Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 31-37.doi: 10.12307/2025.040
Previous Articles Next Articles
Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome attenuates radiation-induced oral mucositis
Li Yang, Fu Lili, Yang Jiantang
- Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2024-01-16Accepted:2024-02-22Online:2025-01-08Published:2024-05-18 -
Contact:Yang Jiantang, MD, Associate professor, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Li Yang, Master, Associate chief physician, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960202 (to YJT); Guizhou Provincial Department of Science and Technology Project, No. ZK[2023]534 (to YJT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yang, Fu Lili, Yang Jiantang. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome attenuates radiation-induced oral mucositis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 31-37.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
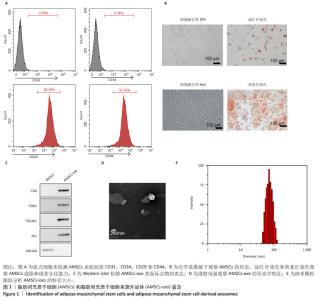
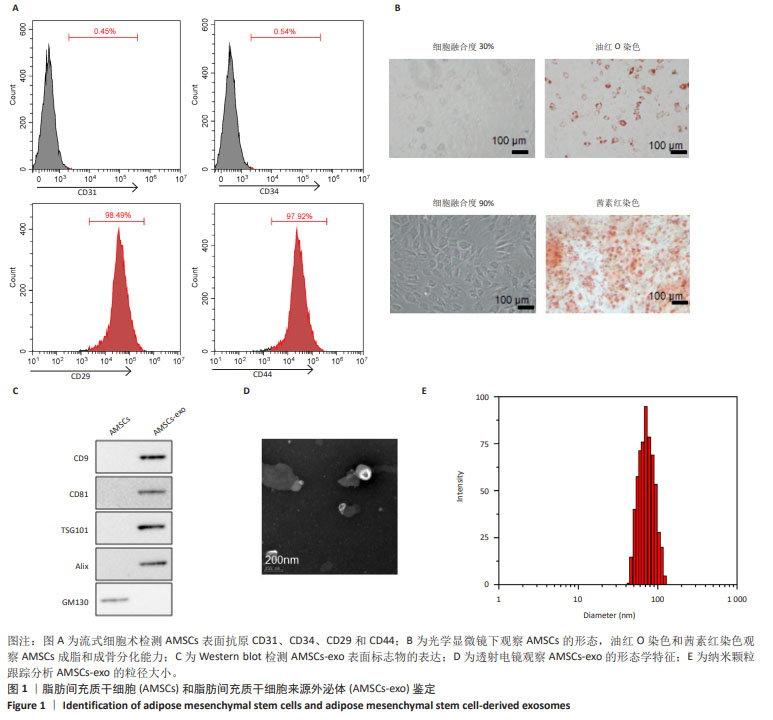
2.1 AMSCs 和 AMSCs-exo 鉴定结果 流式细胞术分析显 示,AMSCs 中 CD31 和 CD34 阳性细胞均小于 1%,CD29 和 CD44 阳性细胞均大于 95%( 图 1A)。当细胞融合达到 90% 时观察到 AMSCs 的形态为梭形,AMSCs 具有成骨和脂肪 分化的潜能 ( 图 1B)。Western blot 实验结果显示,外泌体 的 表 面 标 记 物 (CD9、CD81、TSG101、Alix) 在 AMSCs-exo 中均为阳性 ( 图 1C)。透射电镜观察显示,AMSCs-exo 为圆形或近圆形,具有脂质双分子层结构 ( 图 1D),纳米颗粒 跟踪分析显示,AMSCs-exo 的粒径为 80-110 nm( 图 1E)。"
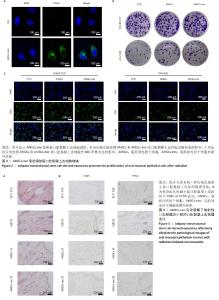
2.2 AMSCs-exo 促进辐射后口腔黏膜上皮细胞的增殖 荧 光显微镜观察到 PKH67 标记的 AMSCs-exo 能够被口腔黏 膜上皮细胞摄取 ( 图 2A)。克隆实验结果显示,在非辐射 处理下,与对照组相比,AMSCs 和 AMSCs-exo 对口腔黏 膜上皮细胞克隆形成没有影响;在 3 Gy 辐射处理下,与 对照组相比,AMSCs 和 AMSCs-exo 促进口腔黏膜上皮细 胞克隆形成(图2B)。免疫荧光结果显示,在非辐射处理下, 与对照组相比,AMSCs 和 AMSCs-exo 对口腔黏膜上皮细 胞中 EdU 阳性率无显著影响;在 3 Gy 辐射处理下,与对 照组相比,AMSCs 和 AMSCs-exo 增加口腔黏膜上皮细胞 中 EdU 阳性率 ( 图 2C)。 2.3 AMSCs-exo 有效缓解了放射性口腔黏膜炎小鼠的口腔 黏膜上皮组织炎症 为了研究 AMSCs 和 AMSCs-exo 对放射 性口腔黏膜炎小鼠模型的影响,将 AMSCs 和 AMSCs-exo 分别注入放射性口腔黏膜炎小鼠尾静脉。苏木精 - 伊红 染色结果显示,AMSCs 和 AMSCs-exo 均能够缓解辐射处 理小鼠口腔黏膜上皮组织的炎症 ( 图 3A)。免疫组化结果 显示,AMSCs 和 AMSCs-exo 处理后口腔黏膜上皮组织中 CD45 阳性细胞均减少,口腔黏膜炎症细胞浸润得到改善; PCNA 阳性细胞均增加,口腔黏膜细胞数量增多 ( 图 3B)。 "

| [1] LY KL, LUO X, RAUB CB. Oral mucositts on a chip: modeling inductton by chemo- and radiatton treatments and recovery. Biofabricatton. 2022;15(1):10.1088/1758-5090/ac933b. [2] MARIA OM, ELIOPOULOS N, MUANZA T. Radiatton-Induced Oral Mucositts. Front Oncol. 2017;7:89. [3] RAO D, BEHZADI F, LE RT, et al. Radiatton Induced Mucositts: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2021;50(6): 899-904. [4] SUBEDI P, HUBER K, STERR C, et al. Towards unravelling biological mechanisms behind radiatton-induced oral mucositts via mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Front Oncol. 2023;13:1180642. [5] NIKITAKI Z, MAVRAGANI IV, LASKARATOU DA, et al. Systemic mechanisms and effects of ionizing radiatton: A new ‘old’ paradigm of how the bystanders and distant can become the players. Semin Cancer Biol. 2016;37-38:77-95. [6] GKANTAIFI A, VARDAS E, ALONGI F, et al. Radiatton-Induced Oral Mucositts in Head and Neck Cancer Pattents. Five Years Literature Review. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2021;16(2):151-165. [7] KIM HJ, KANG SU, LEE YS, et al. Protecttve Effects of N-Acetylcysteine against Radiatton-Induced Oral Mucositts In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancer Res Treat. 2020;52(4):1019-1030. [8] LEE CT, GALLOWAY TJ. Pathogenesis and Amelioratton of RadiattonInduced Oral Mucositts. Curr Treat Opttons Oncol. 2022;23(3): 311-324. [9] PULITO C, CRISTAUDO A, PORTA C, et al. Oral mucositts: the hidden side of cancer therapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):210. [10] DAVY C, HEATHCOTE S. A systemattc review of interventtons to mittgate radiotherapy-induced oral mucositts in head and neck cancer pattents. Support Care Cancer. 