Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (6): 1144-1151.doi: 10.12307/2025.300
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity
Li Yueyao1, Zhang Min2, Yang Jiaju2
- 1Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China; 2Second Hospital of Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-01-29Accepted:2024-03-06Online:2025-02-28Published:2024-06-20 -
Contact:Zhang Min, MD, Chief physician, Second Hospital of Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Li Yueyao, Master candidate, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Project of Shanxi Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (to ZM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yueyao, Zhang Min, Yang Jiaju. Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
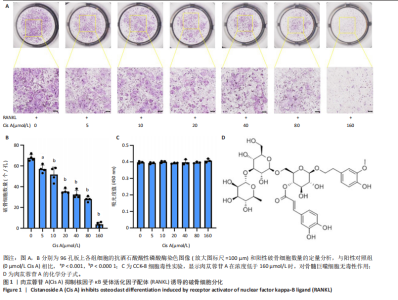
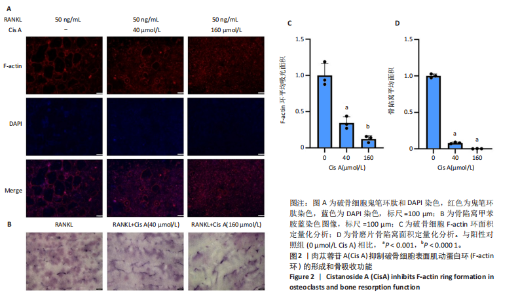
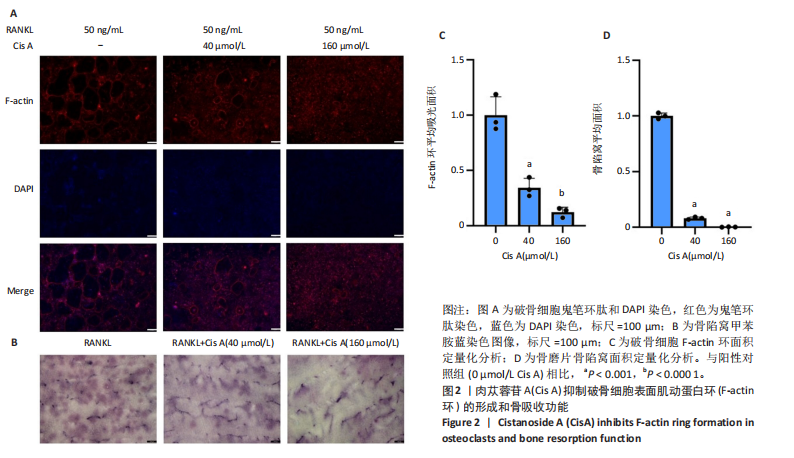
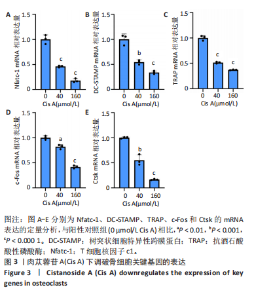
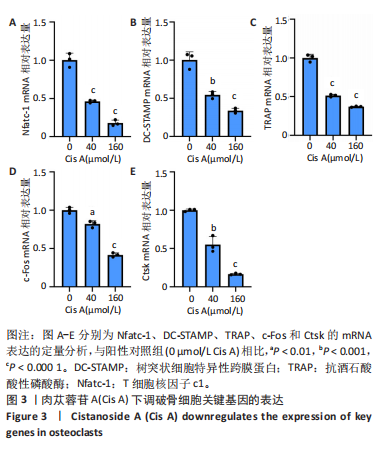
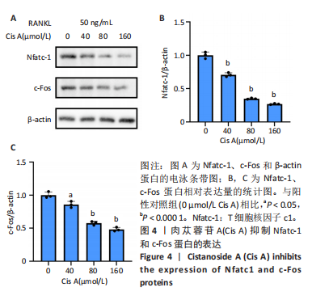
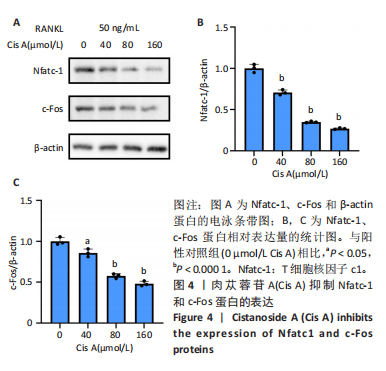
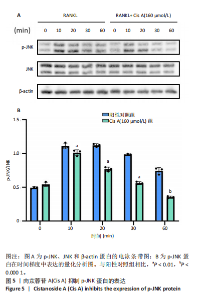
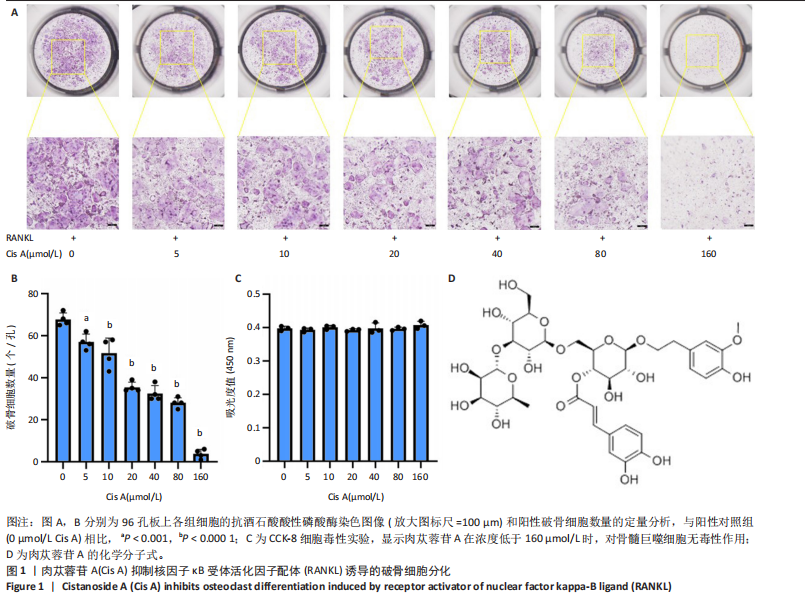
2.1 肉苁蓉苷A抑制RANKL诱导的破骨细胞分化 TRAP染色的结果显示,与对照组相比, 肉苁蓉苷A浓度为5,10,20,40,80,160 μmol/L时的破骨细胞数量明显减少,且肉苁蓉苷A在浓度为160 μmol/L时对破骨细胞生成的抑制作用最强(图1A,B)。CCK-8细胞毒性实验结果表明,在160 μmol/L浓度以下的肉苁蓉苷A对骨髓巨噬细胞无毒性作用(图1C)。 2.2 肉苁蓉苷A抑制破骨细胞表面肌动蛋白环的形成和破骨细胞骨吸收功能 见图2。鬼笔环肽和DAPI荧光染色结果显示,与阳性对照组相比,肉苁蓉苷A低、高剂量组破骨细胞肌动蛋白环面积明显减少,且肉苁蓉苷A高剂量组破骨细胞肌动蛋白环面积小于肉苁蓉苷A低剂量组(图2A,C)。 骨磨片甲苯胺蓝染色结果显示,与阳性对照组相比,肉苁蓉苷A低、高剂量组骨磨片上的骨陷窝面积均显著减小,且肉苁蓉苷A高剂量组的骨陷窝面积小于肉苁蓉苷A低剂量组(图2B,D)。"
| [1] SONG J, ZHAO J, LIU T, et al.Prevalence and Risk Factors of Osteoporosis in a Chinese Population: A Cross-Sectional Study in Xi’an, Shaanxi Province, China. Med Sci Monit. 2023;29:e942346. [2] BARTELT A, BEHLER-JANBECK F, BEIL F, et al.Lrp1 in osteoblasts controls osteoclast activity and protects against osteoporosis by limiting PDGF-RANKL signaling. Bone Res. 2018;26:6:4. [3] JOHNELL O, KANIS JA. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2006; 17(12):1726-1733. [4] TU KN, LIE JD, WAN CKV, et al. Osteoporosis: A Review of Treatment Options.P T. 2018;43(2):92-104. [5] ZUR Y, ROSENFELD L, KESHELMAN CA, et al. A dual-specific macrophage colony-stimulating factor antagonist of c-FMS and αvβ3 integrin for osteoporosis therapy. PLoS Biol. 2018;16(8):e2002979. [6] ARAI F, MIYAMOTO T, OHNEDA O, et al.Commitment and differentiation of osteoclast precursor cells by the sequential expression of c-Fms and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB (RANK) receptors. J Exp Med. 1999;190(12):1741-1754. [7] JEEVARATNAM K, SALVAGE SC, LI M, et al.Regulatory actions of 3’,5’-cyclic adenosine monophosphate