Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (6): 1118-1126.doi: 10.12307/2025.302
Previous Articles Next Articles
Wen-Shen-Tong-Du Decoction promoting spinal cord injury repair in mice
Zhao Ruihua1, 2, Chen Sixian1, 2, Guo Yang2, 3, Shi Lei1, 2, Wu Chengjie2, Wu Mao3, Yang Guanglu2, Zhang Haoheng2, Ma Yong1, 2, 3
- 1School of Chinese Medicine, School of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Laboratory of New Techniques of Restoration & Reconstruction, Institute of Traumatology & Orthopedics, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Jiangsu CM Clinical Innovation Center of Degenerative Bone & Joint Disease, Wuxi TCM Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Wuxi 214071, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2024-01-10Accepted:2024-03-13Online:2025-02-28Published:2024-06-20 -
Contact:Ma Yong, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Chinese Medicine, School of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China; Laboratory of New Techniques of Restoration & Reconstruction, Institute of Traumatology & Orthopedics, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China; Jiangsu CM Clinical Innovation Center of Degenerative Bone & Joint Disease, Wuxi TCM Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Wuxi 214071, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Zhao Ruihua, Master candidate, School of Chinese Medicine, School of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China; Laboratory of New Techniques of Restoration & Reconstruction, Institute of Traumatology & Orthopedics, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 81973885 (to MY) and 82174400 (to WM); a grant from Jiangsu