Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (10): 1634-1640.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2202
Antimicrobial mechanism of antimicrobial peptide and research progress
Zhang Xi1, Gong Lei2
- 1Hospital of Stomatology, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China; 2Department of Esophageal Oncology, Tumor Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, National Clinical Medical Research Center of Cancer, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Tumor Prevention and Treatment, Tianjin Clinical Medical Research Center of Malignant Tumor, Tianjin 300060, China
-
Received:2019-04-03Revised:2019-04-16Accepted:2019-08-01Online:2020-04-08Published:2020-02-18 -
Contact:Gong Lei, Attending physician, Department of Esophageal Oncology, Tumor Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, National Clinical Medical Research Center of Cancer, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Tumor Prevention and Treatment, Tianjin Clinical Medical Research Center of Malignant Tumor, Tianjin 300060, China -
About author:Zhang Xi, MD, Lecturer, Hospital of Stomatology, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81501798, No. 81501994; the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin, No. 18JCYBJC95700; Tianjin Cancer Hospital Clinical Trial Fund, No. C1711; Wu Jieping Medical Foundation-Excellent Surgery Foundation, No. 320.2730.1886
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Xi, Gong Lei. Antimicrobial mechanism of antimicrobial peptide and research progress[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(10): 1634-1640.
share this article
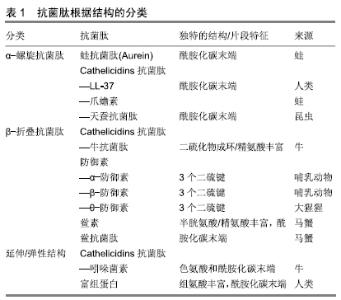
2.1 抗菌肽的来源和分类 2.1.1 抗菌肽的来源 抗菌肽存在于所有形式的生命体中,从细菌到植物、脊椎动物及无脊椎动物。在细菌中,抗菌肽通过杀死其他可能竞争养分和相同生存环境的菌种而有益于本菌种的生存。在植物中,由于植物缺乏适应性免疫功能,因此抗菌肽在防止细菌和真菌感染中发挥基础作用,而且在多种植物中都能发现植物抗菌肽的存在[6]。所有的植物源性抗菌肽富含半胱氨酸且存在很多二硫键。类似于植物,无脊椎动物也缺乏适应性免疫系统,因此完全依赖与生俱来的免疫系统来对抗感染。在目前研究过的无脊椎动物中都发现了抗菌肽,其中大部分是昆虫和海洋无脊椎动物。而脊椎动物拥有先天和后天免疫系统,有多种脊椎动物都发现了抗菌肽,比如鱼类、哺乳动物和两栖动物[7-11]。抗菌肽主要存在于这类动物的各类细胞中,比如白细胞(吞噬细胞、中性粒细胞、巨噬细胞、自然杀伤细胞),以及位于口腔、肺组织或者皮肤的上皮组织中[12-13]。一些脊椎动物抗菌肽也表现出重要的免疫调节功能及炎症控制功能[14-17]。 2.1.2 抗菌肽的分类 抗菌肽是一类特殊的分子,就目前研究过的2 800多条氨基酸序列对抗菌肽进行分类是非常必要的。通常来说,大分子抗菌肽具有100个氨基酸或者更多位氨基酸,有助于裂解、结合营养物或者靶向特定微生物大分子。但抗菌肽的主要类型为小分子蛋白质,主要引起微生物细胞膜功能或者结构的缺陷抑或通过与ATP相互作用直接抑制某些ATP依赖性酶起作用[18]。抗菌肽可以根据很多不同的方式进行分类,包括结构、序列长短或者作用机制。抗菌肽具有多种功能,包括杀死细菌、免疫系统改建、预防生物膜形成、抗肿瘤细胞、抗病毒等功能。尽管如此,抗菌肽具备一些共同的特点,例如:大多数抗菌肽在性质上是带阳离子的,通常携带正电荷在+2到+9之间[19]。它们还具有包括分离的疏水和亲水域的双亲结构,其中正电荷在肽和靶细胞膜之间的静电相互作用模式中起着中心作用。除了抗菌活性和对细菌细胞的渗透之外,抗菌肽的一些特性也会影响其一般活性,这些特性包括电荷(阳离子或阴离子)、大小(通常小于100个氨基酸)、初级序列、构象、结构特征、疏水性等[20]。 抗菌肽根据结构分类:最为人们所接受的分类方法是根据结构特点将抗菌肽分成3个亚类,具体的分类列在表1中。第一种亚类包括具有α螺旋结构的抗菌肽,它们主要存在于青蛙和昆虫的细胞外基质中。这类抗菌肽大多数在水溶液中没有结构,但当它们接触临界浓度的三氟乙醇、清洁剂或者表面活性剂后恢复原有结构,比如十二烷基硫酸钠、微胶粒和胶质体。目前研究的具有α螺旋的人类抗菌肽是LL-37,它是脊椎动物源抗菌肽中的一员。脊椎动物源抗菌肽是一类种类繁多的抗菌肽,主要在一些哺乳动物体内发现,比如鼠、绵羊、山羊、马和牛。脊椎动物源抗菌肽含有12-80位氨基酸而且存在着一些其他结构。除了抗菌性能之外,这类抗菌肽比如说LL-37具有重要的免疫调节及炎症反应[15,21]。另外一个重要的具有α螺旋的是爪蟾抗菌肽,主要提取于非洲爪蟾,具有对抗革兰阳性菌和革兰阴性菌、真菌、酵母和病毒。爪蟾抗菌肽的结构和功能的关系已被阐述,虽然这些抗菌肽首次应用于临床以失败告终,但它的类似物培西加南目前在临床试验中[22]。 "
