Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (3): 538-546.doi: 10.12307/2025.132
Previous Articles Next Articles
Repair strategies for nonunion in old osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a case analysis
Zhao Xingcheng, Wang Jun, Lu Ming
- Orthopedics Department of Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai 201508, China
-
Received:2024-02-01Accepted:2024-02-23Online:2025-01-28Published:2024-06-04 -
Contact:Lu Ming, MD, Chief physician, Orthopedics Department of Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai 201508, China -
About author:Zhao Xingcheng, Master, Attending physician, Orthopedics Department of Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai 201508, China Wang Jun, Master, Attending physician, Orthopedics Department of Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai 201508, China Zhao Xingcheng and Wang Jun contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:Surgical Clinical Subspecialty Construction Incubation Project of Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center Affiliated to Fudan University, No. KY-GW-2018-47 (to LM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Xingcheng, Wang Jun, Lu Ming. Repair strategies for nonunion in old osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a case analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 538-546.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
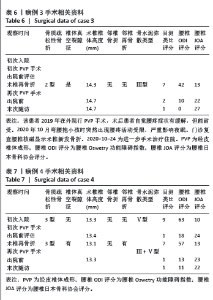
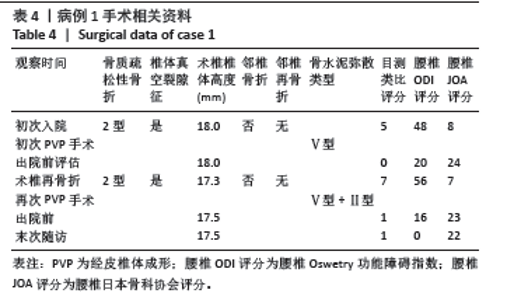
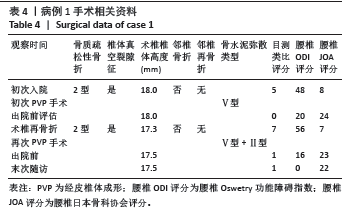
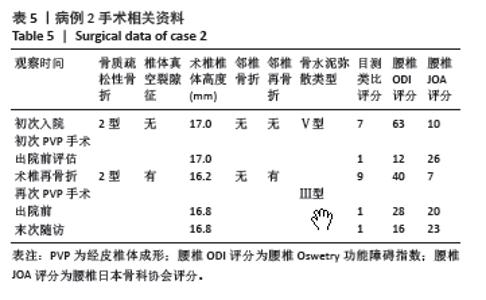
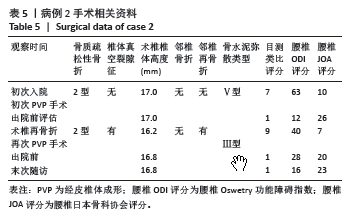
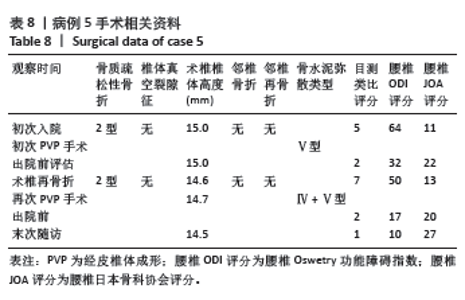
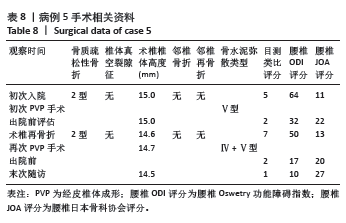
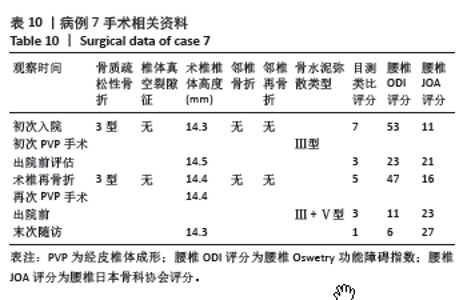
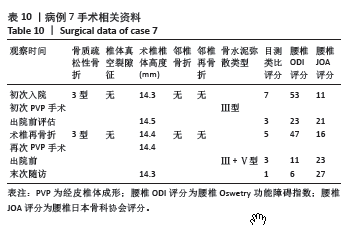
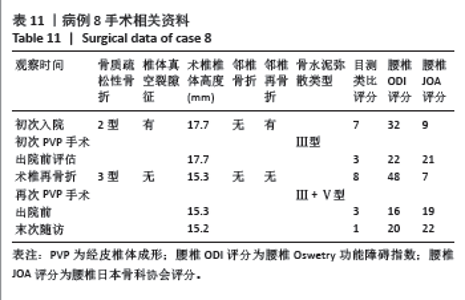
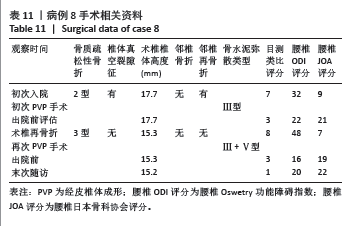
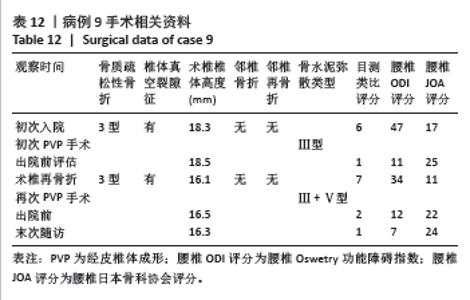
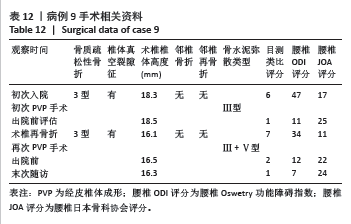
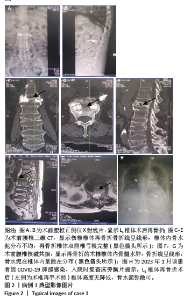
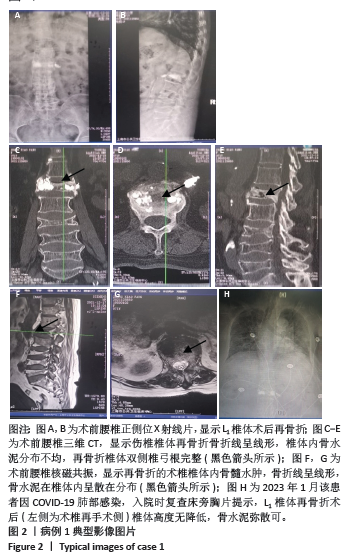
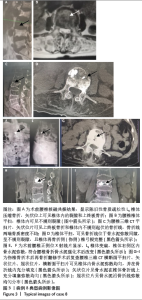
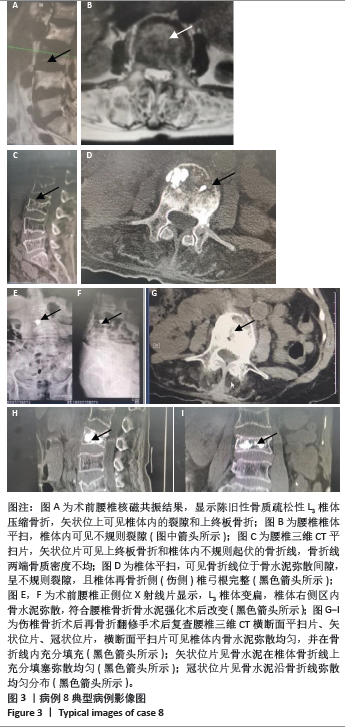
病例3:女性,75岁,主诉弯腰抱小孩后出现腰疼,反复发作逐渐加重1个月。腰椎核磁提示:L1压缩骨折骨不连,无相邻椎体骨折,伤椎上终板无骨折;入院骨密度T值-3.4;行术椎PVP翻修手术,术后给予抗骨质疏松阶梯治疗;末次随访12个月,骨密度T值-2.1。见表6。 病例4:女性,73岁,腰疼反复发作6个月伴加重,严重影响夜眠。腰椎核磁提示:L1椎体压缩骨折骨不连;伤椎上终板无骨折,无相邻椎体骨折,骨密度T值-4.1;入院后给予伤椎PVP手术治疗,术后给予抗骨质疏松治疗,患者自觉腰疼症状缓解。2022年3月因腰疼2周伴加重来院复诊。复查腰椎核磁提示术椎再骨折,伤椎上终板骨折;无相邻椎体骨折;复查骨密度T值-3.7,患者入院后给予术椎PVP翻修手术。术后常规应用钙尔奇D、骨化三醇、鲑降钙素、利塞磷酸钠片抗骨质疏松药物治疗。末次随访3年7个月,骨密度T值-1.9。见表7。"

