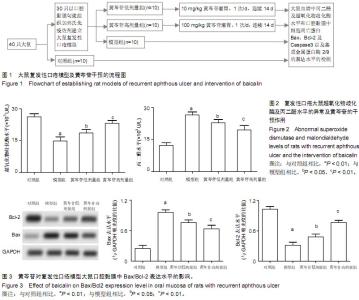
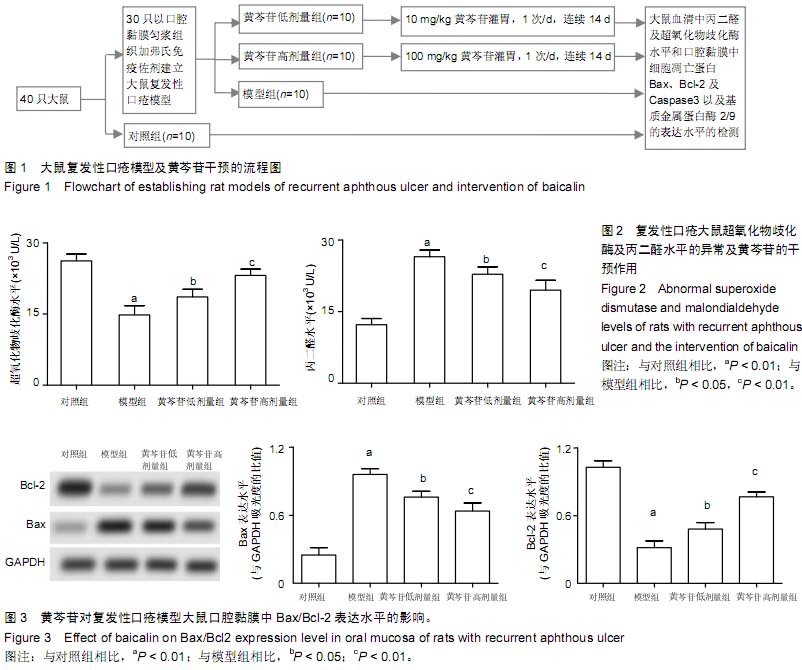
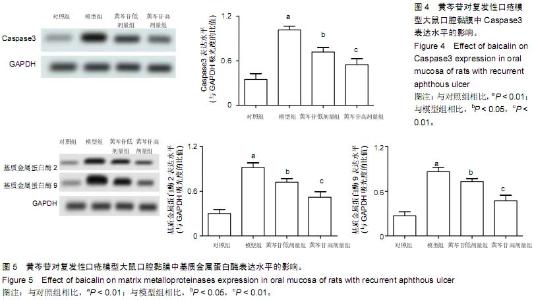
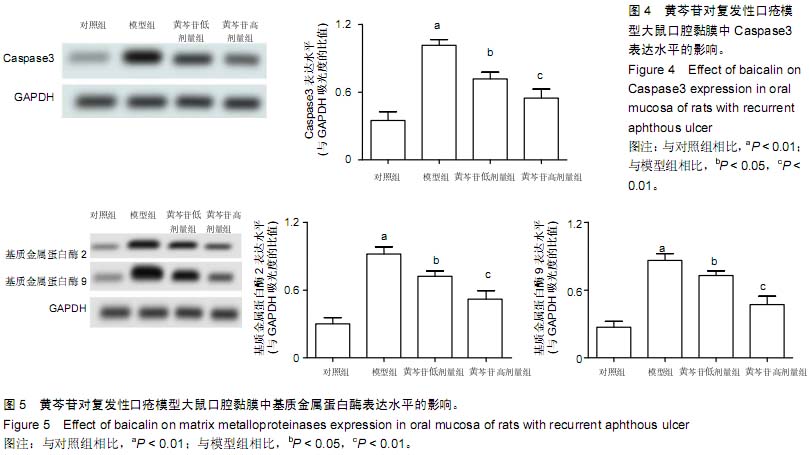
| [1] 刘健,余太平.口炎清冲剂联合氨来呫诺口腔贴片治疗复发性口疮的临床疗效观察[J].现代药物与临床,2013,28(5):763-765.