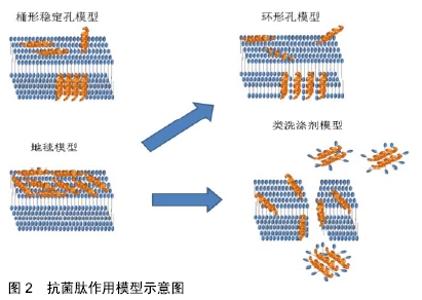
α螺旋抗菌肽另外一类重要的抗菌肽是蛙抗菌肽家族。蛙抗菌肽来自于澳大利亚绿纹树蛙,它们有大概30种,来自5种不同家族,分布在短肽(蛙抗菌肽1-3)到长肽比如蛙抗菌肽4.1和蛙抗菌肽5.1。大部分蛙抗菌肽对于革兰阳性菌比如金黄色葡萄球菌和表皮葡萄球菌有很好的效果[23]。而对于蛙抗菌肽1.2、蛙抗菌肽3.2和蛙抗菌肽3.3这类抗菌肽来说,它们对于30-50种不同癌症有着重要的作用。最新的研究发现,蛙抗菌肽2.2可以形成离子选择性孔,允许特定离子的转运,比如钾离子和镁离子。另外,蛙抗菌肽2.2引起细胞膜透化作用,引起细胞膜降低能量运输从而导致细胞死亡[24]。α螺旋抗菌肽另一个重要的特征是为获得高抗菌性能需要碳端酰胺化来实现。碳端酰胺化增强带有正电荷的多肽和带有负电荷的细菌细胞膜的静电相互作用,从而提高抗菌肽在细菌胞膜界面作用[25]。 抗菌肽的第二种亚类是具有β折叠结构。这类抗菌肽包括防御素和速普肽。几乎所有β折叠抗菌肽都具有可以形成二硫键的半胱氨酸残基[26]。具有β折叠结构的抗菌肽在溶液中具有结构,而且不存在从溶液环境到细胞膜环境变化带来的结构转化[27]。防御素按照二硫键的位置区分亚类见表1。 第三种亚类和最后一种亚类的抗菌肽具有延伸或弹性结构。这一类抗菌肽中的大多数来自组织蛋白酶家族,由2个或多个脯氨酸残基组成,已知这些残基会破坏二级结构元素,如螺旋或薄片。吲哚西丁是一种富含色氨酸的抗菌肽,从牛中性粒细胞中分离出来,仅由13种氨基酸组成,可形成一种独特的“膜相关肽结构”,具有明确的延伸结构[28]。 抗菌肽根据产生方式分类:抗菌肽的产生要么借助于核糖体要么不借助于核糖体,这可以被认为是对这些生物分子进行分类的方法之一。非核糖体合成肽进一步被分类为环肽、糖肽、脂糖肽和脂肽,如Gramicidin、多黏菌素、万古霉素和杆菌肽[29-31]。这些肽具有一些修饰的环状和/或支链结构,如N-甲基和N-甲酰基,或糖基化、酰化、卤代或羟基化。这类抗菌肽是由一种或多种的非核糖体肽合成酶合成的,这种酶的基因通常存在于细菌的单个操纵子或真核生物的基因簇中。另一类是核糖体合成抗菌肽,这一类抗菌肽与上文提到的根据结构分类有所重复,故不再赘述。 2.2 抗菌肽的抗菌机制 2.2.1 抗菌肽的抗菌机制概述 首先,从生物学上讲,抗菌肽与宿主细胞膜的磷脂相互作用。抗菌肽与宿主反应有5个不同的步骤:与目标细胞接触的主要生物化学或生物物理亲和力(例如静电或疏水相互作用);将靶细胞膜进行结构调整(构造成螺旋形或筒形结构);积累到活性化学计量水平;渗透干扰靶膜或去极化,或导致任何其他直接/间接功能异常,这一过程可能是暂时的或稳定的;通过靶细胞膜进入细胞内发挥作用。最初认为膜靶向是抗菌肽唯一的作用机制,但现在越来越多的证据表明还有其他模式[32]。这些作用模式可以分为2类主要的模式:直接杀死和免疫调节。这种直接杀伤作用机制可进一步分为膜靶向和非膜靶向。 2.2.2 通过膜透化直接致死机制 膜靶向抗菌肽可以有受体介导或非受体介导的相互作用。受体介导的途径主要包括细菌产生的抗菌肽,大多数脊椎动物和无脊椎动物抗菌肽靶向定位细胞膜,而不与受体特异性相互作用[33]。这些抗菌肽在微摩尔浓度下对微生物具有典型的体外活性,并通过与膜的成分相互作用发挥作用[34]。革兰阳性菌和革兰阴性菌的外表面含有脂多糖,因此在表面上产生净负电荷,使阳离子抗菌肽具有初始静电引力。更重要的是,抗菌肽的目标在细菌膜和多细胞动物胞膜上有着根本区别。细菌膜中脂质双层的外单层主要由头部带负电荷的脂质组成;而动物胞膜的外叶由两性磷脂、鞘磷脂和其他中性成分(如胆固醇)组成[20]。头部带负电荷的类脂大部分位于面向动物膜细胞质的内叶中。带正电的抗菌肽与细菌膜外叶带负电的磷脂有很强的静电作用。一些抗菌肽也显示出抗癌活性,在癌细胞中负电荷磷脂的内外膜不对称性消失,导致外叶上负电荷磷脂酰丝氨酸含量增加,增强了与抗菌肽的相互作用。此外,其他带负电荷的生物分子,如硫酸肝素、O-糖基化黏蛋白、唾液酸神经节苷脂的过度表达,以及跨膜电位和膜流动性的增加,也使抗菌肽能够特异性靶向癌细胞[35]。 此外,有些抗菌肽甚至对脂类的其他性质敏感,即不仅仅是电荷。例如,与动物细胞膜的主要成分磷脂酰丝氨酸组成的脂质体相比,滑爪蟾素能更有效诱导由磷脂酰甘油组成的脂质体的渗漏,磷脂酰甘油是一种主要存在于细菌膜中的负电荷磷脂。脂类的形状取决于头部和疏水尾部的相对大小。磷脂酰丝氨酸和磷脂酰甘油的分子形状分别类似于锥形和圆柱形,因此显示出不同的膜曲率特性[36]。磷脂酰丝氨酸的头组包含正(氨基)电荷和负(羧基)电荷,它们允许特定的肽-脂相互作用,因此比含有磷脂酰甘油的膜具有更高的活性[37]。这种特异性的相互作用不仅限于抗菌肽等阴离子脂质如植物环肽,还可以特异性地结合到两性离子脂质如磷脂酰乙醇胺,后者大量存在于细菌膜的表面,也大量存在于动物膜的细胞质中。这些研究表明,膜电荷不仅是初始相互作用的重要因素,而且膜曲率等其他特性也可能起到重要作用[38-40]。 在初始的静电和疏水相互作用后,抗菌肽在表面聚集,达到一定浓度后在细菌膜上自组装[41-42]。在这一阶段,各种模型被用来描述抗菌肽的作用,示意图见图2。模型可分为2大类:跨膜孔模型和非孔模型。跨膜孔模型可进一步细分为桶形稳定孔和环形孔模型[43]。在桶形模型中抗菌肽最初平行于膜,但最终垂直插入脂质双层。这促进了侧肽-肽相互作用,方式类似于膜蛋白离子通道。肽双亲结构(α和/或β折叠)在这种成孔机制中是必不可少的,因为疏水区与膜脂相互作用,亲水残基形成通道管腔[44]。 "
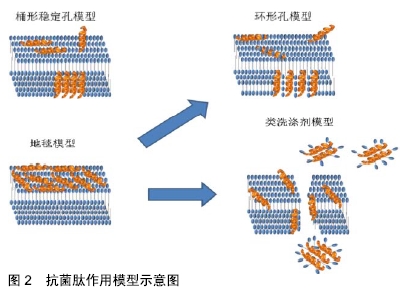
