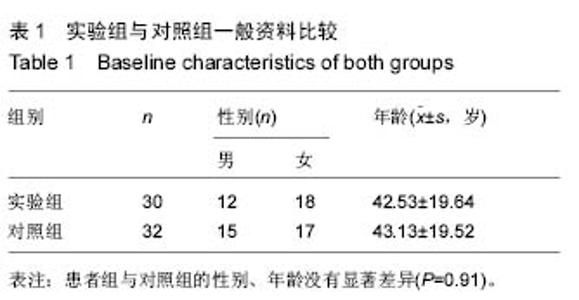
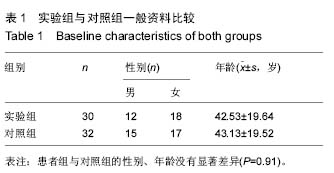
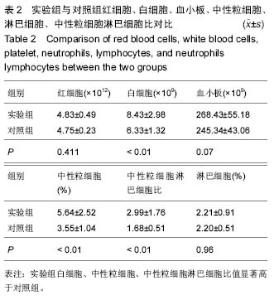
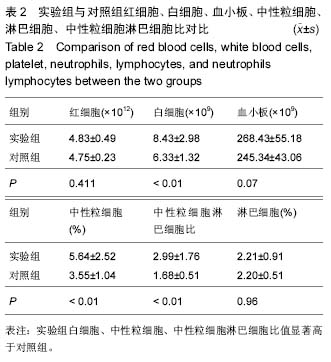
| [1] Yilmaz M,Tarakcioglu M,Bayazit N,et al.Serum cytokine levels in Bell’s palsy.J Neurol Sci.2002; 197: 69-72.
[2] Kefalidis G,Riga M,Argyropoulou P,et al.Is the width of the labyrinthine portion of the fallopian tube implicated in the pathophysiology of Bell’s palsy?: a prospective clinical study using computed tomography. Laryngoscope. 2010;20:1203-1207.
[3] Vianna M,Adams M,Schachem P.Differences in the diameter of facial nerve and facial canal in bell's palsy-a 3-dimensional temporal bone study.Otol Neurotol.2014;35(3):514-518.
[4] Kruger P, Saffarzadeh M, Weber AN,et al.Neutrophils: Between host defence,immune modulation, and tissue injury.PLoS Pathog.2015; 11(3):e1004651.
[5] Özler GS,Günak G.Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio:a new predictive and prognostic factor in patients with Bell palsy.J Craniofac Surg.2014;25(3):944-945.
[6] Bucak A, Ulu S, Oruc S.Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Novel-Potential Marker for Predicting Prognosis of Bell Palsy. Laryngoscope. 2014; 124(7):1678-1681.
[7] Atan D, ?kincio?ullar? A, Köseo?lu S,et al. New Predictive Parameters of Bell’s Palsy: Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio.Balkan Med J.2015;32(2):167-170.
[8] Danese E, Lippi G, Montagnana M.Red blood cell distribution width and cardiovascular diseases.J Thorac Dis.2015;7(10):E402-E411.
[9] 许开祖,林丽明,林金秀,等.红细胞分布宽度与急性心肌梗死患者并发症的关系[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2010, 7: 569-573.
[10] Dogan S, Celikbilek M, Zararsiz G. Red blood cell distribution width as a non-invasive marker for the assessment of inflammation in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatogastroenterology.2015; 62(138): 393-398.
[11] 贾建平,陈生弟.神经病学[M].7版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2013:339-340.
[12] Richards MK,Liu F,Iwasaki H. Pivotal role of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in the development of progenitors in the common myeloid pathway. Blood. 2003;102(10):3562-3568.
[13] Cain W,Snowden PB,Sempowski GD.Inflammation triggers emergency granulopoiesis through a density- dependent feedback mechanism.PLoS One.2011; 6(5):e19957.
[14] Demircan F,Gözel N,K?l?nç F.The Impact of Red Blood Cell Distribution Width and Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio on the Diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorder. Neurol Ther.2015 Dec 19.
[15] Tagawa T, Anraku M, Morodomi Y, et al.Clinical role of a new prognostic score using platelet-tolymphocyte ratio in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma undergoing extrapleural pneumonectomy. J Thorac Dis.2015;7(11):1898-1906.
[16] Eryilmaz A, Basal Y, Tosun A.The neutrophil to lymphocyte ratios of our pediatric patients with Bell's palsy.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015; 79(12): 2374-2377.
[17] Moxon-Emre I, Schlichter LC.Evolution of inflammation and white matter injury in a model of transient focal ischemia.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.2010;69(1):1-15.
[18] Bhat T, Teli S, Rijal J, et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and cardiovascular diseases: a review.Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther.2013;11:55-59.
[19] Proctor MJ, McMillan DC, Morrison DS, et al. A derived neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio predicts survival in patients with cancer.Br J Cancer.2012;107:695-699.
[20] Wang D,Yang JX,Cao DY,et al.Preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte and platelet-lymphocyte ratios as independent predictors of cervical stromal involvement in surgically treated endometrioid adenocarcinoma.Onco Targets Ther.2013;6:211-216.
[21] Emans ME, van der Putten K,van Rooijen KL,et al. Determinants of red cell distribution width (RDW) in cardiorenal patients: RDW is not related to erythropoietin resistance.J Card Fail.2011;17: 626-633.
[22] Allen LA, Felker GM, Mehra MR, et al. Validation and potential mechanisms of red cell distribution width as a prognostic marker in heart failure.J Card Fail.2010; 16: 230-238.
[23] Inuzuka R, Abe J. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width as a Link Between Ineffective Erythropoiesis and Chronic Inflammation in Heart Failure.Circ J. 2015;79(5): 974-975.
[24] Al-Najjar Y,Goode KM Zhang J,et al.Red cell distribution width: an inexpensive and Powerful prognostic marker in heart failure.Eur J Heart Fail.2009; 11(12):1155-1162.
[25] Pascual-Figal DA, Bonaque JC, Redondo B,et al. Red cell distribution width predicts long-term outcome regardless of anaemia status in acute heart failure patients.Eur J Heart Fail.2009;11(9):840-846
[26] Fukuta H, Ohte N, Mukai S.Elevated plasma levels of B-type natriuretic Peptide but not C-reactive protein are associated with higher red cell distribution width in patients with coronary artery disease.Int Heart J.2009; 50(3):301-312.
[27] Montagnana M,Cervellin G,Meschi T,et al.The role of red blood cell distribution width in cardiovascular and thrombotic disorders.Clin Chem Lab Med.2011; 50(4): 635-641.
[28] Oleksiak A, Kruk M, Lenarczyk E.Biomarkers for risk stratification in secondary cardiovascular prevention. A role of red blood cell distribution width and calcium score.Atherosclerosis.2016;246:57-62.
[29] Lippi G,Buonocore R,Cervellin G.Value of Red Blood Cell Distribution Width on Emergency Department Admission in Patients With Venous Thrombosis.Am J Cardiol.2016;117(4):670-675.
[30] Förhécz Z, Gombos T, Borgulya G, et al. Red cell distribution width in heart failure: prediction of clinical events and relationship with markers of ineffective erythropoiesis, inflammation, renal function, and nutritional state. Am Heart J. 2009;158(4):659-666.
[31] Arora NP, Ghali JK. Anemia and iron deficiency in heart failure. Heart Fail Clin,2014,10:281-294.
[32] Weiss G, Goodnough LT. Anemia of chronic disease. N Engl J Med.2005;352:1011-1023. |