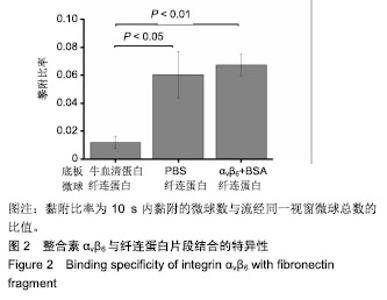
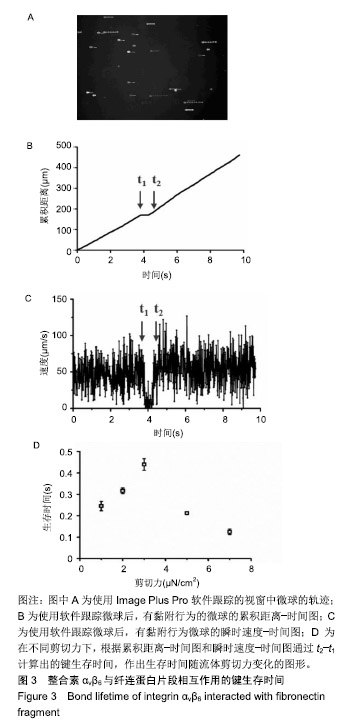
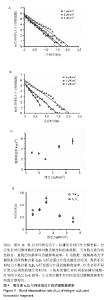
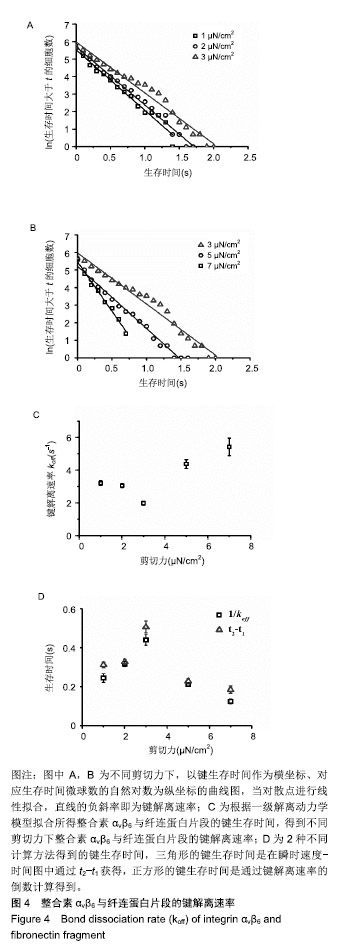
| [1]Hynes RO.Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion.Cell.1992;69(1):11-25.[2]Hynes RO.Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines.Cell.2002;110(6):673-687.[3]Busk M,Pytela R,Sheppard D,et al.Characterization of the integrin alpha v beta 6 as a fibronectin-binding protein.J Biol Chem.1992;267(9):5790-5796.[4]Breuss JM,Gallo J,Delisser HM,et al.Expression of the beta 6 integrin subunit in development, neoplasia and tissue repair suggests a role in epithelial remodeling.J Cell Sci.1995; 108(Pt 6):2241-2251.[5]Luo BH,Carman CV,Springer TA,et al.Structural basis of integrin regulation and signaling.Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25: 619-647.[6]Weis SM,Cheresh DA.alphaV integrins in angiogenesis and cancer.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.2011;1(1):a6478.[7]Ahn SB,Mohamedali A,Anand S,et al.Characterization of the interaction between heterodimeric alphavbeta6 integrin and urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) using functional proteomics.J Proteome Res.2014;13(12): 5956-5964.[8]Bandyopadhyay A,Raghavan S.Defining the role of integrin alphavbeta6 in cancer.Curr Drug Targets.2009;10(7):645-652.[9]Niu J, Li Z,et al.The roles of integrin alphavbeta6 in cancer. Cancer Lett.2017;403:128-137.[10]Desai K,Nair MG,Prabhu JS,et al.High expression of integrin β6 in association with the Rho-Rac pathway identifies a poor prognostic subgroup within HER2 amplified breast cancers. Cancer Med.2016;5(8):2000-2011.[11]Berghoff AS,Kovanda AK,Melchardt T,et al.αvβ3, αvβ5 and αvβ6 integrins in brain metastases of lung cancer.Clin Exp Metastasis.2014;31(7):841-851.[12]Li Z,Biswas S,Liang B,et al.Integrin beta6 serves as an immunohistochemical marker for lymph node metastasis and promotes cell invasiveness in cholangiocarcinoma.Sci Rep.2016;6:30081.[13]Niu Z,Wang J,Muhammad S,et al.Protein expression of eIF4E and integrin alphavbeta6 in colon cancer can predict clinical significance, reveal their correlation and imply possible mechanism of interaction.Cell Biosci.2014;4:23.[14]Weis SM,Cheresh DA.Tumor angiogenesis: molecular pathways and therapeutic targets.Nat Med. 2011;17(11): 1359-1370.[15]Maraveyas A,Johnson MJ,Xiao YP,et al.Malignant melanoma as a target malignancy for the study of the anti-metastatic properties of the heparins.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010; 29(4):777-784.[16]Honn KV,Tang DG,Crissman JD,et al.Platelets and cancer metastasis: a causal relationship?Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1992;11(3-4):325-351.[17]Prieto AL,Edelman GM,Crossin KL,et al.Multiple integrins mediate cell attachment to cytotactin/tenascin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.1993;90(21):10154-10158.[18]Munger JS,Huang X,Kawakatsu H,et al.The integrin alpha v beta 6 binds and activates latent TGF beta 1: a mechanism for regulating pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. Cell. 1999; 96(3):319-328.