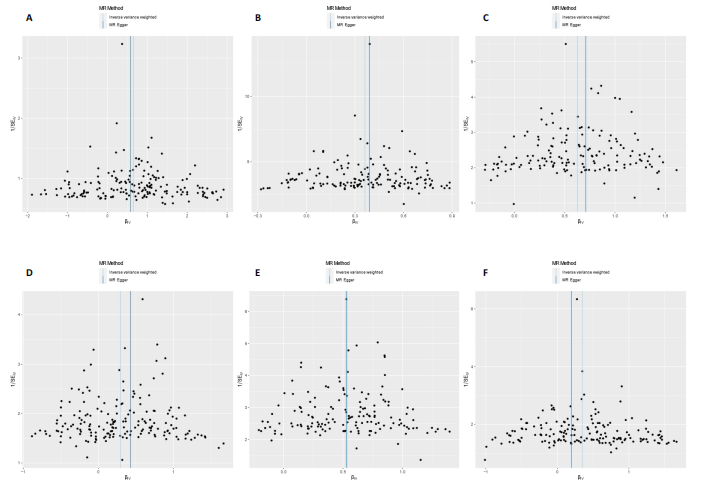
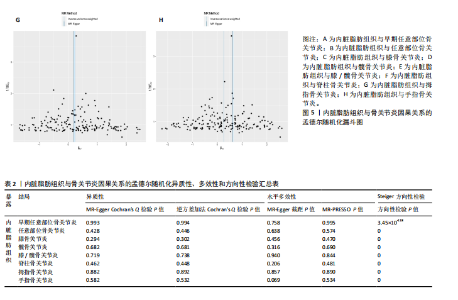
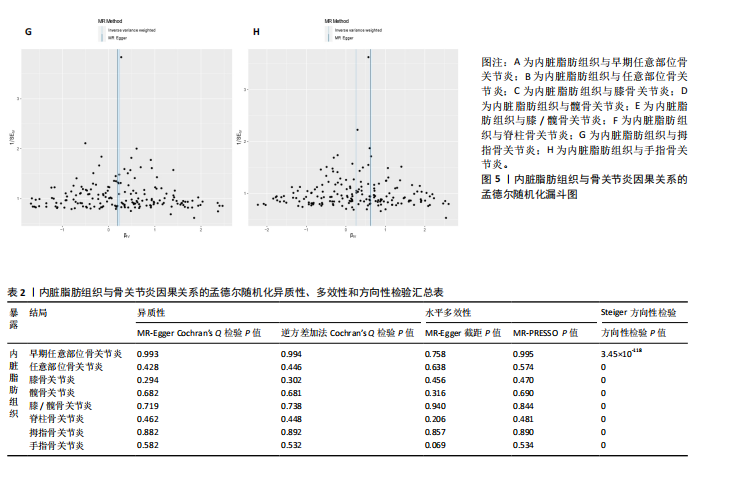
2.1 工具变量 根据此次研究工具变量的筛选标准,首先从暴露数据中筛选出221个与内脏脂肪组织强相关且无连锁不平衡的单核苷酸多态性,然后分别从8个骨关节炎表型中提取结局数据,并删除回文序列,利用Radial-MR包识别并剔除异常值(图2),使用PhenoScanner数据库手动筛选和删除与混杂因素(吸烟、创伤、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇、骨质疏松)和骨关节炎结局相关的单核苷酸多态性,经过一系列地筛选,最终纳入孟德尔随机化分析的单核苷酸多态性数如下:早期任意部位骨关节炎177个单核苷酸多态性、任意部位骨关节炎156个单核苷酸多态性、膝骨关节炎153个单核苷酸多态性、髋骨关节炎180个单核苷酸多态性、膝/髋骨关节炎154个单核苷酸多态性、脊柱骨关节炎168个单核苷酸多态性、拇指骨关节炎177个单核苷酸多态性、手指骨关节炎179个单核苷酸多态性。 2.2 内脏脂肪组织对骨关节炎的影响 逆方差加权法分析结果显示,内脏脂肪组织对早期任意部位骨关节炎(OR=1.91,95%CI:1.64-2.24,P=6.04×10-16)、任意部位骨关节炎(OR=1.44,95%CI:1.38-1.49,P=3.65×10-75)、膝骨关节炎(OR=1.87,95%CI:1.75-2.00,P=1.29×10-79)、髋骨关节炎(OR=1.34,95%CI:1.24-1.45,P=2.84×10-14)、膝/髋骨关节炎(OR=1.71,95%CI:1.62-1.80,P=2.97×10-83)、脊柱骨关节炎(OR=1.42,95%CI:1.31-1.54,P=8.89×10-17)、拇指骨关节炎(OR=1.26,95%CI:1.10-1.44,P=6.21×10-4)、手指骨关节炎(OR=1.29,95%CI:1.13-1.49,P=2.68×10-4)具有正向因果效应,结果表明遗传预测的内脏脂肪组织与8种骨关节炎可能存在因果关联(P < 0.006 25)。 在孟德尔随机化其他分析结果中,虽然早期任意部位骨关节炎中MR-Egger结果(OR=1.78,95%CI:1.10-2.88,P=1.89×10-2)、脊柱骨关节炎中MR-Egger结果(OR=1.22,95%CI:0.95-1.56,P=1.27×10-1)、拇指骨关节炎中MR-Egger结果(OR=1.22,95%CI:0.81-1.82,P=3.38×10-1)和加权中位数法结果(OR=1.31,95%CI:1.04-1.65,P=2.41×10-2)并不支持内脏脂肪组织与其骨关节炎相关表型的因果关联(P > 0.00 625),但早期任意部位骨关节炎、脊柱骨关节炎和拇指骨关节炎中3种孟德尔随机化分析方法的因果效应方向均一致(OR > 1)(图3)。此外,图4的散点图也显示相同的结果,随着内脏脂肪组织的增加,骨关节炎的发病风险升高。总的来说,从遗传的角度来看,内脏脂肪组织可能会增加骨关节炎的风险。 2.3 敏感性分析 为了验证结果的稳健性,进行了一系列的敏感性分析,以评估潜在的水平多效性和异质性。MR-Egger截距和MR-PRESSO分析结果显示,内脏脂肪组织与早期任意部位骨关节炎、任意部位骨关节炎、膝骨关节炎、髋骨关节炎、膝/髋骨关节炎、脊柱骨关节炎、拇指骨关节炎、手指骨关节炎均不存在潜在的水平多效性(P > 0.05)。Cochran’s Q检验显示,内脏脂肪组织与8种骨关节炎的逆方差加权法和MR-Egger分析结果均不存在潜在的异质性(P > 0.05)。同时,Steiger方向性检验表明此次研究不存在反向因果关系(P < 0.05)(表2)。此外,图5漏斗图整体上比较对称,表明此次研究受异质性影响造成结果偏倚的可能性较小。留一法敏感性分析也显示此次研究不存在单个单核苷酸多态性对整体因果估计效应产生影响。"

| [1] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021; 325(6):568-578. [2] RAGNI E, MANGIAVINI L, VIGANÒ M, et al. Management of Osteoarthritis During the COVID‐19 Pandemic. Clin Pharmacol Ther.2020;108(4):719-729. [3] QUICKE JG, CONAGHAN PG, CORP N, et al. Osteoarthritis year in review 2021: epidemiology & therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2):196-206. [4] HUNTER DJ, MARCH L, CHEW M. Osteoarthritis in 2020 and beyond: a Lancet Commission. Lancet. 2020;396(10264): 1711-1712. [5] PAPATHANASIOU I, ANASTASOPOULOU L, TSEZOU A. Cholesterol metabolism related genes in osteoarthritis. Bone. 2021;152: 116076. [6] ALISSA EM, ALZUGHAIBI LS, MARZOUKI ZM. Dietary intake of fatty acids and antioxidants in relation to radiographic knee osteoarthritis: results from a case-control study. J Hum Nutr Diet, 2020;33(3):431-438. [7] KHANNA D, PELTZER C, KAHAR P, et al. Body Mass Index (BMI): A Screening Tool Analysis. Cureus. 2022;14(2):e22119. [8] ARSENAULT BJ, CARPENTIER AC, POIRIER P, et al. Adiposity, type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk: Use and abuse of the body mass index. Atherosclerosis. 2024;14:117546. [9] ZENG Q, WANG L, DONG S, et al. CT-derived abdominal adiposity: Distributions and better predictive ability than BMI in a nationwide study of 59,429 adults in China. Metabolism. 