Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (6): 1312-1320.doi: 10.12307/2025.289
Association between thyroid function levels and phenotypes associated with sarcopenia
Li Jiatong1, Jin Yue1, Liu Runjia1, Song Bowen1, Zhu Xiaoqian1, Li Nianhu2
- 1Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-02-07Accepted:2024-03-13Online:2025-02-28Published:2024-06-24 -
Contact:Li Nianhu, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Li Jiatong, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, No. ZR2019MH044 (to LNH); Shandong Provincial Famous Chinese Medicine (Xu Zhanwang) Inheritance Studio Construction Project, No. [2019]92 (to LNH); Traditional Chinese Medicine Characteristics of Spinal Orthopedic Manipulation, No. [2022]93 (to LNH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Jiatong, Jin Yue, Liu Runjia, Song Bowen, Zhu Xiaoqian, Li Nianhu . Association between thyroid function levels and phenotypes associated with sarcopenia[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1312-1320.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
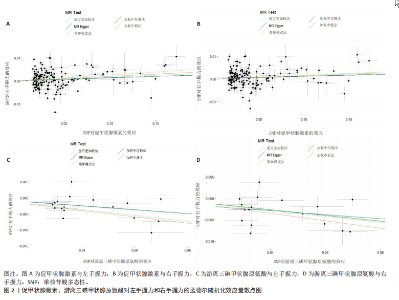
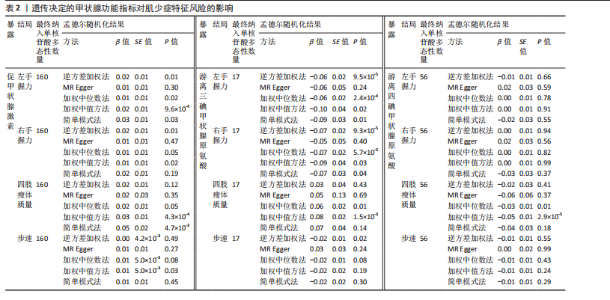
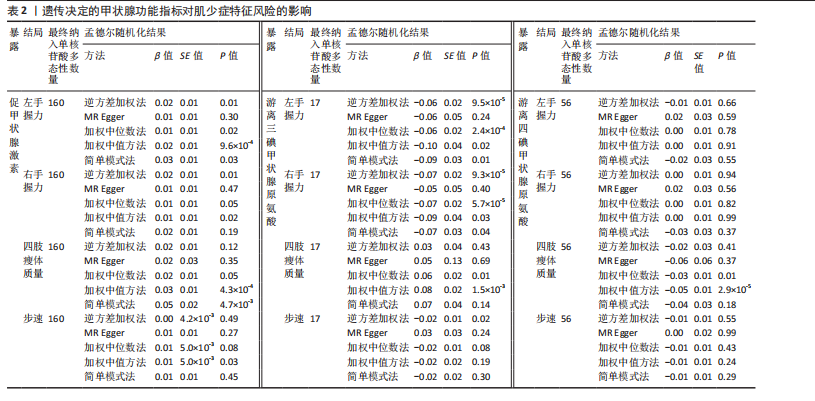
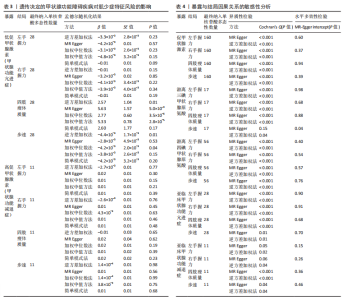
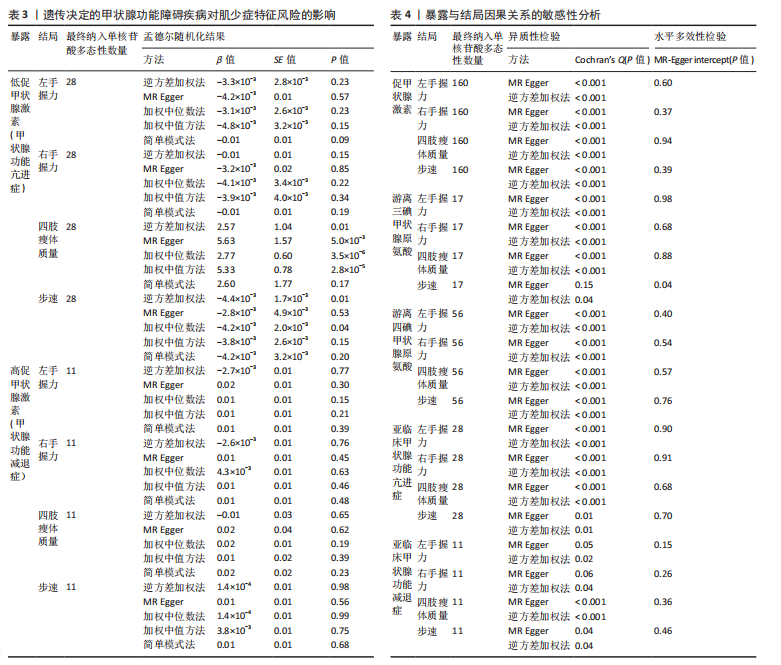
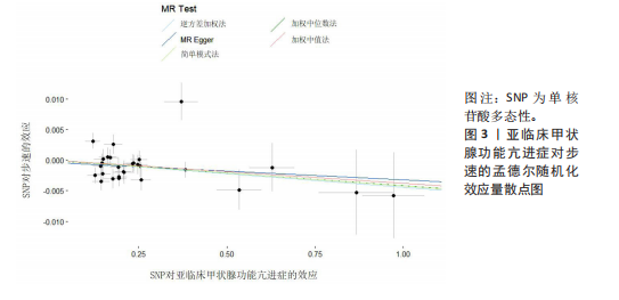
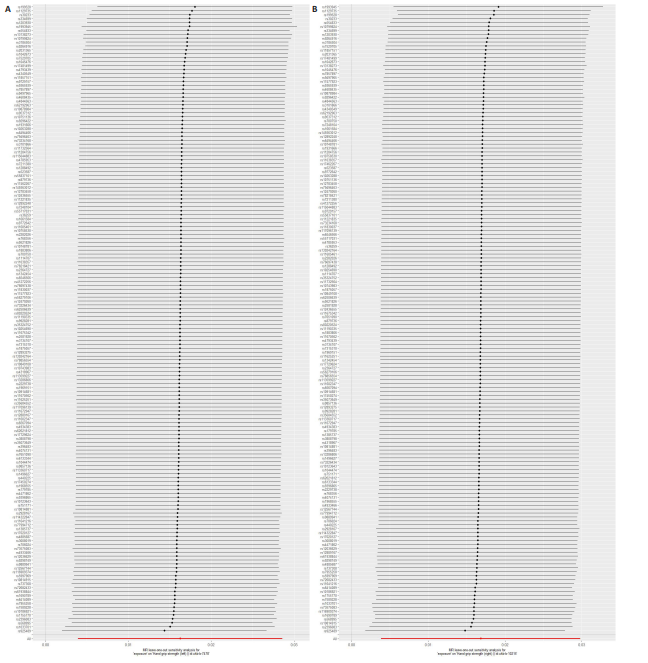
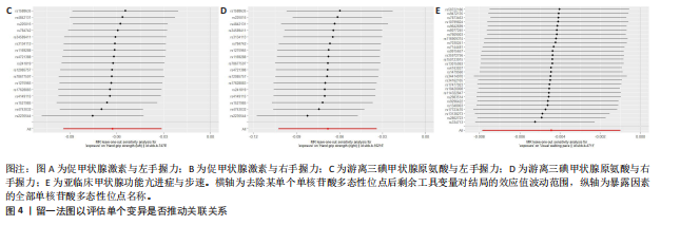
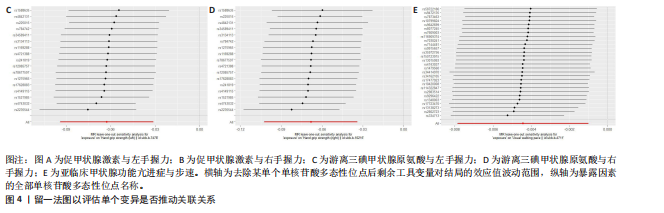
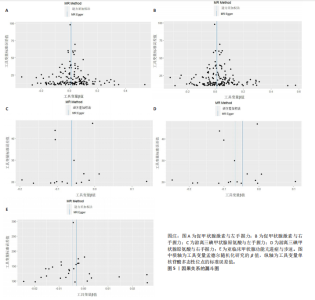
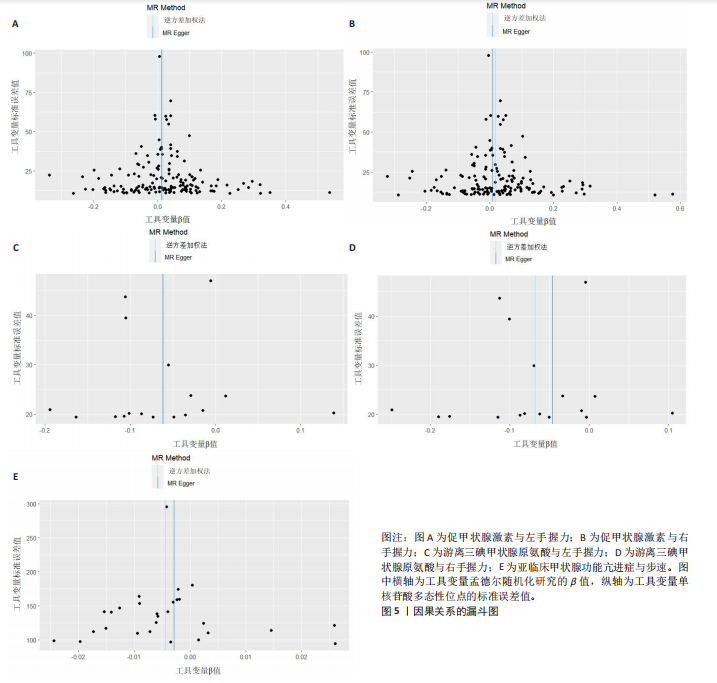
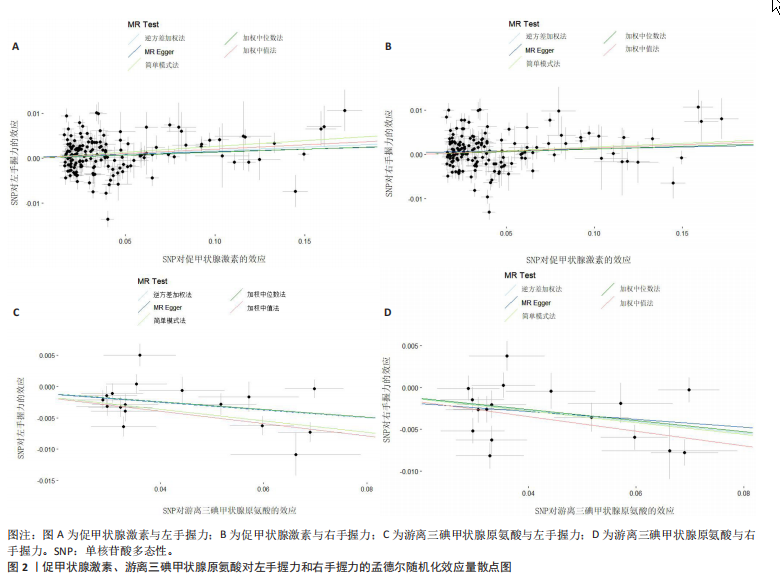
2.1 工具变量 在经过显著相关、去除连锁不平衡、计算F值筛选及调整等位基因情况后,最终纳入与促甲状腺激素相关的单核苷酸多态性164个,与游离三碘甲状腺原氨酸相关的单核苷酸多态性17个,与游离四碘甲状腺原氨酸相关的单核苷酸多态性58个,与亚临床甲状腺功能亢进症相关的单核苷酸多态性28个,与亚临床甲状腺功能减退症相关的单核苷酸多态性11个。在利用这些单核苷酸多态性与结局相关联时,分别丢失了4,0,2,0,0个单核苷酸多态性。 2.2 甲状腺功能指标对肌少症相关特征表型的影响 基于逆方差加权法的结果,提示促甲状腺激素对左手、右手握力存在较为显著的潜在因果效应(β=0.02,SE=0.01,P=0.01),游离三碘甲状腺原氨酸对左手握力(β=-0.06,SE=0.02,P=9.5×10-5) 、右手握力(β=-0.07,SE=0.02,P=9.3×10-5)存在较为显著的潜在因果效应。