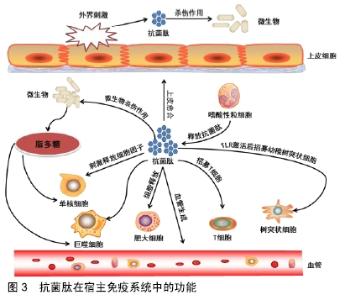
此外在环形孔模型中,肽也垂直插入脂质双层,但不存在特定的肽-肽相互作用。相反,这些肽诱导脂质双层的局部弯曲,部分由肽形成,部分由磷脂头部形成。动态和短暂的脂肽超分子被称为“环形孔”。与桶壁孔相比,该模型的显著特征是双层的净排列:在桶壁孔中,保持脂质的疏水和亲水排列,而在环形孔中,破坏双层的疏水和亲水排列。由于孔在解体后是短暂的,一些肽转移到进入细胞质内小叶,并可能靶向细胞内成分。环形孔的其他特征包括离子选择性和离散尺寸[45]。 抗菌肽也可以在膜上不形成特定的孔,其中一个模型即是地毯模型。在这种模型下,抗菌肽平行于脂质双层吸附,达到覆盖膜表面的阈值浓度,从而形成“地毯”。这会导致膜表面的不良相互作用。因此,膜的完整性丧失了,产生了一种类似清洁剂的效果,最终通过形成胶束使膜崩解。膜双层结构最终崩解成胶束也被称为类洗涤剂模型。地毯模型不需要膜结合肽单体的特定肽-肽相互作用;也不需要肽插入疏水核心形成跨膜通道或特定肽结构[46]。 总体来说,有许多模型来描述抗菌肽的抗菌机制。除上述模型外,还有其他相关模型,如Shai-Huang- Matsazuki模型、界面活性模型和电穿孔模型。而那些模型并没有在图2中展现出来。可能使用不同的膜模型或分析条件获得不同的结果,例如,当肽脂比变化时,某些抗菌肽(如BP100)可能有多个抗菌机制[47],这表明文章所述的模型可能或不可能直接转化为细菌中发生的情况。 2.2.3 非膜靶向致死机制 非膜靶向抗菌肽可分为2大类:靶向细菌细胞壁和靶向细胞内的抗菌肽。与青霉素等常规抗生素类似,抗菌肽也能抑制细胞壁合成。尽管大多数传统抗生素与细胞壁成分合成中涉及的特定蛋白质结合,但抗菌肽通常与细胞壁合成所需的各种前体分子相互作用,高度保守的脂质Ⅱ是一个主要作用目标分子。例如,防御素等抗菌肽与脂质Ⅱ分子中带负电荷的焦磷酸糖部分结合[48-49],这类结合可进一步促进孔的形成和膜的破坏。人β防御素3和α防御素1等抗菌肽依赖于选择性结合到脂质Ⅱ来提供杀菌活性[49]。当抗菌肽首次被发现时,人们认为它们不能有细胞内靶点。对原始α螺旋肽(如滑爪蟾素、杀菌肽和蜂毒肽)的研究表明其靶点为细胞膜。现在已经证实一些抗菌肽具有细胞内靶点,因为其不会在最小有效浓度下引起膜渗透,但仍会导致细菌死亡。从机制上讲,这些抗菌肽先与胞质膜相互作用,然后在细胞内积累,在那里它们可以阻止关键的细胞过程。许多涉及细胞内靶点的新机制已被发现,如抑制蛋白质/核酸合成和破坏酶/蛋白质活性[50]。 2.3 细菌抵抗抗菌肽的机制 基于抗菌肽的广泛应用,预计在葡萄球菌、口腔细菌(包括链球菌)和肠道细菌(包括沙门氏菌)等微生物环境中已发展出许多抵抗策略。抗菌肽抗性基因存在于大多数微生物物种中,这些抗性机制成为将抗菌肽应用于临床过程中的最大的障碍之一。尽管抗菌肽对细菌有广泛的敏感性,但在多种结构和功能模式的影响下,产生的对某些抗菌肽的广泛交叉耐药性这些肽作为杀菌剂的使用受到质疑。一些研究主要讨论了两种截然不同的抗菌肽抗性策略:被动抵抗和诱导或适应性抵抗机制。被动抵抗是指对环境条件的响应,通常在没有抗菌肽的情况下就已存在。诱导抗性机制与抗菌肽存在于在革兰阴性和革兰阳性细菌中或,者由于其存在而引起的应激性细菌分子修饰有关[51]。 对抗菌肽的抵抗以不同的方式发生,包括改变细胞壁和胞质膜的结构或净电荷。细菌抵抗抗菌肽的多种机制包括:通过将抗菌肽捕获并在蛋白质中使其失活,利用蛋白酶将其切割,通过改变细胞表面电荷降低其结合亲和力,改变细菌细胞膜的流动性,在膜中产生流出泵,产生外聚合物和生物膜结构,以及诱导特定基因的表达[32,52]。 细菌可以通过特定感受器感知抗菌肽的存在并激活抗性机制。这些感受器在革兰阳性细菌和革兰阴性细菌的结构和功能上存在显著差异。许多抗抗菌肽的机制都涉及基因调控,因为这是一个消耗能量的过程,这意味着在抗菌肽存在的情况下才激活。 在革兰阴性细菌中,PhoPQ系统是抗菌肽的双组分中央调节器,包括传感器组氨酸激酶(PhoQ)和反应调节器(PhoP)。反应调节器仅在对环境刺激的反应中表达,包括细胞外镁或钙浓度或pH值的变化。抗菌肽与二价阳离子(Mg2+、Ca2+等)竞争结合到传感器组氨酸激酶的高酸性区域。传感器组氨酸激酶位于磷脂膜中,当细胞外负电荷位点被阳离子抗菌肽取代时,传感器组氨酸激酶被激活。抗菌肽向传感器组氨酸激酶发送信号,导致从传感器组氨酸激酶到反应调节器的磷转移增加,从而促使其调节靶基因表达。由于传感器组氨酸激酶系统在许多革兰阴性病原体(如伤寒沙门氏菌)的抗抗菌肽保护中起着重要作用,因此被认为是一种毒力因子。但是在Ca/Mg高浓度时可以抑制PhoPQ系统[53]。 与革兰阴性细菌类似,革兰阳性细菌中也存在检测抗菌肽的传感器,并触发基于基因调节的耐药性反应。在革兰阳性抗菌肽抗性细菌中,主要的转运系统有3种:3组分ABC转运子、两组分ABC转运子和单蛋白多药耐药(MDR)转运子(也称为MDR泵)。这类转运体一般包含2个结构域:跨膜结构域(渗透酶)和核苷酸结合结构域。它们消耗ATP来实现膜内外物质运输。LanFEG系统或3组分ABC转运体是自身免疫机制的一部分,由一种具有3个功能域的蛋白质组成:与核苷酸结合的LanF及包含跨膜域的LanE和LanG。这种转运系统经常被发现伴随着膜相关脂蛋白,对抗菌肽有更大的抵抗力。革兰阳性细菌中的第二类转运系统是双组分转运系统,它通常对包括环肽和一些非肽抗生素在内的多种抗菌肽产生抵抗力。双组分转运体系统首次在表皮葡萄球菌中发现,并命名为抗菌肽传感器(Aps),也称为GraRS或GraRSX。这个转运系统包含3个功能成分,包括与膜结合抗菌肽传感组氨酸激酶(APSS)、ADNA结合反应调节器(ApsR)和功能未知的成分(ApsX)[54-55]。 2.4 抗菌肽在先天免疫系统中的作用 在原核生物(如细菌)和真核生物(如真菌、植物和动物)中都发现了天然抗菌肽[56-57]。在这些生物体中,抗菌肽被认为是先天免疫系统的重要组成部分。尤其是在动物身上,当暴露的组织和器官受到破坏时,抗菌肽是抵御空气中病原体入侵的第一道屏障。此外,许多抗菌肽对白细胞具有趋化作用,或参与细胞增殖、上皮化、血管生成、伤口愈合或适应性免疫的调节。在哺乳动物中,抗菌肽通过某些机制促进免疫系统,如激活T细胞,激发Toll样受体,增强吞噬作用,激活树突细胞,中性粒细胞的吸血作用[58],见图3。 "