Provincial Chinese Medicine Innovation Center for Clinical Degenerative Osteoarticular Disease, No. [2021]4 (to MY); High-level Chinese Medicine Key Disciplines Construction Project of National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. [2023]85 (to MY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Ruihua, Chen Sixian, Guo Yang, Shi Lei, Wu Chengjie, Wu Mao, Yang Guanglu, Zhang Haoheng, Ma Yong. Wen-Shen-Tong-Du Decoction promoting spinal cord injury repair in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1118-1126.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
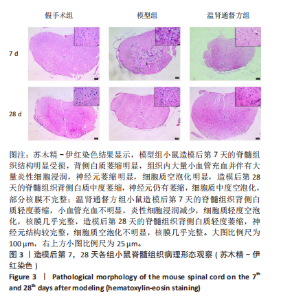
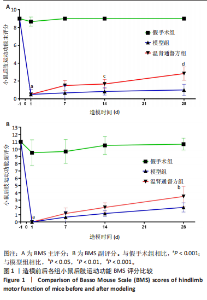
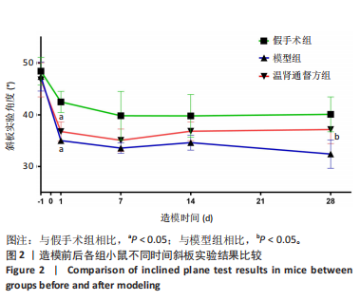
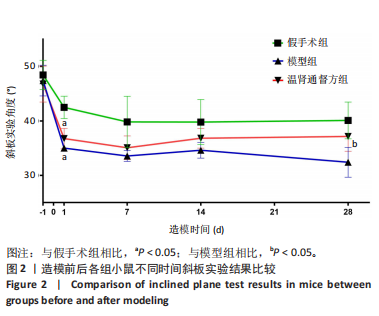
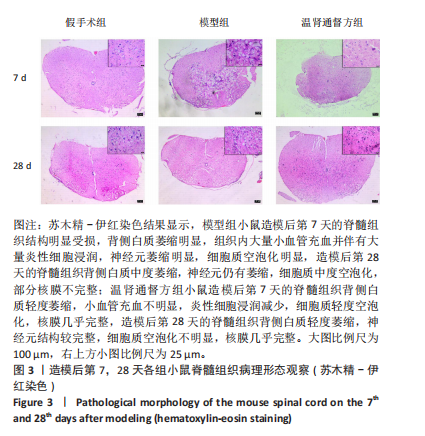
2.4 造模后各组小鼠脊髓组织病理形态学比较 造模后第7,28天各组小鼠脊髓组织病理形态观察,见图3。苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,假手术组小鼠脊髓组织结构完整,背部白质正常,无明显炎细胞浸润表现,神经元结构完整,核膜一体状;模型组小鼠造模后第7天的脊髓组织结构明显受损,背侧白质萎缩明显,组织内大量小血管充血并伴有大量炎性细胞浸润,神经元萎缩明显,细胞质空泡化明显,细胞外间隙增大,造模后第28天的脊髓组织背侧白质中度萎缩,神经元仍有萎缩,细胞质中度空泡化,部分核膜不完整;温肾通督方组小鼠造模后第7天的脊髓组织背侧白质轻度萎缩,小血管充血不明显,炎性细胞浸润减少,细胞质轻度空泡化,核膜几乎完整,胞体缩小,造模后第28天的脊髓组织背侧白质轻度萎缩,神经元结构较完整,细胞质空泡化不明显,核膜几乎完整。"
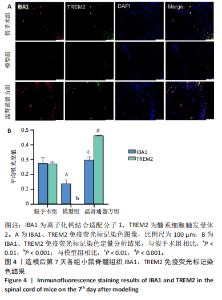
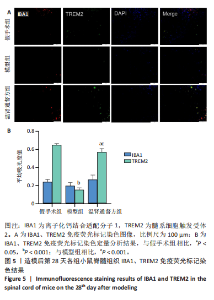
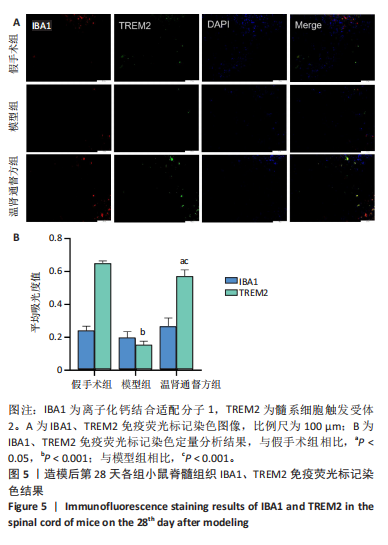
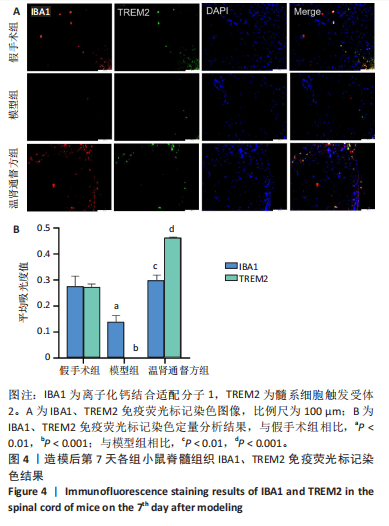
2.5 造模后各组小鼠脊髓组织中IBA1、TREM2蛋白免疫荧光染色结果 造模后第7天各组小鼠脊髓组织免疫荧光染色双标法检测IBA1、TREM2蛋白表达,见图4。与假手术组相比,模型组小鼠脊髓损伤后脊髓组织中IBA1和TREM2蛋白表达低于假手术组(P < 0.01),温肾通督方组小鼠脊髓组织中IBA1和TREM2蛋白表达高于模型组(P < 0.01)。 造模后第28天各组小鼠脊髓组织免疫荧光染色双标法检测IBA1、TREM2蛋白表达,见图5。与假手术组相比,模型组小鼠脊髓组织中TREM2蛋白表达降低(P < 0.001),IBA1蛋白表达无明显变化(P > 0.05);与模型组相比,温肾通督方组小鼠脊髓组织中TREM2蛋白表达升高(P < 0.001),IBA1蛋白表达无明显变化(P > 0.05)。"
