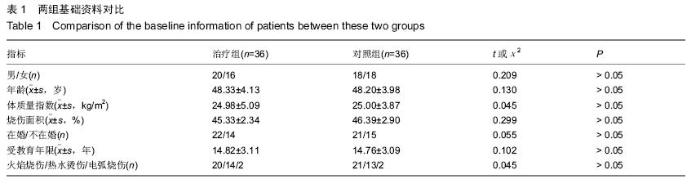
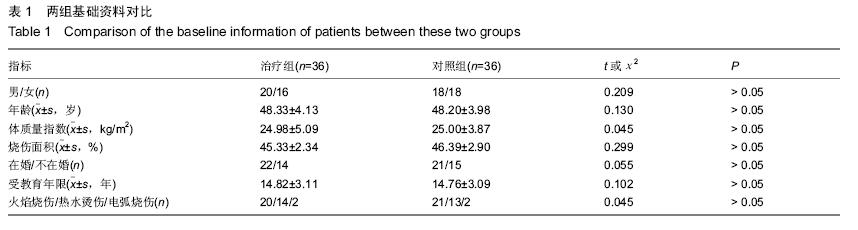
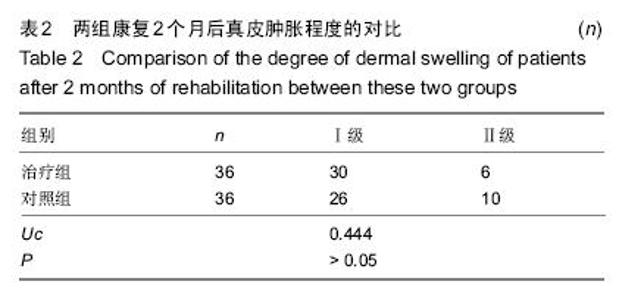
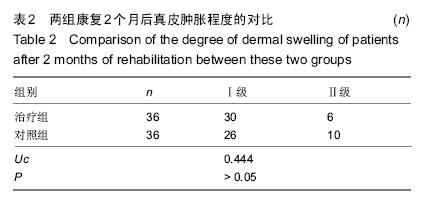
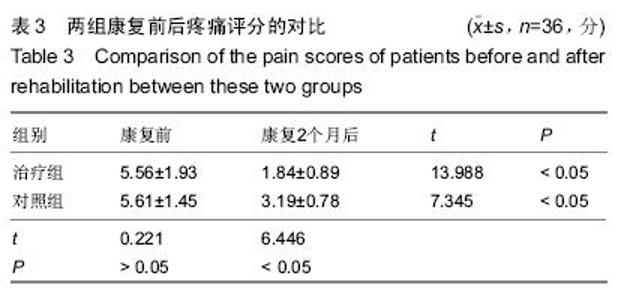
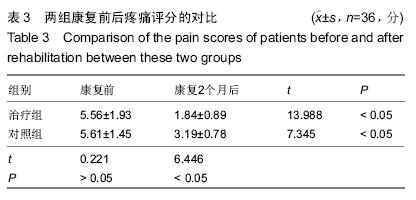
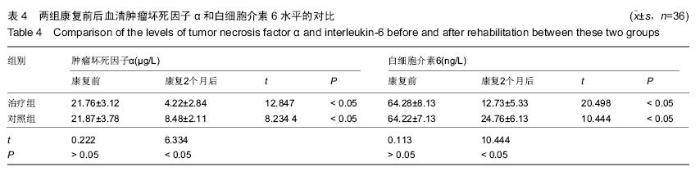
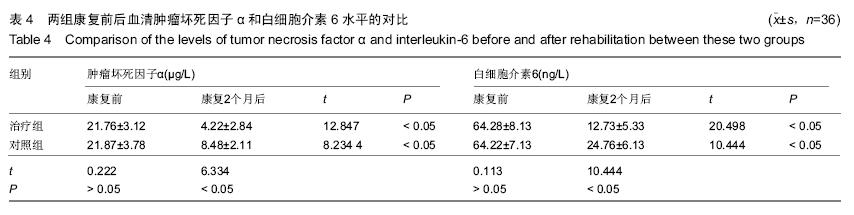
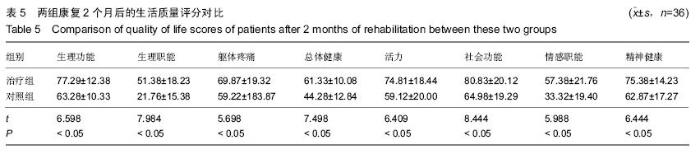
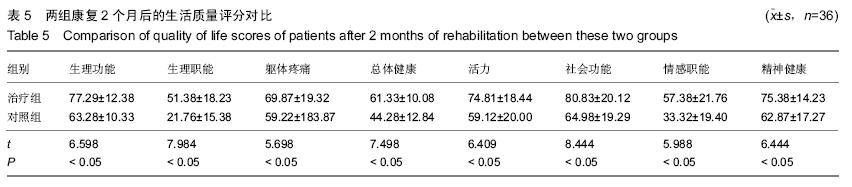
| [1] 田维庆,王凌峰.异种脱细胞真皮基质治疗大面积深度烧伤的研究进展[J].北方药学,2015,1(9):97-98. [2] 宁勇,刘明锁,刘文文,等.分批次微粒皮移植治疗大面积深度烧伤患者临床效果观察[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2014, 24(2): 4509-4511. [3] Li X,Meng X,Wang X,et al. Human acellular dermal matrix allograft: A randomized, controlled human trial for the long-term evaluation of patients with extensive burns. Burns. 2015;41(4):689-699. [4] 王配合,杨建民,李建全,等.脱细胞异体真皮和自体刃厚皮复合移植在功能部位深度烧伤早期治疗中的临床应用[J].疑难病杂志, 2014,3(9):297-299. [5] Bonitz RP,Hanna MK.Use of human acellular dermal matrix during classic bladder exstrophy repair.J Pediatr Urol.2015.pii: S1477-5131(15)00395-2.doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2015.10.005. [Epub ahead of print] [6] Yang L,Yang F,Li W,et al.[Experience of applying acellular dermal matrix in the head and neck tumor surgery].Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015;50(7):579-582. [7] Vedak P,St John J,Watson A,et al.Delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction to porcine acellular dermal matrix masquerading as infection resulting in multiple debridements.Hernia.2015.[Epub ahead of print] [8] Gowda AU,Chang SM,Chopra K,et al.Porcine acellular dermal matrix (PADM) vascularises after exposure in open necrotic wounds seen after complex hernia repair.Int Wound J.2015.doi: 10.1111/iwj.12558.[Epub ahead of print] [9] Apte A,Walsh M,Chandrasekharan S,et al.Single-stage immediate breast reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix: Experience gained and lessons learnt from patient reported outcome measures.Eur J Surg Oncol.2016;42(1):39-44. [10] Thakare P,Baliga V,Bhongade ML.Comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of acellular dermal matrix allograft and subepithelial connective tissue to coronally advanced flap alone in the treatment of multiple gingival recessions: A clinical study.J Indian Soc Periodontol.2015;19(5):537-544. [11] Shirakata Y,Sculean A,Shinohara Y,et al.Healing of localized gingival recessions treated with a coronally advanced flap alone or combined with an enamel matrix derivative and a porcine acellular dermal matrix: a preclinical study.Clin Oral Investig. 2015. [Epub ahead of print] [12] Ma T,Zhang H,Liu F,et al.Communication: First results of cases series of one-stage repair of gastroschisis using human acellular dermal matrix in 7 neonates.