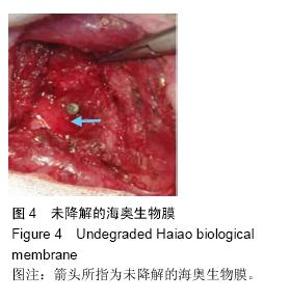
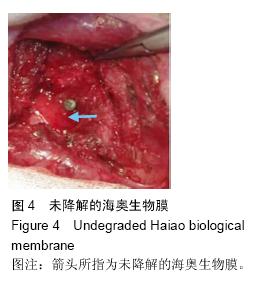
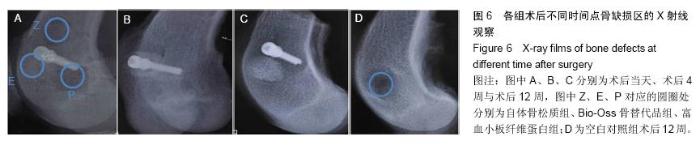
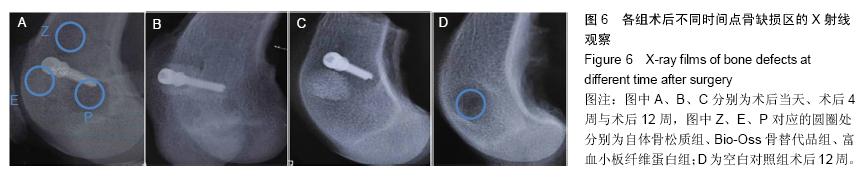
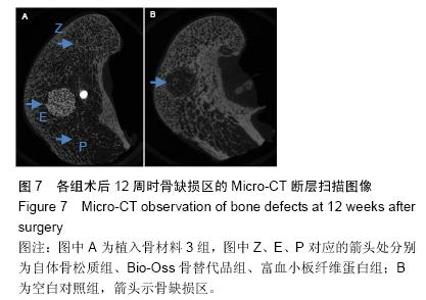
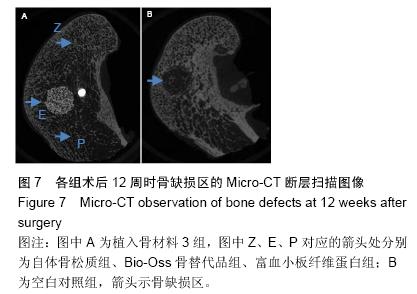
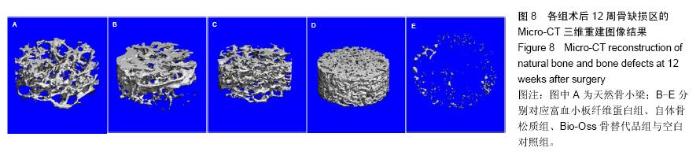
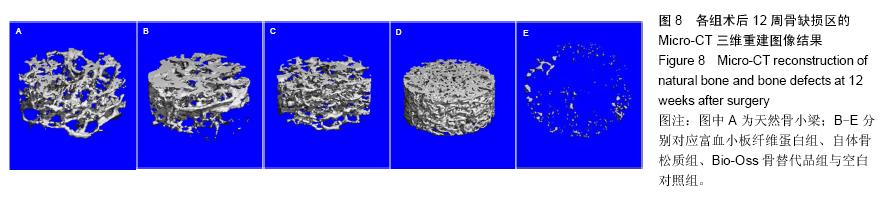
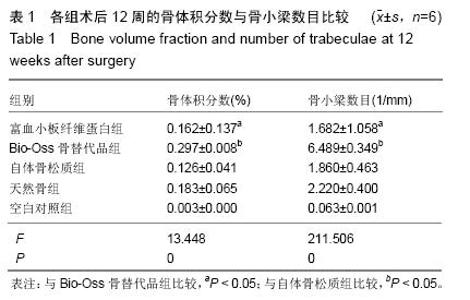
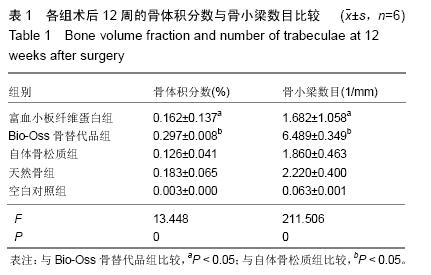
| [1] Lindhe J,Cecchinato D,Donati M,et al.Ridge preservation with the use of deproteinized bovine bone mineral.Clin Oral Implants Res.2014;25(7):786-790.
[2] Dohan DM,Choukroun J,Diss A,et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part I: technological concepts and evolution.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2006;101(3):e37-44.
[3] Naik B,Karunakar P,Jayadev M,et al.Role of Platelet rich fibrin in wound healing: A critical review.J Conserv Dent. 2013; 16 (4):284-293.
[4] 刘东光,韦正超,蔡道章,等.多孔羟基磷灰石与富血小板血浆和纤维蛋白胶复合修复骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17 (25): 4561-4569.
[5] Tatullo M,Marrelli M,Cassetta M,et al.Platelet Rich Fibrin (P.R.F.) in reconstructive surgery of atrophied maxillary bones: clinical and histological evaluations.Int J Med Sci. 2012; 9 (10):872-880.