同时用其他4种方法来确认结果的稳健性,其中加权中位数法、简单模式法和加权中值法的分析结果支持促甲状腺激素与左手握力相关,加权中位数法和加权中值法的分析结果支持促甲状腺激素与右手握力相关,加权中位数法、简单模式法和加权中值法的分析结果支持游离三碘甲状腺原氨酸与左手、右手握力相关,虽然MR-Egger等方法不支持该结论,但5种统计方法结果总效应值的方向一致,呈正相关,见表2。此外,MR-PRESSO方法在异常值校正前后的因果估计是一致的,散点图同样显示了5个方法的回归线基本一致,见图2。以上表明孟德尔随机化分析的结果是可靠的。孟德尔随机化分析并未发现促甲状腺激素与四肢瘦体质量、步速;游离三碘甲状腺原氨酸与四肢瘦体质量;游离四碘甲状腺原氨酸与握力、四肢瘦体质量、步速等肌少症相关表型间的显著关联。 2.3 两种亚临床甲状腺功能障碍疾病对肌少症相关特征表型的影响 逆方差加权法结果显示,基因预测亚临床甲状腺功能亢进症对步速(β=-4.4×10-3,SE=1.7×10-3,P=0.01)存在较为显著的潜在因果效应。同时用其他4种方法来确认结果的稳健性,均支持亚临床甲状腺功能亢进症与步速指标相关,5种统计方法结果总效应值的方向一致,呈负相关,见表3。MR-PRESSO方法在异常值校正前后的因果估计是一致的,散点图同样显示了5个方法的回归线基本一致,见图3。结果并未发现亚临床甲状腺功能亢进症与左手握力、右手握力、四肢瘦体质量,亚临床甲状腺功能减退症与左手握力、右手握力、四肢瘦体质量、步速等肌少症相关表型间的显著关联。 2.4 敏感性分析 基因预测游离三碘甲状腺原氨酸对步速(β=-0.02,SE=0.01,P=0.02)存在较为显著的潜在因果效应,但MR-Egger-intercept结果P < 0.05,存在一定的水平多效性。这意味着用于孟德尔随机化分析的工具变量可能通过暴露以外的路径影响结局,可靠性不足。对于其他指标MR-Egger-intercept分析未检测到潜在的水平多效性(促甲状腺激素对左手握力:P=0.60;促甲状腺激素对右手握力:P=0.37;游离三碘甲状腺原氨酸对左手握力:P=0.98;游离三碘甲状腺原氨酸对右手握力:P=0.68;亚临床甲状腺功能亢进症对步速:P=0.70),说明工具变量并不显著通过暴露以外的途径影响结局。Cochran’s Q异质性检验发现了一定的异质性,但采用逆方差加权法随机效应模型并考虑核心假设2中的水平多效性检验,确保了分析结果的可靠性,见表4。"
| [1] ROSENBERG IH. Sarcopenia: origins and clinical relevance. J Nutr. 1997;127(5 Suppl): 990S-991S. [2] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1):16-31. [3] CHEN LK, WOO J, ASSANTACHAI P, et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020; 21(3):300-307.e2. [4] 阳建政,邹丽华,杨涛,等.2型糖尿病患者并发肌肉减少症的影响因素分析[J].陆军军医大学学报,2023,45(14):1562-1568. [5] AHN SH, SEO DH, CHO Y, et al. Different Relationships Between Thyrotropin and Muscle Strength According to Sex and Age in Euthyroid Koreans (The 6th Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey 2014-2015). Thyroid. 2020;30(12):1710-1717. [6] SZLEJF C, SUEMOTO CK, JANOVSKY CCPS, et al. Thyroid Function and Sarcopenia: Results from the ELSA-Brasil Study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020;68(7):1545-1553. [7] DU PUY RS, POORTVLIET RKE, SNEL M, et al. Associations of Elevated Antithyroperoxidase Antibodies with Thyroid Function, Survival, Functioning, and Depressive Symptoms in the Oldest Old: The Leiden 85-plus Study. Thyroid. 