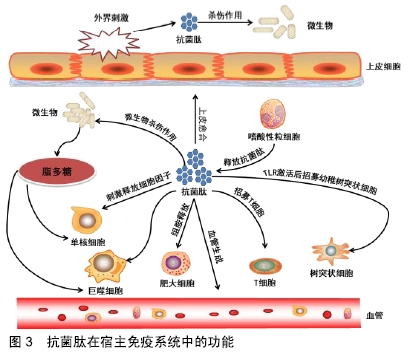

不同的细胞,包括上皮细胞、组织吞噬细胞、中性粒细胞、淋巴细胞、角蛋白细胞和心肌细胞,在身体的不同部位,如淋巴系统、胃肠道、生殖泌尿道和免疫系统产生抗菌肽。一般来说,随着对抗菌肽表达的研究进展,抗菌肽的产生可能是组成性的(更频繁),也可能是由炎症或损伤引起的[59-60]。一些免疫系统细胞如巨噬细胞和中性粒细胞,组成性地产生抗菌肽,而另一些免疫系统细胞如上皮细胞,由于黏膜表面的诱导而产生抗菌肽。例如,α-防御素和皮屑素(参与皮肤防御的抗菌肽的前体)通常是组成性产生的,而大多数β-防御素是诱导性的[59]。防御素是宿主防御肽,分为3类:α-防御素、β-防御素和θ-防御素。这些肽有助于宿主细胞-受体相互作用;作为免疫系统细胞的化学引诱剂;有助于中性粒细胞的募集、免疫活性T细胞的活化、细胞黏附和经典补体途径的激 活[61]。LL-37也是一种典型的宿主防御抗菌肽,由不同类型的细胞产生,作为中性粒细胞和肥大细胞的化学引诱剂,从而防止中性粒细胞和角蛋白细胞凋亡。这种肽刺激趋化因子的产生和血管生成、单核细胞分化和血管内皮细胞增殖,并具有抗炎和抗内毒素作用。巨噬细胞是哺乳动物先天免疫系统中大量存在的另一类细胞,它们产生溶酶体并保护宿主免受感染细菌的侵害[62]。 在真核生物中,抗菌肽直接保护宿主免受广泛的感染因子,包括革兰阴性细菌、病毒、真菌甚至原生动物,并且是宿主先天防御系统的重要组成部分。虽然某些抗菌肽通过直接影响病原体而参与先天免疫功能,但某些抗菌肽通过改变特殊宿主基因的表达间接影响宿主防御机制,这些特殊宿主基因的产物可以连接宿主的先天免疫系统和适应性免疫系统,或在感染期间干预宿主的炎症反应。例如,抗菌肽(如CAP18、CAP35)和乳铁蛋白衍生物可通过阻断巨噬细胞释放的脂多糖诱导的细胞因子来降低炎症反应[63]。此外,抗菌肽可能作为趋化因子发挥作用,触发细胞凋亡或激活自身免疫反应。 2.5 解决抗菌肽抗性策略 与传统抗生素相比,抗菌肽的优点包括光谱抗菌活性、快速杀灭活性和低水平诱导耐药性。然而,病原体使用不同的机制来抵抗抗菌肽;近年来发现了许多有关细菌针对抗菌肽抗性机制的细节,有助于发现一些科学解决方案。在这方面抗菌肽分子结构的变化,比如添加、去除和/或替换一个或多个氨基酸及对其氨基或羧基末端的修饰,是需要考虑的一些解决方案。此外,一些研究者还提出了它们生化特性的变化,包括阳离子性、疏水性和两性。最后,抗菌肽与某些物质(如普通抗生素)联合应用可以通过协同作用降低耐药性[64-66]。例如,研究表明氨苄西林对达托霉素诱导的生长抑制和杀灭、表面电荷及对宿主防御阳离子抗菌肽(如LL-37和HNP-1)的敏感性都是有效的。因此,氨苄西林诱导净阳性细菌表面电荷的减少,与体外达托霉素和其他阳离子肽的杀菌效果增强相关。与这些结果类似,合成阳离子肽(CM11: WKLFKKILKVL-NH2)与青霉素、头孢他啶、诺氟沙星和环丙沙星等抗生素的体外协同作用,已被证实分别对金黄色葡萄球菌、铜绿假单胞菌、肺炎克雷伯菌和大肠杆菌的多药耐药菌株有协同作用。链霉素、复方新诺明联合CM11肽对布氏杆菌耐药菌株也有协同作用。这些发现证实了抗生素和肽的结合可以增强它们的抑制作用,同时降低它们的有效剂量,特别是对耐药细菌的分离株。 "

| [1] VESTERGAARD M, FREES D, INGMER H. Antibiotic Resistance and the MRSA Problem.Microbiol Spectr. 2019;7(2). doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0057-2018 [2] RELLO J, KALWAJE ESHWARA V, CONWAY-MORRIS A, et al. Perceived differences between intensivists and infectious diseases consultants facing antimicrobial resistance: a global cross-sectional survey.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis.2019;38(7):1235-1240. [3] CATTOIR V, FELDEN B.Future antibacterial strategies: from basic concepts to clinical challenges.J Infect Dis.2019;220(3):350-360. [4] BECHINGER B, GORR SU.Antimicrobial Peptides: Mechanisms of Action and Resistance.J Dent Res.2017;96(3):254-260. [5] NUTI R, GOUD NS, SARASWATI AP, et al.Antimicrobial Peptides: A Promising Therapeutic Strategy in Tackling Antimicrobial Resistance. Curr Med Chem.2017;24(38):4303-4314. [6] NAWROT R, BARYLSKI J, NOWICKI G, et al.Plant antimicrobial peptides.Folia Microbiol(Praha).2014;59(3):181-96. [7] ZANJANI NT, MIRANDA-SAKSENA M, CUNNINGHAM AL, et al. Antimicrobial Peptides of Marine Crustaceans: The Potential and Challenges of Developing Therapeutic Agents.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(19):2245-2259. [8] VINEETH KUMAR TV, SANIL G. A Review of the Mechanism of Action of Amphibian Antimicrobial Peptides Focusing on Peptide-Membrane Interaction and Membrane Curvature.