[6] Pearce AI,Richards RG,Milz S,et al.Animal models for implant biomaterial research in bone: a review.Eur Cell Mater. 2007; 13:1-10.
[7] Choi S,Liu IL,Yamamoto K,et al.Implantation of tetrapod-shaped granular artificial bones or beta-tricalcium phosphate granules in a canine large bone-defect model.J Vet Med Sci.2014;76(2):229-235.
[8] 宿玉成.现代口腔种植学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2004: 207 -216.
[9] Wilson TG Jr,Schenk R,Buser D,et al.Implants placed in immediate extraction sites: a report of histologic and histometric analyses of human biopsies.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.1998;13(3):333-341.
[10] Horner EA,Kirkham J,Wood D,et al.Long bone defect models for tissue engineering applications: criteria for choice.Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2010;16(2):263-271.
[11] Rudert M.Histological evaluation of osteochondral defects: consideration of animal models with emphasis on the rabbit, experimental setup, follow-up and applied methods.Cells Tissues Organs.2002;171(4):229-240.
[12] Lee HJ,Choi BH,Jung JH,et al.Maxillary sinus floor augmentation using autogenous bone grafts and platelet-enriched fibrin glue with simultaneous implant placement. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2007;103(3):329-333.
[13] Jung RE,Philipp A,Annen BM,et al.Radiographic evaluation of different techniques for ridge preservation after tooth extraction: a randomized controlled clinical trial.J Clin Periodontol.2013;40(1):90-98.
[14] Kobayashi M,Kawase T,Horimizu M,et al.A proposed protocol for the standardized preparation of PRF membranes for clinical use.Biologicals.2012;40(5):323-329.
[15] Dohan Ehrenfest DM.How to optimize the preparation of leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF, Choukroun's technique) clots and membranes: introducing the PRF Box.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;110(3):275-278.
[16] Li Q,Reed DA,Min L,et al.Lyophilized platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) promotes craniofacial bone regeneration through Runx2.Int J Mol Sci.2014;15(5):8509-8525.
[17] Dohan DM,Choukroun J,Diss A,et al.Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part II: platelet-related biologic features.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2006;101(3):e45-50.
[18] Li Q,Pan S,Dangaria SJ,et al.Platelet-rich fibrin promotes periodontal regeneration and enhances alveolar bone augmentation.Biomed Res Int.2013;2013:638043.
[19] Dohan Ehrenfest DM,Diss A,Odin G,et al.In vitro effects of Choukroun's PRF (platelet-rich fibrin) on human gingival fibroblasts, dermal prekeratinocytes, preadipocytes, and maxillofacial osteoblasts in primary cultures.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2009;108(3):341-352.
[20] Lee JW,Kim SG,Kim JY,et al.Restoration of a peri-implant defect by platelet-rich fibrin.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol.2012;113(4):459-463.
[21] Hauser F,Gaydarov N,Badoud I,et al.Clinical and histological evaluation of postextraction platelet-rich fibrin socket filling: a prospective randomized controlled study.Implant Dent.2013; 22(3):295-303
[22] 万永.富血小板纤维蛋白在牙槽嵴位点保存应用中的临床研究[D].泸州医学院,2014.
[23] Fickl S,Zuhr O,Wachtel H,et al.Hard tissue alterations after socket preservation: an experimental study in the beagle dog.Clin Oral Implants Res.2008;19(11):1111-1118.
[24] Vignoletti F,Discepoli N,Müller A,et al.Bone modelling at fresh extraction sockets: immediate implant placement versus spontaneous healing: an experimental study in the beagle dog.J Clin Periodontol.2012;39(1):91-97.
[25] Border WA,Noble NA.Transforming growth factor beta in tissue fibrosis.N Engl J Med.1994;331(19):1286-1292.
[26] Lucarelli E,Beccheroni A,Donati D,et al.Platelet-derived growth factors enhance proliferation of human stromal stem cells.Biomaterials.2003;24(18):3095-3100.
[27] Winkler R,Pasleau F,Boussif N,et al.The IGF system: summary and recent data[J]. Rev Med Liege. 2000; 55 (7): 725-739.
[28] Dohan DM,Choukroun J,Diss A,et al.Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part III: leucocyte activation: a new feature for platelet concentrates.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2006;101(3):e51-55.
[29] Dohan Ehrenfest DM,Doglioli P,de Peppo GM,et al. Choukroun's platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) stimulates in vitro proliferation and differentiation of human oral bone mesenchymal stem cell in a dose-dependent way.Arch Oral Biol.2010;55(3):185-194.
[30] Freeman TA,Patel P,Parvizi J,et al.Micro-CT analysis with multiple thresholds allows detection of bone formation and resorption during ultrasound-treated fracture healing.J Orthop Res.2009;27(5):673-679.
[31] 王军,毕龙,白建萍,等.显微CT与组织切片技术在骨形态计量研究中的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(5):381-384
[32] Luu AN,Anez-Bustillos L,Aran S,et al. Microstructural, densitometric and metabolic variations in bones from rats with normal or altered skeletal states.PloS One. 2013;8(12): e82709. |