2019; 29(9):1201-1208. [8] GRECO F, MOULTON C, ANTINOZZI C, et al. Relationship between Euthyroidism and Muscle Mass and Strength: A Systematic Review. Int J Sports Med. 2023;44(10): 704-710. [9] SHENG Y, MA D, ZHOU Q, et al. Association of thyroid function with sarcopenia in elderly Chinese euthyroid subjects. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2019;31(8):1113-1120. [10] BRENNAN MD, POWELL C, KAUFMAN KR, et al. The impact of overt and subclinical hyperthyroidism on skeletal muscle. Thyroid. 2006;16(4):375-380. [11] 周海洋,罗佐杰.患者握力、步速及四肢骨骼肌质量在甲亢肌病诊断中的应用[J].山东医药,2021,61(27):77-80. [12] EMDIN CA, KHERA AV, KATHIRESAN S. Mendelian Randomization. JAMA. 2017; 318(19):1925-1926. [13] YANG J, LIU P, WANG S, et al. Causal relationship between sarcopenia and osteoarthritis: a bi-directional two-sample mendelian randomized study. Eur J Med Res. 2023;28(1):327. [14] BURGESS S, DAVEY SMITH G, et al. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations: update for summer 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2023; 4:186. [15] STERENBORG RBTM, STEINBRENNER I, LI Y, et al. Multi-trait analysis characterizes the genetics of thyroid function and identifies causal associations with clinical implications. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):888. [16] KIM BJ, LEE SH, ISALES CM, et al. Association of Serum TSH With Handgrip Strength in Community-Dwelling Euthyroid Elderly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(11):3986-3992. [17] LEE JC, SONG BS, KANG YM, et al. Effect of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Suppression on Muscle Function After Total Thyroidectomy in Patients With Thyroid Cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021; 12:769074. [18] GU Y, MENG G, WU H, et al. Thyroid Function as a Predictor of Handgrip Strength Among Middle-Aged and Older Euthyroid Adults: The TCLSIH Cohort Study. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2019;20(10):1236-1241. [19] SPIRA D, BUCHMANN N, DEMUTH I, et al. Association of Thyroid Function with Handgrip Strength: Data from the Study of Health in Pomerania and the Berlin Aging Study II. Thyroid. 2019;29(9):1220-1226. [20] LU L, TIAN L. Postmenopausal osteoporosis coexisting with sarcopenia: the role and mechanisms of estrogen. J Endocrinol. 2023;259(1):e230116. [21] VIRGINI VS, RODONDI N, CAWTHON PM, et al. Subclinical Thyroid Dysfunction and Frailty Among Older Men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(12):4524-4532. [22] HU X, ZHANG L, ZHANG M, et al. Correlation of subclinical hypothyroidism with sarcopenia and its components in the Chinese older adults. Endocrine. 2023 Dec 27. doi: 10.1007/s12020-023-03654-7. [23] NETZER S, CHOCANO-BEDOYA P, FELLER M, et al. The effect of thyroid hormone therapy on muscle function, strength and mass in older adults with subclinical hypothyroidism-an ancillary study within two randomized placebo controlled trials. Age Ageing. 2023;52(1):afac326. [24] LI C, ZHAO C, YU Z, et al. Low free triiodothyronine levels are associated with frail phenotype in hospitalized inpatients with cirrhosis. Postgrad Med. 2022;134(5):516-523. [25] ZHANG L, TU YY, ZHAO Z, et al. Lower serum FT3 within the reference range is associated with mortality for older adults over 80 years of age with sarcopenia. BMC Geriatr. 2023; 23(1):77. [26] 沈雷,王俊杰,韩军,等.胃癌病人术前甲状腺激素水平与肌少症的相关性研究[J].肠外与肠内营养,2022,29(5):257-262. [27] ROEF G, LAPAUW B, GOEMAERE S, et al.Body composition and metabolic parameters are associated with variation in thyroid hormone levels among euthyroid young men. Eur J Endocrinol. 2012;167(5): 719-726. [28] TAWFIK I, GOTTSCHALK B, JARC A, et al. T3-induced enhancement of mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake as a boost for mitochondrial metabolism. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;181: 197-208. [29] TIERNEY MT, SACCO A. Satellite Cell Heterogeneity in Skeletal Muscle Homeostasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2016;26(6): 434-444. [30] AMBROSIO R, DE STEFANO MA, DI GIROLAMO D, et al. Thyroid hormone signaling and deiodinase actions in muscle stem/progenitor cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017;459:79-83. [31] WEITH M, BEYER A. The next step in Mendelian randomization. Elife. 2023;12: e86416. |
| [1] | Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319. |
| [2] | Ding Yu, Chen Jingwen, Chen Xiuyan, Shi Huimin, Yang Yudie, Zhou Meiqi, Cui Shuai, . Circulating inflammatory proteins and myocardial hypertrophy: large sample analysis of European populations from GWAS Catalog and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1047-1057. |
| [3] | Dong Tingting, Chen Tianxin, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei. Causal relationship between modifiable factors and joint sports injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1953-1962. |
| [4] |
Zhao Wensheng, Li Xiaolin, Peng Changhua, Deng Jia, Sheng Hao, Chen Hongwei, Zhang Chaoju, He Chuan.
Gut microbiota and osteoporotic fractures #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1296-1304.
|
| [5] | Wu Guangtao, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Fan Yidong, Li Weicai, Zhu Baogang, Cao Ying . Causal relationship between immune cells and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1081-1090. |
| [6] | Wang Xuepeng, , He Yong, . Effect of insulin-like growth factor family member levels on inflammatory arthritis: a FinnGen biobank-based analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7656-7662. |
| [7] | Wu Zhenhua, Zhang Xiwei, Wang Yipin, Li Qianqian. Relationship between seven serum lipid traits and osteoarthritis: a large sample analysis of European population in IEU OPEN GWAS database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 7004-7014. |
| [8] | Luo Weidong, Pu Bin, Gu Peng, Huang Feng, Zheng Xiaohui, Chen Fuhong. Mendelian randomization study on the association between telomere length and 10 common musculoskeletal diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 654-660. |