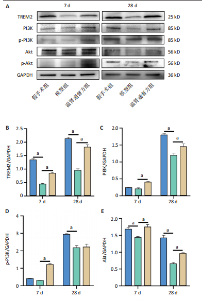
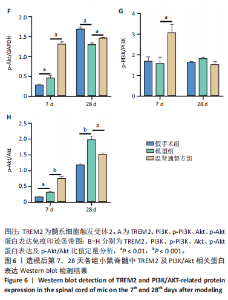
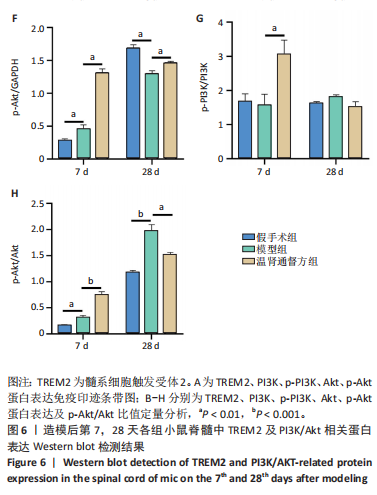
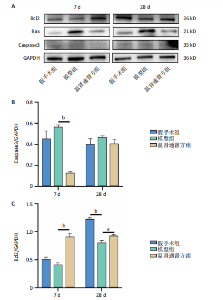
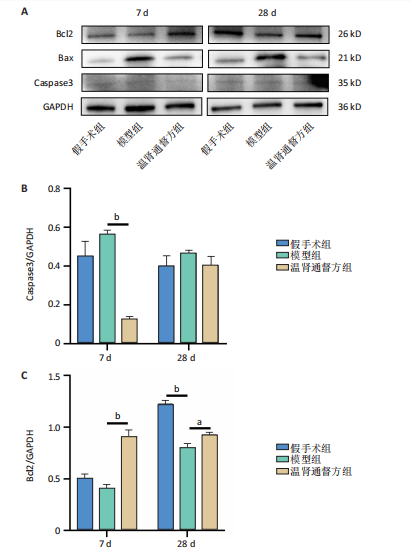
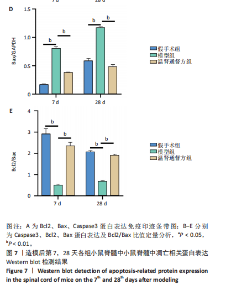
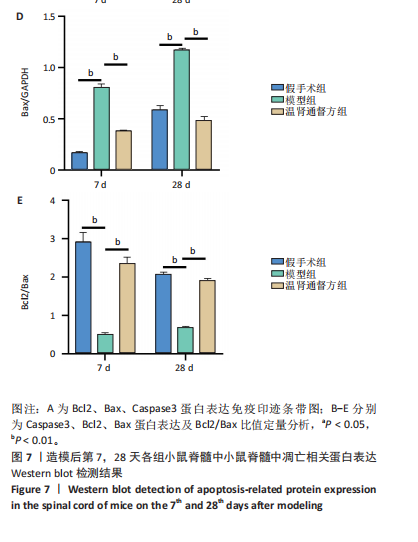
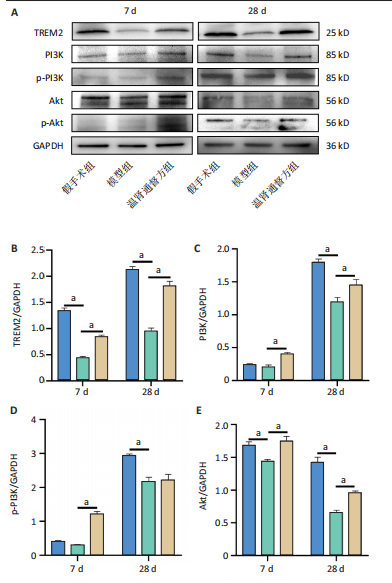
2.6 造模后各组小鼠脊髓组织中相关蛋白表达Western blot检测结果 造模后第7,28天各组小鼠脊髓组织中TREM2、PI3K、p-PI3K、Akt、p-Akt蛋白表达,见图6。造模后第7天,与假手术组相比,模型组TREM2、Akt蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01),p-Akt蛋白表达及p-Akt/Akt比值升高(P < 0.01);与模型组相比,温肾通督方组TREM2、PI3K、p-PI3K、Akt、p-Akt蛋白表达及p-PI3K/PI3K比值升高(P < 0.01),p-Akt/Akt比值升高(P < 0.001)。造模后第28天,与假手术组相比,模型组TREM2、PI3K、p-PI3K、Akt、p-Akt蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01);与模型组相比,温肾通督方组TREM2、PI3K、Akt、p-Akt蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01),其中TREM2蛋白表达检测结果与免疫荧光染色结果一致。 造模后第7,28天各组小鼠脊髓组织中Bcl2、Bax、Caspase3蛋白表达,见图7。造模后第7天,与假手术组相比,模型组Bax蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01),Bcl2蛋白表达无明显变化(P > 0.05),Bcl2/Bax比值降低(P < 0.01);与模型组相比,温肾通督方组Bcl2蛋白表达及Bcl2/Bax比值升高(P < 0.01),Bax、Caspase3蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01)。造模后第28天,与假手术组相比,模型组Bcl2蛋白表达及Bcl2/Bax比值降低(P < 0.01),Bax蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01),Caspase3蛋白表达无明显变化(P > 0.05);与模型组相比,温肾通督方组Bcl2蛋白表达及Bcl2/Bax比值升高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),Bax蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01),Caspase3蛋白表达无明显变化(P > 0.05)。"