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017; 18(12):1263-1272. [9] BUONOCORE F, PICCHIETTI S, PORCELLI F, et al. Fish-derived antimicrobial peptides: Activity of a chionodracine mutant against bacterial models and human bacterial pathogens.Dev Comp Immunol. 2019;96:9-17. [10] WANG X, REN S, GUO C, et al. Identification and functional analyses of novel antioxidant peptides and antimicrobial peptides from skin secretions of four East Asian frog species. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).2017;49(6):550-559. [11] SANG M, WU Q, XI X, et al. Identification and target-modifications of temporin-PE: A novel antimicrobial peptide in the defensive skin secretions of the edible frog, Pelophylax kl. esculentus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2018;495(4):2539-2546. [12] FINDLAY F, PROUDFOOT L, STEVENS C, et al. Cationic host defense peptides; novel antimicrobial therapeutics against Category A pathogens and emerging infections.Pathog Glob Health. 2016;110 (4-5):137-147. [13] KHURSHID Z, NASEEM M, SHEIKH Z, et al.Oral antimicrobial peptides: Types and role in the oral cavity.Saudi Pharm J.2016;24(5):515-524. [14] MEADE KG, O'FARRELLY C.beta-Defensins: Farming the Microbiome for Homeostasis and Health. Frontiers in immunology.Front Immunol. 2019;9:3072. [15] HANCOCK RE, HANEY EF, GILL EE.The immunology of host defence peptides: beyond antimicrobial activity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16(5): 321-334. [16] HANEY EF, HANCOCK RE. Peptide design for antimicrobial and immunomodulatory applications. Biopolymers.2013;100(6):572-583. [17] VELDHUIZEN EJ, SCHNEIDER VA, AGUSTIANDARI H, et al. Antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activities of PR-39 derived peptides.PLoS One.2014;9(4):e95939. [18] ZHANG LJ, GALLO RL. Antimicrobial peptides.Curr Biol. 2016;26(1): R14-19. [19] FARKAS A, MAROTI G, KERESZT A, et al.Comparative analysis of the bacterial membrane disruption effect of two natural plant antimicrobial peptides.Front Microbiol.2017;8:51-62. [20] GUILHELMELLI F, VILELA N, ALBUQUERQUE P, et al. Antibiotic development challenges: the various mechanisms of action of antimicrobial peptides and of bacterial resistance.Front Microbiol. 2013;9(4):353-364. [21] YANG H, BIERMANN MH, BRAUNER JM, et al. New Insights into Neutrophil Extracellular Traps: Mechanisms of Formation and Role in Inflammation.Front Immunol.2016;12(7):302-309. [22] FOX JL.Antimicrobial peptides stage a comeback. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;31(5):379-382. [23] MADANCHI H, AKBARI S, SHABANI AA, et al. Alignment-based design and synthesis of new antimicrobial Aurein-derived peptides with improved activity against Gram-negative bacteria and evaluation of their toxicity on human cells.Drug Dev Res.2019;80(1):162-170. [24] WENZEL M, SENGES CH, ZHANG J, et al. Antimicrobial Peptides from the Aurein Family Form Ion-Selective Pores in Bacillus subtilis. Chembiochem.2015;16(7):1101-1108. [25] MURA M, WANG J, ZHOU Y, et al. The effect of amidation on the behaviour of antimicrobial peptides. Eur Biophys J. 2016;45(3):195-207. [26] BAYER A, LAMMEL J, TOHIDNEZHAD M, et al.The Antimicrobial Peptide Human Beta-Defensin-3 Is Induced by Platelet-Released Growth Factors in Primary Keratinocytes.Mediators Inflamm. 2017; 2017:6157491. [27] LEE TH, HALL KN, AGUILAR MI. Antimicrobial Peptide Structure and Mechanism of Action: A Focus on the Role of Membrane Structure. Curr Top Med Chem.2016;16(1):25-39. [28] KHANAL N, GAYE MM, CLEMMER DE.Multiple solution structures of the disordered peptide indolicidin from IMS-MS analysis.Int J Mass Spectrom.2018;427:52-58. [29] TAJBAKHSH M, KARIMI A, FALLAH F, et al.Overview of ribosomal and non-ribosomal antimicrobial peptides produced by Gram positive bacteria.Cell Mol Biol(Noisy-le-grand). 2017;63(10):20-32. [30] TATARKIEWICZ J, STANISZEWSKA A, BUJALSKA-ZADROZNY M. New agents approved for treatment of acute staphylococcal skin infections.Arch Med Sci.2016;12(6):1327-1336. [31] ZHAO P, XUE Y, LI X, et al.Fungi-derived lipopeptide antibiotics developed since 2000. Peptides.2019;113:52-65. [32] JOO HS, FU CI, OTTO M. Bacterial strategies of resistance to antimicrobial peptides. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.2016; 371(1695).pii: 20150292. doi:10.1098/rstb.2015.0292. [33] MITCHELL SA, TRUSCOTT F, DICKMAN R, et al.Simplified lipid II-binding antimicrobial peptides: Design, synthesis and antimicrobial activity of bioconjugates of nisin rings A and B with pore-forming peptides. Bioorg Med Chem.2018;26(21):5691-5700. [34] LEE EY, ZHANG C, DI DOMIZIO J, et al.Helical antimicrobial peptides assemble into protofibril scaffolds that present ordered dsDNA to TLR9. Nat Commun.2019;10(1):1012-1021. [35] FELICIO MR, SILVA ON, GONCALVES S, et al.Peptides with Dual Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities. Front Chem.2017;5:5-14. [36] JOUHET J.Importance of the hexagonal lipid phase in biological membrane organization. Front Plant Sci.2013;4:494-499. [37] ALVARES DS, RUGGIERO NETO J, AMBROGGIO EE. Phosphatidylserine lipids and membrane order precisely regulate the activity of Polybia-MP1 peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2017;1859(6):1067-1074. [38] STROMSTEDT AA, KRISTIANSEN PE, GUNASEKERA S, et al. Selective membrane disruption by the cyclotide kalata