[2] 林晶.活性芦荟缓释药膜对复发性口疮动物模型的研究[D].延吉:延边大学,2013.
[3] 何建明,钱玉荣,顾惠萍,等.青黛复方糊剂在治疗老年患者复发性口腔溃疡中的作用[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2013,11(3):164-165.
[4] 尹文国.儿童复发性口疮血清微量元素与免疫功能检测结果分析[J].中国医药导报,2012,9(4):85-86.
[5] 顾健峰,孙亚珍,李瑜芳,等.雷公藤多苷对复发性口疮患者血浆脂质过氧化水平及超氧化水平及超氧化物岐化酶活性影响的研究[J].中国医药导报,2012,9(10):95-96.
[6] 韩冰,殷沛.参芪片治疗复发性口疮的临床疗效观察[J].中医学报, 2012,27(6):752-753.
[7] 周芳,李东,王丹杨,等.复发性口腔溃疡大鼠模型免疫功能与血清因子的变化分析[J].陕西医学杂志,2014(8):942-944.
[8] 马晓喆,李言君,付爱丽,等.IFN-γR和sIL-2R在复发性口腔溃疡患者中的表达及意义[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2015,12(7):23-26.
[9] 邹玉红,杨静,陈春华.复发性口腔溃疡患者血清中TNF-α、IL-2,6与免疫功能的相关性研究[J].海南医学院学报,2015,17(1): 39-42.
[10] 王金凤,刘文辉,荆雪宁,等.甘草泻心汤与其配方颗粒对复发性口腔溃疡模型大鼠的药效学比较[J].中国药房,2014,16(31):2884- 2886.
[11] 张剑飞,汤晓飞,葛丽华,等.细胞凋亡信号调节酶1在口腔白斑细胞凋亡中的作用[J].北京口腔医学,2014,22(2):65-69.
[12] 满莹,唐国瑶,王万春,等.口腔扁平苔藓、白斑及鳞癌组织Bak蛋白表达特点及其与细胞凋亡相关性研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2014, 18(3):136-142.
[13] 陈琦,李少伟,贾宇臣,等.蓝莓花青素通过下调p53基因DNA甲基化抑制口腔癌KB细胞增殖及诱导细胞凋亡[J].遗传,2014,14(6): 566-573.
[14] 赵莉琳,刘阳.PCNA对口腔鳞癌细胞凋亡和增殖的影响[J].解放军医学杂志,2014,39(10):795-799.
[15] 邓冠红,陈作良,陈宏柏,等.T细胞免疫和细胞凋亡在口腔扁平苔藓发病中的作用[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2009,27(3):256-259.
[16] 魏美荣.KGF对口腔黏膜上皮细胞凋亡及增殖的影响[D].济南:山东大学,2012.
[17] 雷蕾,詹丽华,谭为霞,等.口腔扁平苔藓局部浸润淋巴细胞颗粒酶B和穿孔素蛋白表达与上皮细胞凋亡的关系[J].第三军医大学学报, 2011,21(18):1943-1946.
[18] 魏美荣,李国菊,张达,等.角质细胞生长因子对口腔黏膜上皮细胞凋亡的作用研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2013,10(6):565-568.
[19] 侯敏,张敏,景新颖,等.口腔癌生长过程中缺氧与细胞凋亡的相关性研究[J].北京口腔医学,2013,21(3):135-138.
[20] 刘友良,唐瞻贵,方晓明,等.基质金属蛋白酶-9及基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂-1在口腔鳞状细胞癌中的表达研究[J].口腔医学,2010, 30(2): 80-82.
[21] 王波,汲坤,张丽艳,等.葡萄糖调节蛋白78和基质金属蛋白酶在口腔鳞状细胞癌中的表达[J].中国医科大学学报,2014,43(9):786-789.
[22] 张洁,唐荣冰,赵倩,等.四种口腔溃疡治疗药物对小鼠成纤维细胞氧化应激反应的影响[J].中药材,2014,37(3):485-487.
[23] 付洁,宿颖,关晓兵,等.三氧化二砷对口腔鳞癌细胞系Nrf2通路的激活作用[J]. 北京口腔医学,2012,20(5):260-265.