| [1] HU KZ, CHEN SC, XU L. Comparison of percutaneous balloon dilation kyphoplasty and percutaneous vertebroplasty in treatment for thoracolumbar vertebral compression fractures. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(1 Suppl):96-102. [2] 叶敬尧.基于“筋骨再平衡”理论研究后路短节段减压内固定治疗退变性腰椎侧凸的临床疗效[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2021. [3] 邱贵兴.老年骨质疏松性骨折的治疗策略[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2015,1(1):1-5. [4] 王胜.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折骨不连的CT及MRI影像学表现分析[J].影像研究与医学应用,2020,4(23):66-68. [5] 常莹,麦筱莉,辛小燕,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折骨不连的X射线平片和CT及MRI影像学表现[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2019,33(3): 279-282. [6] XU Z, HAO D, HE L, et al. An assessment system for evaluating the severity of thoracolumbar osteoporotic fracture and its clinical application: a retrospective study of 381 cases. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015;139:70-75. [7] 谢辉,陈浩鹏,王本杰,等.骨水泥弥散分布类型对不同部位骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折治疗效果的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(28): 4505-4510. [8] SCHNAKE KJ, BLATTERT TR, HAHN P, et al. Classification of osteoporotic thoracolumbar spine fractures: recommendations of the spine section of the german society for orthopaedics and trauma (DGOU). Global Spine J. 2018;8(2 Suppl):46S-49S. [9] SILVERMAN SL. The clinical consequences of vertebral compression fracture. Bone. 1992;13 Suppl 2:S27-S31. [10] MANSON NA, PHILLIPS FM. Minimally invasive techniques for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(8):1862-72. [11] ROUSSOULY P, PINHEIRO-FRANCO J, LABELLE H,等.海涌,李利,李危石,等译.脊柱矢状位平衡-从生理到病理:治疗策略的关键[M].北京:中国科学技术出版社,2020. [12] 越雷,陈浩,李淳德,等.脊柱矢状位动态平衡的研究和应用进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2021,31(11):1034-1038. [13] CHEN D, AN ZQ, SONG S, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty compared with conservative treatment in patients with chronic painful osteoporotic spinal fractures. J Clin Neurosci. 2014;21(3):473-477. [14] LANGE A, KASPERK C, ALVARES L, et al. Survival and cost comparison of kyphoplasty and percutaneous vertebroplasty using German claims data. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(4):318-326. [15] LEE JK, JEONG HW, JOO IH, et al. Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of very severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a case-control study. Spine J. 2018;18(6):962-969. [16] ATALAY B, CANER H, GOKCE C, et al. Kyphoplasty: 2 years of experience in a neurosurgery department. Surg Neurol. 