[19]Jovanovic J,Takagi J,Choulier L,et al.alphaVbeta6 is a novel receptor for human fibrillin-1. Comparative studies of molecular determinants underlying integrin-rgd affinity and specificity.J Biol Chem.2007;282(9):6743-6751.[20]Eberlein C,Kendrew J,Mcdaid K,et al.A human monoclonal antibody 264RAD targeting alphavbeta6 integrin reduces tumour growth and metastasis, and modulates key biomarkers in vivo.Oncogene.2013;32(37):4406-4416.[21]Li W, Liu Z, Zhao C,et al.Binding of MMP-9-degraded fibronectin to beta6 integrin promotes invasion via the FAK-Src-related Erk1/2 and PI3K/Akt/Smad-1/5/8 pathways in breast cancer.Oncol Rep(Oncology reports). 2015;34(3): 1345-1352[22]Thomas GJ,Lewis MP,Whawell SA,et al.Expression of the alphavbeta6 integrin promotes migration and invasion in squamous carcinoma cells.J Invest Dermatol. 2001;1(117): 67-73.[23]Gopal S,Veracini L,Grall D,et al.Fibronectin-guided migration of carcinoma collectives.Nat Commun.2017;8:14105.[24]Wang Y,Ni H.Fibronectin maintains the balance between hemostasis and thrombosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(17): 3265-3277.[25]Desgrosellier JS,Cheresh DA.Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10(1):9-22.[26]Chen W,Lou J,Zhu C,et al.Forcing switch from short- to intermediate- and long-lived states of the alphaA domain generates LFA-1/ICAM-1 catch bonds.J Biol Chem. 2010; 285(46):35967-35978.[27]Kong F,Garcia A J,Mould AP,et al.Demonstration of catch bonds between an integrin and its ligand.J Cell Biol. 2009; 185(7):1275-1284.[28]Fiore VF,Ju L,Chen Y,et al.Dynamic catch of a Thy-1-alpha5beta1+syndecan-4 trimolecular complex.Nat Commun.2014;5:4886.[29]Rosetti F,Chen Y,Sen M,et al.A Lupus-Associated Mac-1 Variant Has Defects in Integrin Allostery and Interaction with Ligands under Force.Cell Rep.2015;10(10):1655-1664.[30]Lou J,Yago T, Klopocki AG,et al.Flow-enhanced adhesion regulated by a selectin interdomain hinge.J Cell Biol. 2006; 174(7):1107-1117.[31]Lou J,Zhu C.A structure-based sliding-rebinding mechanism for catch bonds.Biophys J(Biophysical journal). 2007;92(5): 1471-1485.[32]Guo B,Guilford WH.Mechanics of actomyosin bonds in different nucleotide states are tuned to muscle contraction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(26):9844-9849[33]Yakovenko O,Sharma S,Forero M,et al.FimH forms catch bonds that are enhanced by mechanical force due to allosteric regulation.J Biol Chem.2008;283(17):11596-11605.[34]Yago T,Lou J,Wu T,et al.Platelet glycoprotein Ibalpha forms catch bonds with human WT vWF but not with type 2B von Willebrand disease vWF.J Clin Invest.2008;118(9):3195-3207.[35]Li Z,Lee H,Zhu C,et al.Molecular mechanisms of mechanotransduction in integrin-mediated cell-matrix adhesion.Exp Cell Res.2016;349(1):85-94.[36]Springer TA.Structural basis for selectin mechanochemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(1):91-96.[37]Waldron TT,Springer TA.Transmission of allostery through the lectin domain in selectin-mediated cell adhesion.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2009;106(1):85-90.[38]Al-Hazmi N,Thomas GJ,Speight PM,et al.The 120 kDa cell-binding fragment of fibronectin up-regulates migration of alphavbeta6-expressing cells by increasing matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 secretion.Eur J Oral Sci. 2007; 115(6):454-458. |