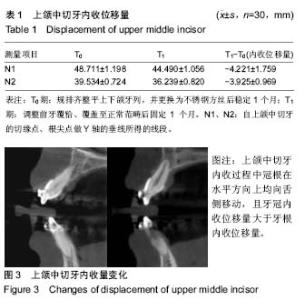
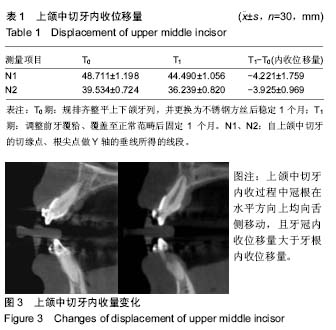
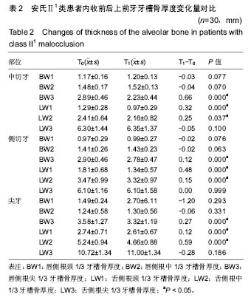
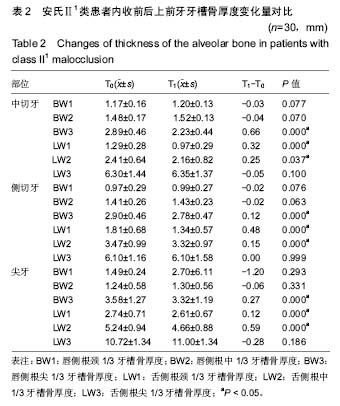
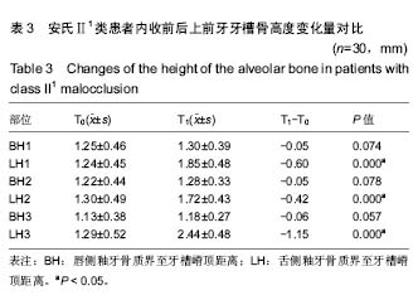
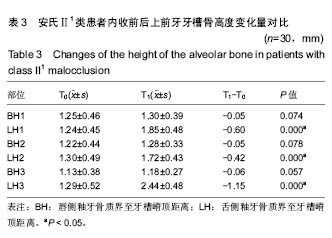
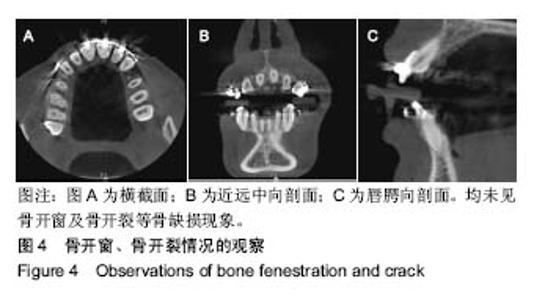
| [1] 傅民魁,张丁,王邦康,等.中国25392名儿童与青少年错合畸形患病率的研究[J].华口腔医学杂志, 2002,37(5):371-373.[2] 林久祥,许.赵.口腔正畸学[M].北京: 人民卫生出版社,2011:177-178.[3] Huang M, Hu Y, Yu J, et al.Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation of the temporomandibular joint and dental characteristics of patients with Class II subdivision malocclusion and asymmetry. Korean J Orthod.2017;47(5):277-288.[4] Janson G, Branco NC, Morais JF, et al.Smile attractiveness in patients with Class II division 1 subdivision malocclusions treated with different tooth extraction protocols.Eur J Orthod.2014;36(1):1-8.[5] Schwab DT.The borderline patient and tooth removal. Am J Orthod. 1971;59(2):126-145..[6] Williams R, Hosila FJ. The effect of different extraction sites upon incisor retraction. Am J Orthod. 1976;69(4):388-410.[7] de Castro N. Second-premolar extraction in clinical practice. Am J Orthod. 1974;65(2):115-137.[8] Drobocky OB, Smith RJ. Changes in facial profile during orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1989;95(3):220-230.[9] Makedonas D, Lund H, Hansen K. Root resorption diagnosed with cone beam computed tomography after 6 months and at the end of orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances. Angle Orthod. 2013;83(3): 389-393.[10] Hua Y, Nackaerts O, Duyck J,et al.Bone quality assessment based on cone beam computed tomography imaging. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20(8): 767-771.[11] 刘映鸿,周泽渊,赵奎,等.青少年患者前牙内收过程中牙槽骨改建情况的锥形束CT研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2016,1(34): 78-84.[12] Nauert K, Berg R.Evaluation of labio-lingual bony support of lower incisors in orthodontically untreated adults with the help of computed tomography. J Orofac Orthop. 1999;60(5):321-334.[13] Vardimon AD, Graber TM, Voss LR,et al.Determinants controlling iatrogenic external root resorption and repair during and after palatal expansion. Angle Orthod.1991;61(2): 113-122; discussion 123-124.[14] Ahn HW, Moon SC, Baek SH. Morphometric evaluation of changes in the alveolar bone and roots of the maxillary anterior teeth before and after en masse retraction using cone-beam computed tomography. Angle Orthod. 2013;83(2):212-221.[15] 陈香,张向凤,黄倩倩,等.微种植体支抗辅助内收上切牙后牙槽骨改建的锥形束CT研究[J].上海口腔医学,2018,27(2): 150-155.[16] 许天民, 刘妍, 江久汇,等.正畸内收上切牙对上颌牙槽骨改建的临床研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2004,20(4):431-433.[17] Sarikaya S, Haydar B, Ci?er S,et al.Changes in alveolar bone thickness due to retraction of anterior teeth. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002;122(1):15-26. [18] Guo QY, Zhang SJ, Liu H, et al.Three-dimensional evaluation of upper anterior alveolar bone dehiscence after incisor retraction and intrusion in adult patients with bimaxillary protrusion malocclusion. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2011;12(12):990-997.[19] Marks SC Jr, Cahill DR, Wise GE. The cytology of the dental follicle and adjacent alveolar bone during tooth eruption in the dog. Am J Anat. 1983;168(3):277-289.[20] 林薇薇,陈金武, 成人前牙内收前后切牙牙槽骨高度变化的研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2014. 30(6): 823-826.[21] Cobo J,Argüelles J,Puente M,et al.Dentoalveolar stress from bodily tooth movement at different levels of bone loss. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.1996;110(3):256-262. [22] Tanne K,Nagataki T,Inoue Y,et al.Patterns of initial tooth displacements associated with various root lengths and alveolar bone heights.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.1991;100(1):66-71.[23] 姜若萍,傅民魁.正常汉族成年人前牙区牙槽宽度及根尖位置的研究[J].口腔正畸学,2008,15(1):16-19.[24] 杨雪,钱玉芬.上前牙内收过程中转矩控制的影像学研究[J].上海口腔医学, 2016,25(4): 469-474. |