2005;64 Suppl 2:S72-S76. [17] BACH HG, LIM RD. Minimally invasive spine surgery for low back pain. Dis Mon. 2005;51(1):34-57. [18] LEGAYE J, DUVAL-BEAUPÈRE G, HECQUET J, et al. Pelvic incidence: a fundamental pelvic parameter for three-dimensional regulation of spinal sagittal curves. Eur Spine J. 1998;7(2):99-103. [19] VIALLE R, LEVASSOR N, RILLARDON L, et al. Radiographic analysis of the sagittal alignment and balance of the spine in asymptomatic subjects. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(2):260-267. [20] DUVAL-BEAUPÈRE G, SCHMIDT C, COSSON P. A barycentremetric study of the sagittal shape of spine and pelvis: the conditions required for an economic standing position. Ann Biomed Eng. 1992;20(4):451-462. [21] 赵鹏,慈元,李志君,等.经椎间孔入路椎体成形术治疗Kümmell病的临床疗效[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(2):184-188. [22] SUN K, LIEBSCHNER MA. Evolution of vertebroplasty: a biomechanical perspective. Ann Biomed Eng. 2004;32(1):77-91. [23] 田云虎,刘亚,管春和.经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2002,17(5):335-337. [24] BARR JD, BARR MS, LEMLEY TJ, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for pain relief and spinal stabilization. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(8):923-928. [25] CHEN B, LI Y, XIE D, et al. Comparison of unipedicular and bipedicular kyphoplasty on the stiffness and biomechanical balance of compression fractured vertebrae. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(8):1272-1280. [26] CHEN L, YANG H, TANG T. Unilateral versus bilateral balloon kyphoplasty for multilevel osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a prospective study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(7):534-540. [27] LIU JT, LIAO WJ, TAN WC, et al. Balloon kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a prospective, comparative, and randomized clinical study. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21(2):359-364. [28] ITSHAYEK E, MILLER P, BARZILAY Y, et al. Vertebral augmentation in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures: review and new insights from recent studies. J Clin Neurosci. 2012;19(6):786-791. [29] GARFIN SR, YUAN HA, REILEY MA. New technologies in spine: kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for the treatment of painful osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1511-1515. [30] BELKOFF SM, MATHIS JM, JASPER LE, et al. The biomechanics of vertebroplasty. The effect of cement volume on mechanical behavior. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1537-1541. [31] MARTINČIČ D, BROJAN M, KOSEL F, et al. Minimum cement volume for vertebroplasty. Int Orthop. 2015;39(4):727-733. |