B7: complex ions and essential functional groups in the phosphatidylethanolamine binding pocket.Biochim Biophys Acta.2016;1858(6):1317-1327. [39] PHOENIX DA, HARRIS F, MURA M, et al.The increasing role of phosphatidylethanolamine as a lipid receptor in the action of host defence peptides.Prog Lipid Res.2015;59:26-37. [40] SCHMIDT NW, WONG GC. Antimicrobial peptides and induced membrane curvature: geometry, coordination chemistry,and molecular engineering.Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci. 2013;17(4):151-163. [41] EPAND RM,WALKER C,EPAND RF,et al.Molecular mechanisms of membrane targeting antibiotics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1858(5): 980-987. [42] ANDERSSON DI, HUGHES D, KUBICEK-SUTHERLAND JZ. Mechanisms and consequences of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial peptides.Drug Resist Updat.2016;26:43-57. [43] KRAUSON AJ, HE J, WIMLEY AW, et al.Synthetic molecular evolution of pore-forming peptides by iterative combinatorial library screening. ACS Chem Biol.2013;8(4):823-831. [44] KUMAR P, KIZHAKKEDATHU JN, STRAUS SK. Antimicrobial Peptides: Diversity, Mechanism of Action and Strategies to Improve the Activity and Biocompatibility In Vivo. Biomolecules.2018;8(1).pii: E4. doi:10.3390/biom8010004. [45] PAZDERKOVA M, MALON P, ZIMA V, et al.Interaction of Halictine-Related Antimicrobial Peptides with Membrane Models.Int J Mol Sci.2019;20(3).pii: E631.doi:10.3390/ijms20030631. [46] KRISHNAN RS, SATHEESAN R, PUTHUMADATHIL N, et al. Autonomously Assembled Synthetic Transmembrane Peptide Pore.J Am Chem Soc.2019;141(7):2949-2959. [47] MANZINI MC, PEREZ KR, RISKE KA, et al.Peptide:lipid ratio and membrane surface charge determine the mechanism of action of the antimicrobial peptide BP100.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1838(7): 1985-1999. [48] MALANOVIC N, LOHNER K. Antimicrobial Peptides Targeting Gram-Positive Bacteria. Pharmaceuticals(Basel).2016;9(3).pii: E59. doi:10.3390/ph9030059. [49] MUNCH D, SAHL HG. Structural variations of the cell wall precursor lipid II in Gram-positive bacteria - Impact on binding and efficacy of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1848(11 Pt B): 3062-3071. [50] SHARMA H, NAGARAJ R. Human beta-defensin 4 with non-native disulfide bridges exhibit antimicrobial activity.PLoS One. 2015;10(3): e0119525. [51] KANG KM, PARK JH, KIM SH, et al.Potential role of host defense antimicrobial peptide resistance in increased virulence of health care-associated MRSA strains of sequence type (ST) 5 versus livestock-associated and community-associated MRSA strains of ST72.Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis.2019;62:13-18. [52] KOPRIVNJAK T, PESCHEL A. Bacterial resistance mechanisms against host defense peptides.