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg.2015.pii: S1748-6815(15)00519-7.doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2015.10.035. [Epub ahead of print] No abstract available. [13] Wang HL,Suárez-López Del Amo F,Layher M,et al.Comparison of Freeze-Dried and Solvent-Dehydrated Acellular Dermal Matrix for Root Coverage: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent.2015;35(6):811-817. [14] Blythe JN,Koraitim M,Arcuri F,et al.Novel approach in the treatment of a persistent iatrogenic parotid fistula using AlloDerm® - an allogenic acellular dermal matrix.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2016;54(1):109-110. [15] Wagner DS.Discussion: Use of Acellular Dermal Matrix in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction: Are All Acellular Dermal Matrices Created Equal?Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015; 136(4):654-656. [16] Ranganathan K,Santosa KB,Lyons DA,et al.Use of Acellular Dermal Matrix in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction: Are All Acellular Dermal Matrices Created Equal?Plast Reconstr Surg.2015;136(4):647-653. [17] 宁勇,刘明锁,刘文文,等.自体微粒皮移植配合全厚型脱细胞异种真皮基质覆盖治疗大面积烧伤效果观察[J].延边医学, 2014, 32 (12):34-35 [18] Roussalis JL.Novel use of an acellular dermal matrix allograft to treat a chronic scalp wound with bone exposure: a case study.Int J Burns Trauma.2014;4(2):49-52. [19] 陈彬,首家保,杨小辉,等.人工真皮复合自体刃厚皮片移植治疗烧伤后关节瘢痕挛缩[J].中国美容整形外科杂志, 2014, 25(6): 353-355. [20] 宁勇,刘明锁,刘文文,等.异种脱细胞真皮基质覆盖自体微粒皮治疗大面积深度烧伤疗效观察[J].山东医药,2014,44(11):91-92. [21] Guo R,Teng J,Xu S,et al.Comparison studies of the in vivo treatment of full-thickness excisional wounds and burns by an artificial bilayer dermal equivalent and J-1 acellular dermal matrix.Wound Repair Regen.2014;22(3):390-398. [22] 王杨,孙树,王锦文,等.自体头皮与脱细胞异体真皮复合移植修复巨大色素痣[J].中华皮肤科杂志,2014,47(10):711-714. [23] 翁旭豪,徐优芬,马小亚,等.腹部真皮下血管网皮瓣修复深度手热压伤[J].临床军医杂志,2014,42(3):323. [24] Han Y,Tao R,Han Y,et al.Microencapsulated VEGF gene-modified umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells promote the vascularization of tissue-engineered dermis: an experimental study.Cytotherapy.2014;16(2):160-169. [25] 李峰永,李森恺,周传德,等.自体口腔黏膜微粒联合脱细胞异体真皮基质再造阴道[J].中华整形外科杂志,2015,31(1):29-33. [26] 韩立显,马新亮,朱守莉,等.胸锁乳突肌瓣联合异体脱细胞真皮基质预防腮腺部分切除术后 Frey 综合征的临床观察[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2015,3(13):345-347. [27] Deshpande P,Ralston DR,MacNeil S.The use of allodermis prepared from Euro skin bank to prepare autologous tissue engineered skin for clinical use.Burns.2013;39(6):1170-1177. [28] 刘倩,张晨,刘林嶓.巨痣脱细胞真皮基质残留黑色素颗粒脱除的研究[J].中华整形外科杂志,2014,30(2):122-125. [29] 赵筱卓,宁方刚,杜伟力,等.导入透明质酸的脱细胞羊皮联合自体微粒皮复合移植治疗大面积烧伤[J].中华外科杂志, 2014, 52(4): 285-288. [30] 李华强,张中原,张青.脱细胞异体真皮支架网加刃厚皮一步法移植的临床疗效[J].中华实验外科杂志,2014,31(9):2068. |