| [1] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [2] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [3] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [4] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [5] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [6] | Li Yueyao, Zhang Min, Yang Jiaju. Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151. |
| [7] | Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [8] |
Huang Xiaobin, Ge Jirong, Li Shengqiang, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, He Yanyan, Xue Lipeng.
Mechanisms of different yin nourishing and kidney tonifying methods on osteoclastysis pathway in ovariectomized rats #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1214-1219.
|
| [9] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [10] | Wang Dongyang, Yang Qiaohui, Lin Xinchao. Relationship between vitamin D levels and reproductive characteristics and exercise dietary situation in postmenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1021-1025. |
| [11] | Lan Shuangli, Xiang Feifan, Deng Guanghui, Xiao Yukun, Yang Yunkang, Liang Jie. Naringin inhibits iron deposition and cell apoptosis in bone tissue of osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 888-898. |
| [12] | Zhang Lichuang, Yang Wen, Ding Guangjiang, Li Peikun, Xiao Zhongyu, Chen Ying, Fang Xue, Zhang Teng. Dispersion effect of bone cement after vertebroplasty using individualized unilateral external pedicle approach and bilateral pedicle approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 800-808. |
| [13] | Zhang Xiongjinfu, Chen Yida, Cheng Xinyi, Liu Daihui, Shi Qin . Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of young rats to reverse senescence in aged rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7709-7718. |
| [14] | Yan Jing, Qin Qiujun, Li Fen, Zhou Jun, Ding Yuanyuan, Jin Chunlin. A systematic review of osteoporosis-specific quality-of-life scales [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7649-7655. |
| [15] | Yang Lei, Liu Sanmao, Sun Huanwei, Che Chao, Tang Lin. Comparison of six machine learning models suitable for use in medicine: support for osteoporosis screening and initial diagnosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7499-7510. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||