[24] 侯燕琴.泼尼松龙联合氯己定对口腔溃疡大鼠黏膜活性氧水平的影响[J].中国现代医生,2012,50(33):7-8.
[25] 李婧,武云霞,管翠强,等.加味导赤散与维生素B12联合灌胃对大鼠复发性口腔溃疡模型外周血T淋巴细胞亚群的影响[J].山西医科大学学报,2014,45(7):573-575.
[26] 侯冬枝,梁晓晖,赵世洪,等.微柱离心结合双波长考马斯亮蓝法/酶标仪法测定牛血清白蛋白脂质体的包封率[J].中国药房,2011, 13(21): 1987-1989.
[27] 董娜,贾艳菊,张晓,等.考马斯亮蓝法测定奶粉真蛋白的研究[J].食品科技,2011,23(11):272-274.
[28] 王孝平,邢树礼.考马斯亮蓝法测定蛋白含量的研究[J].天津化工, 2009,23(3):40-42.
[29] 李婧.加味导赤散与维生素B12联合治疗复发性口腔溃疡的动物实验研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2014.
[30] 李秀荣.复发性口腔溃疡的临床诊治探析[J].吉林医学,2014, 35(1): 59-60.
[31] 管翠强,武云霞,郭洪波.复发性口腔溃疡血清叶酸和维生素B12的临床观察[J].山西医科大学学报,2014,45(5):395-397.
[32] 赵宗萍.复发性口腔溃疡行中药内服外敷治疗的疗效分析[J].中医临床研究,2014,12(20):105-106.
[33] 张静.复发性口腔溃疡患者外周血T淋巴细胞亚群的分析[J].放射免疫学杂志,2013,26(2):251-252.
[34] 许韩美,杨艳杰,桑涛,等.复发性口腔溃疡患者生存质量的初步研究[J].口腔医学,2013,13(7):484-486.
[35] 范才斌.复发性口腔溃疡药物治疗的研究进展[J].上海医药,2013, 4(10): 34-37.
[36] 赵瑞泉.复发性口腔溃疡的治疗现状[J].慢性病学杂志,2013,8(6): 465-467.
[37] 彭晓红.复发性口腔溃疡的临床治疗分析[J].中国现代药物应用, 2013,7(21):95-99.
[38] 唐国旗.复方丹参滴丸联合转移因子治疗复发性口疮疗效观察[J].白求恩军医学院学报,2013(5):469-470.
[39] 王贺增.溃疡方治疗复发性口腔溃疡的临床研究[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2013.
[40] 李世超.滋阴清热法治疗糖尿病并发口疮的临床研究[D].长春:长春中医药大学,2013.
[41] 周毅,罗学来,杨传永,等.口腔黏膜细胞凋亡率与患者手术前后营养状况的关系[J].中华实验外科杂志,2006,23(6):670-672.
[42] 亓翠玲,周鑫磊,叶杰,等.穿心莲内酯对口腔癌生长的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2014,30(3):400-403.
[43] 刘振宇,张立田,蔡攀,等.MMP-2的抑制作用在治疗大鼠口腔溃疡中的实验研究[J].口腔医学研究,2013(7):613-616.
[44] 张立田,刘振宇,蔡攀,等.强力霉素凝胶治疗大鼠口腔溃疡的实验研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2013,22(18):1957-1959.
[45] 孙睿,范永峰,屈重霄,等.基质金属蛋白酶系统在口腔鳞状细胞癌中的表达[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2015,4(1):12-19.
[46] 朱丽芳,易安华.基质金属蛋白酶2在中国人口腔鳞状细胞癌中表达的Meta分析[J].口腔医学研究,2015,9(4):388-392.
[47] 韦明霞.基质金属蛋白酶在口腔炎症中的表达研究[J].中国冶金工业医学杂志,2013,30(1):27-29.
[48] 浦光瑞,张虹.基质金属蛋白酶在口腔扁平苔藓、白斑及鳞癌中的研究进展[J].大连医科大学学报,2013,35(2):193-196.
[49] 魏宏琳,宋宇峰.组织因子和基质金属蛋白酶-2在口腔鳞癌生长和转移中的作用[J].贵州医药,2012,36(8):675-678. |