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68(13): 2243-2254. [53] COATES-BROWN R, MORAN JC, PONGCHAIKUL P, et al. Comparative Genomics of Staphylococcus Reveals Determinants of Speciation and Diversification of Antimicrobial Defense.Front Microbiol. 2018;9:2753. [54] NAWROCKI KL, CRISPELL EK, MCBRIDE SM. Antimicrobial Peptide Resistance Mechanisms of Gram-Positive Bacteria.Antibiotics(Basel). 2014;3(4):461-492. [55] SUAREZ JM, EDWARDS AN, MCBRIDE SM. The Clostridium difficile cpr locus is regulated by a noncontiguous two-component system in response to type A and B lantibiotics.J Bacteriol.2013;195(11):2621-2631. [56] ISHAQ N, BILAL M, IQBAL HMN. Medicinal Potentialities of Plant Defensins: A Review with Applied Perspectives.Medicines(Basel). 2019;6(1).pii: E29.doi:10.3390/medicines6010029. [57] GOUR S, KUMAR V, SINGH A, et al. Mammalian antimicrobial peptide protegrin-4 self assembles and forms amyloid-like aggregates: Assessment of its functional relevance.J Pept Sci. 2019;25(3):e3151. [58] MORAVEJ H, MORAVEJ Z, YAZDANPARAST M, et al. Antimicrobial Peptides: Features, Action, and Their Resistance Mechanisms in Bacteria. Microb Drug Resist.2018;24(6):747-767. [59] ZHAO L, LU W. Defensins in innate immunity.Curr Opin Hematol. 2014;21(1):37-42. [60] HOLLY MK, DIAZ K, SMITH JG. Defensins in Viral Infection and Pathogenesis.Annu Rev Virol. 2017;4(1):369-391. [61] AL-RAYAHI IA, SANYI RH.The overlapping roles of antimicrobial peptides and complement in recruitment and activation of tumor-associated inflammatory cells.Front Immunol.2015;6:2. [62] STEPHAN A, BATINICA M, STEIGER J, et al.LL37:DNA complexes provide antimicrobial activity against intracellular bacteria in human macrophages.Immunology.2016;148(4):420-432. [63] AGEITOS JM, SANCHEZ-PEREZ A, CALO-MATA P, et al. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs): Ancient compounds that represent novel weapons in the fight against bacteria.Biochem Pharmacol. 2017;133:117-138. [64] MOJSOSKA B, JENSSEN H. Peptides and Peptidomimetics for Antimicrobial Drug Design. Pharmaceuticals(Basel). 2015;8(3): 366-415. [65] AMANI J, BARJINI KA, MOGHADDAM MM, et al. In vitro synergistic effect of the CM11 antimicrobial peptide in combination with common antibiotics against clinical isolates of six species of multidrug-resistant pathogenic bacteria. Protein Pept Lett.2015;22(10):940-951. [66] MOHAMMADI AZAD Z, MORAVEJ H, FASIHI-RAMANDI M, et al. In vitro synergistic effects of a short cationic peptide and clinically used antibiotics against drug-resistant isolates of Brucella melitensis. J Med Microbiol.2017;66(7):919-926. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||