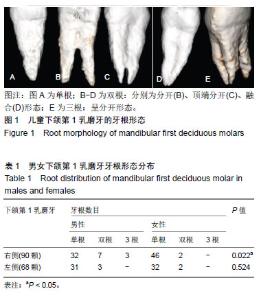
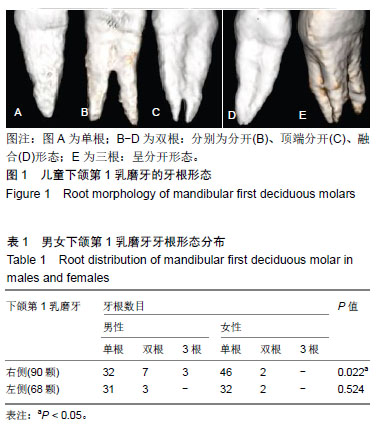
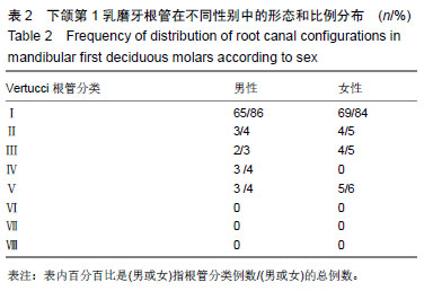
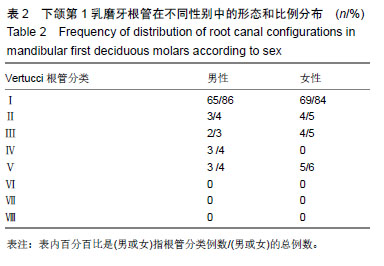
| [1]陆洋, 董青.下颌第1乳磨牙近中根管分析[J]. 牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2016,26(11):682-684.[2]Ozcan G,Sekerci AE,Kocoglu F.C-shaped mandibular primary first molar diagnosed with cone beam computed tomography: A novel case report and literature review of primary molars' root canal systems. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2016;34(4):397-404.[3]Yue W,Kim E.Nonsurgical Endodontic Management of a Molar-Incisor Malformation-affected Mandibular First Molar: A Case Report. J Endod. 2016;42(4):664-668.[4]D'Souza KM,Aras MA.Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the stress distribution pattern in a mandibular first molar tooth restored with five different restorative materials. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2017;17(1):53-60.[5]Albatayneh OB,Shaweesh AI,Alsoreeky ES.Timing and sequence of emergence of deciduous teeth in Jordanian children. Arch Oral Biol. 2015;60(1):126-133.[6]Asgary S,Nikneshan S,Akbarzadehbagheban A,et al.Evaluation of diagnostic accuracy and dimensional measurements by using CBCT in mandibular first molars. J Clin Exp Dent. 2016;8(1):e1-8 [7]Mokhtari H,Niknami M,Zonouzi HR,et al.Accuracy of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography in Determining the Root Canal Morphology of Mandibular First Molars. Iran Endod J. 2016 ;11(2): 101-105. [8]Kamburo?lu K,Sönmez G,Berkta? ZS,et al.Effects of various cone-beam computed tomography settings on the detection of recurrent caries under restorations in extracted primary teeth. Imaging Sci Dent. 2017;47(2):109-115. [9]Kashyap RR,Beedubail SP,Kini R,et al.Assessment of the number of root canals in the maxillary and mandibular molars: A radiographic study using cone beam computed tomography.J Conserv Dent. 2017;20(5):288-291.[10]Mahesh BS, P Shastry S, S Murthy P, et al.Role of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Evaluation of Radicular Cyst mimicking Dentigerous Cyst in a 7-year-old Child: A Case Report and Literature Review. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2017;10(2):213-216.[11]Dhingra A,Manchanda N.Modifications in Canal Anatomy of Curved Canals of Mandibular First Molars by two Glide Path Instruments using CBCT. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8(11):ZC13-7. [12]张贤华.CBCT在重度牙周病诊断和辅助制定治疗计划的应用[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2014 ,12(1):4325-4327.[13]朱敏,林梓桐,文珊辉,等.CBCT根管形态三维容积重建可视化技术的研究[J].口腔医学研究,2015,35(6):601-603.[14]Madani ZS, Mehraban N,Moudi E,et al.Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular Molars in a Selected Iranian Population Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. Iran Endod J. 2017; 12(2):143-148.[15]王琨,刘波,冯汝舟,等.乳磨牙根管系统的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2018,24(1):112-116.[16]张丹,陈俊宏,兰贵华,等.中国人下颌第一前磨牙牙根及根管形态的研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2016,38(10):1188-1194.[17]Ni N,Cao S,Han L,et al.Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of root canal morphology in mandibular first molars in a Chinese population: a clinical study. Evidence-Based Endodontics. 2018,3(1):1-4[18]刘钦捷,罗明,梁衍平,等.下颌第一前磨牙3牙根3根管临床报告及文献回顾[J].口腔疾病防治,2017, 25(10):656-660.[19]Self CJ.Tooth Roots and the Periodontal Ligament: Morphology, Modeling and Behavior.2015; 243(24):56-58.[20]Baziar H,Daneshvar F,Mohammadi A,et al.Endodontic management of a mandibular first molar with four canals in a distal root by using cone-beam computed tomography: a case report. J Oral Maxillofac Res. 2014;5(1):e5.[21]Harlamb S.Management of incompletely developed teeth requiring root canal treatment. Aust Dent J. 2016;61 Suppl 1:95-106.[22]Madero-Ayora MJ,Reina-Tosina J,Crespo-Cadenas C.Characterization of mandibular molar root and canal morphology using cone beam computed tomography and its variability in Belgian and Chilean population samples. Imaging Sci Dent. 2015;45(2):95-101.[23]Nur BG,Ok E,Altunsoy M,et al.Evaluation of the root and canal morphology of mandibular permanent molars in a south-eastern Turkish population using cone-beam computed tomography.Eur J Dent. 2014;8(2):154-159. |