2021;115:154456. [10] DHOKTE S, CZAJA K. Visceral Adipose Tissue: The Hidden Culprit for Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients. 2024;16(7):1015. [11] TOUSSIROT E, MICHEL F, BEREAU M, et al. Serum adipokines, adipose tissue measurements and metabolic parameters in patients with advanced radiographic knee osteoarthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2017; 36(11):2531-2539. [12] LI S, SCHWARTZ AV, LAVALLEY MP, et al. Association of Visceral Adiposity With Pain but Not Structural Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(7):1103-1110. [13] CHEN LG, TUBBS JD, LIU Z, et al. Mendelian randomization: causal inference leveraging genetic data. Psychol Med. 2024;19:1-14. [14] GILL D, WALKER VM, MARTIN RM, et al. Comparison with randomized controlled trials as a strategy for evaluating instruments in Mendelian randomization. Int J Epidemiol. 2020;49(4):1404-1406. [15] KARLSSON T, RASK-ANDERSEN M, PAN G, et al. Contribution of genetics to visceral adiposity and its relation to cardiovascular and metabolic disease. Nat Med. 2019; 25(9):1390-1395. [16] BOER CG, HATZIKOTOULAS K, SOUTHAM L, et al. Deciphering osteoarthritis genetics across 826,690 individuals from 9 populations. Cell. 2021;184(24):6003-6005. [17] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Avoiding bias from weak instruments in Mendelian randomization studies. Int J Epidemiol. 2011;40(3):755-764. [18] BURGESS S, BUTTERWORTH A, THOMPSON SG. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet Epidemiol. 2013;37(7):658-665. [19] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SG, HAYCOCK PC, et al. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016;40(4): 304-314. [20] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SG, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525. [21] DAVEY SG, HEMANI G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(R1):R89-R98. [22] BOWDEN J, SPILLER W, DEL GMF, et al. Improving the visualization, interpretation and analysis of two-sample summary data Mendelian randomization via the Radial plot and Radial regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2018;47(4):1264-1278. [23] VERBANCK M, CHEN CY, NEALE B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet. 2018;50(5):693-698. [24] ZHAO Q, CHEN Y, WANG J, et al. Powerful three-sample genome-wide design and robust statistical inference in summary-data Mendelian randomization. Int J Epidemiol. 2019;48(5):1478-1492. [25] HEMANI G, TILLING K, DAVEY SG. Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data. PLoS Genet. 2017;13(11):e1007081. [26] BURGESS S, BOWDEN J, FALL T, et al. Sensitivity Analyses for Robust Causal Inference from Mendelian Randomization Analyses with Multiple Genetic Variants. Epidemiology. 2017;28(1):30-42. [27] CURTIN F, SCHULZ P. Multiple correlations and Bonferroni’s correction. Biol Psychiatry. 1998;44(8):775-777. [28] HEMANI G, ZHENG J, ELSWORTH B, et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife. 2018;7:e34408. [29] REYES C, LEYLAND KM, PEAT G, et al. Association Between Overweight and Obesity and Risk of Clinically Diagnosed Knee, Hip, and Hand Osteoarthritis: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(8):1869-1875. [30] MAGNUSSON K, SLATKOWSKY-CHRISTENSEN B, VAN DER HEIJDE D, et al. Body mass index and progressive hand osteoarthritis: data from the Oslo hand osteoarthritis cohort. Scand J Rheumatol. 