on osteoclast function: possible roles of Epac-mediated signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018;1433(1):18-28. [8] LUO J, YANG Z, MA Y, et al. LGR4 is a receptor for RANKL and negatively regulates osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. Nat Med. 2016;22(5):539-546. [9] XIAO L, ZHONG M, HUANG Y, et al.Puerarin alleviates osteoporosis in the ovariectomy-induced mice by suppressing osteoclastogenesis via inhibition of TRAF6/ROS-dependent MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways.Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(21):21706-21729. [10] 姚辛敏,周晓洁,周妍妍. 肉苁蓉化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J].中医药学报,2021,49(2):93-97. [11] BETH-TASDOGAN NH, MAYER, B, HUSSEIN, H, et al.Interventions for managing medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022;7(7):CD012432. [12] NAN ZD, ZENG KW, SHI SP, et al.Phenylethanoid glycosides with anti-inflammatory activities from the stems of Cistanche deserticola cultured in Tarim desert. Fitoterapia. 2013:89:167-174. [13] XIONG Q, KADOTA S, TANI T, et al.Antioxidative effects of phenylethanoids from Cistanche deserticola. Biol Pharm Bull. 1996; 19(12):1580-1585. [14] XIONG Q, TEZUKA Y, KANEKO T, et al.Inhibition of nitric oxide by phenylethanoids in activated macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000; 400(1):137-144. [15] LUO H, CAO R, WANG L, et al. Protective effect of Cistanchis A on ethanol-induced damage in primary cultured mouse hepatocytes. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016:83:1071-1079. [16] XU X, ZHANG Z, WANG W, et al.Therapeutic Effect of Cistanoside A on Bone Metabolism of Ovariectomized Mice. Molecules. 2017;22(2):197. [17] 王代荣. 藁本内酯对RANKL诱导的破骨细胞生成和钛颗粒诱导的颅骨骨溶解的作用机制研究[D]. 南宁:广西医科大学,2019. [18] 中国老年学和老年医学学会骨质疏松分会中医药专家委员会,葛继荣, 王和鸣, 等. 中医药防治原发性骨质疏松症专家共识(2020)[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(12):1717-1725. [19] WEIVODA MM, BRADLEY EW.Macrophages and Bone Remodeling. J Bone Miner Res. 2023;38(3):359-369. [20] BOYLE WJ, SIMONET WS, LACEY DL.Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 2003;423(6937):337-342. [21] VEIS DJ, O’BRIEN CA.Osteoclasts, Master Sculptors of Bone. Annu Rev Pathol. 2023;18:257-281. [22] KIM JM, LIN C, STAVRE Z, GREENBLATT MB, et al.Osteoblast-Osteoclast Communication and Bone Homeostasis. 2020;9(9):2073. [23] ANASTASILAKIS AD, MAKRAS P, POLYZOS SA, et al.The Five-Year Effect of a Single Zoledronate Infusion on Bone Mineral Density Following Denosumab Discontinuation in Women with Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2023;113(4):469-473. [24] MURDOCH R, MELLAR A, HORNE AM., et al.Effect of a Three-Day Course of Dexamethasone on Acute Phase Response Following Treatment With Zoledronate: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2023;38(5):631-638. [25] MOON JK, PARK J, YOO Y, et al. The efficacy of Denosumab in the treatment of femoral head osteonecrosis: a retrospective comparative study. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):4140. [26] EBSTEIN E, BROCARD P, SOUSSI G, et al. Burden of comorbidities: Osteoporotic vertebral fracture during non-small cell lung cancer - the BONE study.Eur J Cancer. 2024:200:113604. [27] 冯朵,王靖,蒋勇军,等. 肉苁蓉总苷对HepG2肝癌荷瘤小鼠的影响 [J]. 食品科学,2024,45(6):120-129. [28] OKAMOTO K, NAKASHIMA T, SHINOHARA M, et al. Osteoimmunology: The Conceptual Framework Unifying the Immune and Skeletal Systems. Physiol Rev. 2017;97(4):1295-1349. [29] WEI CM, LIU Q, SONG FM, et al. Artesunate inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in vitro and prevents LPS-induced bone loss in vivo. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(1):476-485. [30] SHARMA N, WEIVODA MM, SØE K.Functional Heterogeneity Within Osteoclast Populations-a Critical Review of Four Key Publications that May Change the Paradigm of Osteoclasts. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2022;20(5):344-355. [31] VÄÄNÄNEN HK, ZHAO H, MULARI M; et al.The cell biology of osteoclast function. J Cell Sci.2000;113(Pt 3):377-381. [32] SALTEL F, DESTAING O, BARD F, et al. Apatite-mediated actin dynamics in resorbing osteoclasts.Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15(12):5231-5241. [33] UDAGAWA N, KOIDE M, NAKAMURA M, et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021; 39(1):19-26. [34] CHANG EJ, HA J, HUANG H, et al.The JNK-dependent CaMK pathway restrains the reversion of committed cells during osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Sci. 2008;121(Pt 15):2555-2564. [35] BARDWELL AJ, ABDOLLAHI M, BARDWELL L. Docking sites on mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinases, MAPK phosphatases and the Elk-1 transcription factor compete for MAPK binding and are crucial for enzymic activity. Biochem J. 2003;370(Pt 3):1077-1085. [36] GRIGORIADIS AE, WANG ZQ, CECCHINI MG, et al.c-Fos: a key regulator of osteoclast-macrophage lineage determination and bone remodeling. Science. 1994;266(5184):443-448. [37] TAKAYANAGI H.The role of NFAT in osteoclast formation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1116:227-237. [38] 党祎,姚红林,袁能华. NFATc1在骨质疏松症中的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2024,30(2):257-262+274. [39] KIVIRANTA R, MORKO J, ALATALO SL, et al.Impaired bone resorption in cathepsin K-deficient mice is partially compensated for by enhanced osteoclastogenesis and increased expression of other proteases via an increased RANKL/OPG ratio. Bone. 2005;36(1):159-172. [40] TAKAGI T, INOUE H, TAKAHASHI, N, et al.Sulforaphene attenuates multinucleation of pre-osteoclasts by suppressing expression of cell-cell fusion-associated genes DC-STAMP, OC-STAMP, and Atp6v0d2. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017;81(6):1220-1223. [41] JIANG T, GU H, WEI J.Echinacoside Inhibits Osteoclast Function by Down-Regulating PI3K/Akt/C-Fos to Alleviate Osteolysis Caused by Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:930053. |
| [1] | Wen Guangwei, Zhen Yinghao, Zheng Taikeng, Zhou Shuyi, Mo Guoye, Zhou Tengpeng, Li Haishan, Lai Yiyi. Effects and mechanisms of isoginkgetin on osteoclastogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| [2] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [3] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [4] | Zhang Haiwen, Zhang Xian, Xu Taichuan, Li Chao. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and trends of senescence in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [5] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [6] | Zhou Jian, Zhang Tao, Zhou Weili, Zhao Xingcheng, Wang Jun, Shen Jie, Qian Li, Lu Ming. Effects of resistance training on quadriceps mass and knee joint function in patients with osteoporosis and sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1081-1088. |
| [7] | Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [8] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [9] | Wang Meng, Lu Tan, Li Minjie, Liu Zhicheng, Guo Xiaoyong. Finite element analysis of stress distribution of anchors at different implantation depths under different bone density conditions in rotator cuff tears [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 561-569. |
| [10] | Xu Jiamu, Yang Cheng, Li Weimin, Wang Chunqing. Role and pathogenesis of pyroptosis and inflammatory factors in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 691-700. |
| [11] | Yang Fengli, Zhou Chao, Xiong Wei, Zhou Yuxiang, Li Dengshun, Wang Xin, Li Zhanzhen. 3D printed poly-L-lactic acid bone scaffolds in repair of bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 507-515. |
| [12] | Yu Manya, Cui Xing. Contribution and interaction of various cells in bone marrow microenvironment to exosomal circular RNA associated with multiple myeloma bone disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 101-110. |
| [13] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [14] | Han Haihui, Ran Lei, Meng Xiaohui, Xin Pengfei, Xiang Zheng, Bian Yanqin, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [15] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||