[1] LOBENHOFFER P, AGNESKIRCHNER JD. Improvements in surgical technique of valgus high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2003; 11(3):132-138.
[2] STAUBLI AE, DE SIMONI C, BABST R, et al. TomoFix: a new LCP-concept for open wedge osteotomy of the medial proximal tibia--early results in 92 cases. Injury. 2003;34 Suppl 2:B55-B62.
[3] FLOERKEMEIER S, STAUBLI AE, SCHROETER S, et al. Outcome after high tibial open-wedge osteotomy: a retrospective evaluation of 533 patients[J]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(1):170-180.
[4] LEE SS, KIM JH, KIM S, et al. Avoiding Overcorrection to Increase Patient Satisfaction After Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(9):2453-2461.
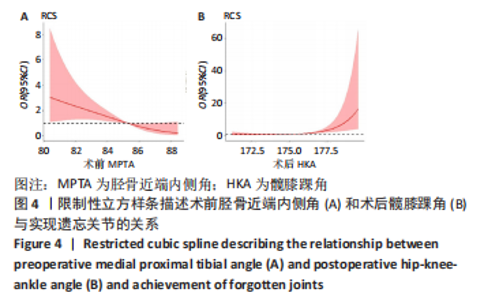
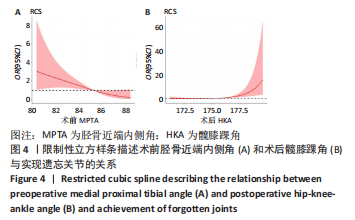
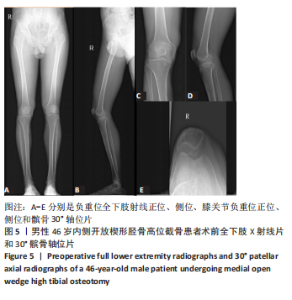
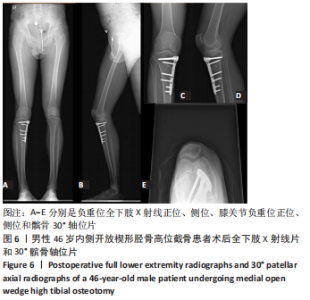
[5] 徐奎帅,张靓,陈进利,等.内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨后早期力线改变对下肢关节的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(6): 821-826.
[6] THIENPONT E, VANDEN BERGHE A, SCHWAB PE, et al. Joint awareness in osteoarthritis of the hip and knee evaluated with the ‘Forgotten Joint’ Score before and after joint replacement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(10):3346-3351.
[7] YAMATE S, HAMAI S, KAWAHARA S, et al. Multiple Imputation to Salvage Partial Respondents: Analysis of the Forgotten Joint Score-12 After Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022;104(24):2195-2203.
[8] ITOH M, JUNYA I, UMITO K, et al. Good Validity and High Internal Consistency of the Forgotten Joint Score-12 in Patients After Medial Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(8): 2691-2697.
[9] COLLINS M, LAVIGNE M, GIRARD J, et al. Joint perception after hip or knee replacement surgery. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(3):275-280.
[10] PULIERO B, BLAKENEY WG, BEAULIEU Y, et al. Joint Perception After Total Hip Arthroplasty and the Forgotten Joint. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(1):65-70.
[11] ZAMPOGNA B, VASTA S, AMENDOLA A, et al. Assessing Lower Limb Alignment: Comparison of Standard Knee Xray vs Long Leg View. Iowa Orthop J. 2015;35:49-54.
[12] CALEK AK, ANDREAS L, LUKAS J, et al. Tibial joint line orientation has no effect on joint awareness after mechanically aligned total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(2):389-396.
[13] WANG Z, DENG W, SHAO H, et al. Predictors of a forgotten joint after medial fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2022;37:103-111.
[14] BEHRENDT P, AKOTO R, BARTELS I, et al. Preoperative joint line convergence angle correction is a key factor in optimising accuracy in varus knee correction osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31(4): 1583-1592.
[15] KOGA H, NAKAMURA T, NAKAGAWA Y, et al. Simultaneous Correction of Varus Deformity and Posterior Tibial Slope by Modified Hybrid Closed-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy. Arthrosc Tech. 2022;11(11):e2081-e2089.
[16] WATANABE S, AKAGI R, NINOMIYA T, et al. Comparison of joint awareness after medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty and high tibial osteotomy: a retrospective multicenter study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022;142(6):1133-1140.
[17] NAKAYAMA H, STEFFEN S, CHIE Y, et al. Large correction in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy with resultant joint-line obliquity induces excessive shear stress on the articular cartilage. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(6):1873-1878.
[18] AKAMATSU Y, KUMAGAI K, KOBAYASHI H, et al. Effect of Increased Coronal Inclination of the Tibial Plateau After Opening-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy. Arthroscopy. 2018;34(7):2158-2169.
[19] GOSHIMA K, SAWAGUCHI T, SHIGEMOTO K, et al. Comparison of Clinical and Radiologic Outcomes Between Normal and Overcorrected Medial Proximal Tibial Angle Groups After Open-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy. Arthroscopy. 2019;35(10):2898-2908.
[20] LIU X, CHEN Z, GAO Y, et al. High Tibial Osteotomy: Review of Techniques and Biomechanics. J Healthc Eng. 2019;2019:8363128.
[21] LEE SS, LEE HIL, CHO ST, et al. Comparison of the outcomes between two different target points after open wedge high tibial osteotomy: The Fujisawa point versus the lateral tibial spine. Knee. 2020;27(3):915-922.
[22] HASEGAWA M, NAITO Y, TONE S, et al. Correction to: High rates of outliers in computer-assisted high tibial osteotomy with excellent mid-term outcomes. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31(2):406.
[23] MATSUSHITA T, WATANABE S, ARAKI D, et al. Differences in preoperative planning for high-tibial osteotomy between the standing and supine positions. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2021;33(1):8.
[24] LEE DH, PARK SC, PARK HJ, et al. Effect of soft tissue laxity of the knee joint on limb alignment correction in open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(12):3704-3712.
[25] SO SY, LEE SS, JUNG EY, et al. Difference in joint line convergence angle between the supine and standing positions is the most important predictive factor of coronal correction error after medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(5): 1516-1525.
[26] LEE CL, YANG HJ, HWANG YJ. Comparison of the outcomes of nasal bone reduction using serial imaging. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2021;22(4):193-198.
[27] BATAILLER C, GICQUEL T, BOUGUENNEC N, et al. A predictive score of high tibial osteotomy survivorship to help in surgical decision-making: the SKOOP score. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022. doi: 10.1007/s00402-022-04694-w.
[28] LANDSMEER MLA, RUNHAAR J, VAN MIDDELKOOP M, et al. Predicting Knee Pain and Knee Osteoarthritis Among Overweight Women. J Am Board Fam Med. 2019;32(4):575-584.
[29] GUARINO A, FARINELLI L, IACONO V, et al. Long-Term Survival and Predictors of Failure of Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(4):1002-1007.
|