2015;44(4):331-336. [31] HOVEIDAEI AH, NAKHOSTIN-ANSARI A, CHALIAN M, et al. Burden of Hand Osteoarthritis in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA): An Epidemiological Analysis From 1990 to 2019. J Hand Surg Am. 2023; 48(3):245-256. [32] GLOERSEN M, STEEN PP, NEOGI T, et al. Associations of Body Mass Index With Pain and the Mediating Role of Inflammatory Biomarkers in People With Hand Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022;74(5):810-817. [33] YUAN J, WANG D, ZHANG Y, et al. Genetically predicted obesity and risk of hip osteoarthritis. Eat Weight Disord. 2023;28(1):11. [34] FUNCK BRENTANO T, NETHANDER M, MOVÉRARE SKRTIC S, et al. Causal Factors for Knee, Hip, and Hand Osteoarthritis: A Mendelian Randomization Study in the UK Biobank. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71(10):1634-1641. [35] GRECO F, PICCOLO CL, D’ANDREA V, et al. Fat Matters: Exploring Cancer Risk through the Lens of Computed Tomography and Visceral Adiposity. J Clin Med. 2024;13(2): 453. [36] BELEN E, KARAMAN O, CALISKAN G, et al. An indicator of subclinical cardiovascular disease in patients with primary osteoarthritis: epicardial fat thickness. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(6):9491-9497. [37] VISSER AW, IOAN-FACSINAY A, DE MUTSERT R, et al. Adiposity and hand osteoarthritis: the Netherlands Epidemiology of Obesity study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(1):R19. [38] LEVESCOT A, CHANG MH, SCHNELL J, et al. IL-1beta-driven osteoclastogenic Tregs accelerate bone erosion in arthritis. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(18):e141008. [39] LIU S, DENG Z, CHEN K, et al. Cartilage tissue engineering: From proinflammatory and anti‑inflammatory cytokines to osteoarthritis treatments (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2022;25(3):99. [40] LIN J, JIA S, ZHANG W, et al. Recent Advances in Small Molecule Inhibitors for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. J Clin Med. 2023;12(5):1986. [41] DU X, LIU ZY, TAO XX, et al. Research Progress on the Pathogenesis of Knee Osteoarthritis. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(9): 2213-2224. [42] MOLNAR V, MATISIC V, KODVANJ I, et al. Cytokines and Chemokines Involved in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci.2021;22(17):9208. [43] WANG T, HE C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: The link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018;44:38-50. [44] KOYAMA T, UCHIDA K, FUKUSHIMA K, et al. Elevated levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in the synovial tissue of patients with labral tear: a comparative study with hip osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):33. [45] AIT ELDJOUDI D, CORDERO BARREAL A, GONZALEZ-RODRÍGUEZ M, et al. Leptin in Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Player or Bystander? Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(5):2859. [46] CASADO ME, COLLADO-PEREZ R, FRAGO LM, et al. Recent Advances in the Knowledge of the Mechanisms of Leptin Physiology and Actions in Neurological and Metabolic Pathologies. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1422. [47] JIANG M, HE J, SUN Y, et al. Leptin Induced TLR4 Expression via the JAK2-STAT3 Pathway in Obesity-Related Osteoarthritis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:7385160. [48] CORDERO-BARREAL A, GONZALEZ-RODRIGUEZ M, RUIZ-FERNANDEZ C, et al. An Update on the Role of Leptin in the Immuno-Metabolism of Cartilage. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2411. [49] FU Y, BATUSHANSKY A, KINTER M, et al. Effects of Leptin and Body Weight on Inflammation and Knee Osteoarthritis Phenotypes in Female Rats. JBMR Plus. 2023;7(7):e10754. [50] CUZDAN CN, AY S, EVCIK FD, et al. Adiponectin: is it a biomarker for assessing the disease severity in knee osteoarthritis patients? Int J Rheum Dis. 2017;20(12):1942-1949. [51] TANG Q, HU Z, SHEN L, et al. Association of osteoarthritis and circulating adiponectin levels: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2018;17(1):189. [52] ILIA I, NITUSCA D, MARIAN C. Adiponectin in Osteoarthritis: Pathophysiology, Relationship with Obesity and Presumptive Diagnostic Biomarker Potential. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;12(2):455. |
| [1] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei, Zhou Jiatan. Based on Mendelian randomization, the causal relationship between 1400 metabolites and sarcopenia and the correlation analysis of cardiovascular disease were investigated [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [3] | Ma Chi, Wang Ning, Chen Yong, Wei Zhihan, Liu Fengji, Piao Chengzhe. Application of 3D-printing patient-specific instruments combined with customized locking plate in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
| [4] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [5] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [6] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [7] | Dong Tingting, Chen Tianxin, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei. Causal relationship between modifiable factors and joint sports injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1953-1962. |
| [8] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [9] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [10] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [11] | Wang Peiguang, Zhang Xiaowen, Mai Meisi, Li Luqian, Huang Hao. Generalized equation estimation of the therapeutic effect of floating needle therapy combined with acupoint embedding on different stages of human knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [12] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [13] | Chen Yueping, Chen Feng, Peng Qinglin, Chen Huiyi, Dong Panfeng . Based on UHPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular dynamics simulation to explore the mechanism of Panax notoginseng in treating osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [14] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [15] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||