| [9] | Chai Jinlian, Sun Tiefeng, Li Wei, Zhang Bochun, Li Guangzheng, Shao Xuekun, Wang Ping, Liang Xuezhen. Cathepsins and osteonecrosis: analysis based on European samples from the FinnGen Database and IEU OpenGWAS Database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5254-5262. |
| [10] | Tang Xiaochen, Yang Jingyan, Cheng Yupei, Hao Huatao, Li Hanyu, Yu Dong. Association between monounsaturated fatty acids and low back pain and patient all-cause mortality: causal inferences based on NHANES epidemiology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4361-4368. |
| [11] | Wang Zikun, Li Shudong, Gao Shuang, Fan Shuhao, Li Cheng, Meng Chunyang. Relationship between intervertebral disc degeneration and 473 gut microbiotas: what can be learned from big data information in the FinnGen database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4369-4378. |
| [12] | Huo Jiang, Ding Yu, Yuan Jie. Immune cells mediate the association between different lipids and knee osteoarthritis: a genome-wide association analysis of European individuals [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3934-3940. |
| [13] | Fang Zhijie, Ma Qiangping, Dong Wantao, Wu Junyuan, Lu Yunlin. Genetic causal relationship between gut microbiota and osteoporosis: analysis of 211 gut microbiota from the UK database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3941-3947. |
| [14] | Zhu Kai, Liu Wanxin, Luo Haobing, Feng Shengyi, Wang Qiugen. Association between plasma proteins and osteoporosis and identification of potential therapeutic targets: information analysis based on the UK Biobank database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3948-3960. |
| [15] | Tang Xiran, Chen Weijian, Jiang Tao, Tan Xianyun, Liu Wengang . Types and contents of fatty acids and the risk of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3724-3731. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||