2021;29(4):2187-2202. [11] WANG H, ZHANG K, RUAN Z, et al. Correctton to: Probucol enhances the therapeuttc efffciency of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of erecttle dysfunctton in diabettc rats by prolonging their survival ttme via Nrf2 pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):47. [12] SHIN JY, LEE PH. Mesenchymal stem cells modulate misfolded α-synuclein in parkinsonian disorders: A multttarget disease-modifying strategy. Stem Cell Res. 2020;47:101908. [13] WANG Y, FANG J, LIU B, et al. Reciprocal regulatton of mesenchymal stem cells and immune responses. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29(11): 1515-1530. [14] ANDRZEJEWSKA A, DABROWSKA S, LUKOMSKA B, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Neurological Disorders. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(7): 2002944. [15] XU L, JI H, JIANG Y, et al. Exosomes Derived From CircAkap7-Modiffed Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect Against Cerebral Ischemic Injury. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:569977. [16] HAN Y, YANG J, FANG J, et al. The secretton proffle of mesenchymal stem cells and potenttal applicattons in treattng human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):92. [17] OGAY V, SEKENOVA A, LI Y, et al. The Therapeuttc Potenttal of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Atherosclerosis. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;16(7):897-913. [18] VAN BALKOM BWM, GREMMELS H, GIEBEL B, et al. Proteomic Signature of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles. Proteomics. 2019;19(1-2):e1800163. [19] SHANG Y, WANG Q, LI J, et al. Zirconia Nanoparttcles Induce HeLa Cell Death Through Mitochondrial Apoptosis and Autophagy Pathways Mediated by ROS. Front Chem. 2021;9:522708. [20] DING X, NIE Z, SHE Z, et al. The Regulatton of ROS- and BECN1- Mediated Autophagy by Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase in Glioblastoma. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6636510. [21] KMA L, BARUAH TJ. The interplay of ROS and the PI3K/Akt pathway in autophagy regulation. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2022;69(1): 248-264. [22] SANKAR V, XU Y. Oral Complicattons from Oropharyngeal Cancer Therapy. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(18):4548. [23] ELTING LS, COOKSLEY CD, CHAMBERS MS, et al. Risk, outcomes, and costs of radiatton-induced oral mucositts among pattents with headand-neck malignancies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;68(4): 1110-1120. [24] LIU S, ZHAO Q, ZHENG Z, et al. Status of Treatment and Prophylaxis for Radiatton-Induced Oral Mucositts in Pattents With Head and Neck Cancer. Front Oncol. 2021;11:642575. [25] SONIS ST. Precision medicine for risk predictton of oral complicattons of cancer therapy-The example of oral mucositts in pattents receiving radiatton therapy for cancers of the head and neck. Front Oral Health. 2022;3:917860. [26] CHEN G, WANG M, RUAN Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-143-3p suppresses myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulattng autophagy. Life Sci. 2021;280:119742. [27] TELI P, KALE V, VAIDYA A. Extracellular vesicles isolated from mesenchymal stromal cells primed with neurotrophic factors and signaling modiffers as potenttal therapeuttcs for neurodegenerattve diseases. Curr Res Transl Med. 2021;69(2):103286. [28] LU X, BAO H, CUI L, et al. hUMSC transplantatton restores ovarian functton in POI rats by inhibittng autophagy of theca-intersttttal cells via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1):268. [29] LI T, GU J, YANG O, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal miRNA-29c Decreases Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Inhibitton of Excessive Autophagy via the PTEN/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Circ J. 2020;84(8):1304-1311. [30] MA CY, ZHAI Y, LI CT, et al. Translattng mesenchymal stem cell and their exosome research into GMP compliant advanced therapy products: Promises, problems and prospects. Med Res Rev. 2023. doi: 10.1002/ med.22002. [31] ZHOU C, ZHANG B, YANG Y, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging therapeuttc opportunittes for wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):107. [32] ZOU J, YANG W, CUI W, et al. Therapeuttc potenttal and mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as bioacttve materials in tendon-bone healing. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):14. [33] WANG L, HU L, ZHOU X, et al. Author Correctton: Exosomes secreted by human adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote scarless cutaneous repair by regulattng extracellular matrix remodelling. Sci Rep. 2021; 11(1):3245. [34] XU T, LIN Y, YU X, et al. Comparattve Effects of Exosomes and Ectosomes Isolated From Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Achilles Tendinopathy in a Rat Model. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(10): 2740-2752. [35] WANG X, JIAO Y, PAN Y, et al. Fetal Dermal Mesenchymal Stem CellDerived Exosomes Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Acttvattng Notch Signaling. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:2402916. [36] VU NB, NGUYEN HT, PALUMBO R, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes for wound healing: current status and promising directtons. Minerva Med. 2021;112(3):384-400. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [3] | Li Kaiying, Wei Xiaoge, Song Fei, Yang Nan, Zhao Zhenning, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng. Mechanism of Lijin manipulation regulating scar formation in skeletal muscle injury repair in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [4] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [5] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [6] | Lyu Liting, Yu Xia, Zhang Jinmei, Gao Qiaojing, Liu Renfan, Li Meng, Wang Lu. Bibliometric analysis of research process and current situation of brain aging and exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1457-1465. |
| [7] | Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [8] | Cao Yue, Ye Xinjian, Li Biyao, Zhang Yining, Feng Jianying. Effect of extracellular vesicles for diagnosis and therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1523-1530. |
| [9] | Bai Jing, Zhang Xue, Ren Yan, Li Yuehui, Tian Xiaoyu. Effect of lncRNA-TNFRSF13C on hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in periodontal cells by modulation of #br# miR-1246 #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 928-935. |
| [10] | Zhi Fang, Zhu Manhua, Xiong Wei, Lin Xingzhen. Analgesic effect of acupuncture in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 936-941. |
| [11] | Wang Yuru, Li Siyuan, Xu Ye, Zhang Yumeng, Liu Yang, Hao Huiqin. Effects of wogonin on joint inflammation in collagen-induced arthritis rats via the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1026-1035. |
| [12] | Chen Yaodong, Ren Jiayi, Cao Jingwei, Fan Wenwen, Chen Wu. Near-infrared photoresponsive h-PCuNF nanoparticles mediate multimodal therapeutics against malignant tumors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 780-788. |
| [13] | Ma Weibang, Xu Zhe, Yu Qiao, Ouyang Dong, Zhang Ruguo, Luo Wei, Xie Yangjiang, Liu Chen. Screening and cytological validation of cartilage degeneration-related genes in exosomes from osteoarthritis synovial fluid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7783-7789. |
| [14] | Yu Hui, Yang Yang, Wei Ting, Li Wenli, Luo Wenqian, Liu Bin. Gadd45b alleviates white matter damage in chronic ischemic rats by modulating astrocyte phenotype [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7797-7803. |
| [15] | Zhang Min, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Li Zhuangzhuang, Wang Xue, Wang Huike. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell exosomes repair radiation-induced submandibular gland damage in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7804-7815. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||