| [1] HU X, XU W, REN Y, et al. Spinal cord injury: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):245. [2] QUADRI SA, FAROOQUI M, IKRAM A, et al. Recent update on basic mechanisms of spinal cord injury. Neurosurg Rev. 2020;43(2):425-441. [3] WANG JW, WU M, HUANG GC. Effect of Jisuikang () on kinetic dysfunction in patients after spinal injury. Chin J Integr Med. 2008; 14(3):190-193. [4] 石磊,吴承杰,陈思娴,等.温肾通督方对脊髓损伤模型小鼠脾脏B细胞影响的蛋白组学研究[J].中医杂志,2023,64(22):2329-2338. [5] 吴承杰,郭杨,石磊,等.温肾通督方对脊髓损伤后微血管内皮细胞吞噬髓鞘碎片的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2023,38(5):2073-2078. [6] WU C, ZHOU Y, TU P, et al. Jisuikang Promotes the Repair of Spinal Cord Injury in Rats by Regulating NgR/RhoA/ROCK Signal Pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:9542359. [7] GUO Y, MA Y, PAN YL, et al. Jisuikang, a Chinese herbal formula, increases neurotrophic factor expression and promotes the recovery of neurological function after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(9):1519-1528. [8] RONG Y, LIU W, LV C, et al. Neural stem cell small extracellular vesicle-based delivery of 14-3-3t reduces apoptosis and neuroinflammation following traumatic spinal cord injury by enhancing autophagy by targeting Beclin-1. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(18):7723-7745. [9] GAO J, SUN Z, XIAO Z, et al. Dexmedetomidine modulates neuroinflammation and improves outcome via alpha2-adrenergic receptor signaling after rat spinal cord injury. Br J Anaesth. 2019; 123(6):827-838. [10] BAKER G, MATVEYCHUK D, MACKENZIE EM, et al. Attenuation of the effects of oxidative stress by the MAO-inhibiting antidepressant and carbonyl scavenger phenelzine. Chem Biol Interact. 2019;304:139-147. [11] SHERROD B, KARSY M, GUAN J, et al. Spine trauma and spinal cord injury in Utah: a geographic cohort study utilizing the National Inpatient Sample. J Neurosurg Spine, 2019;31(1):93-102. [12] WANG C, SUN C, HU Z, et al. Improved Neural Regeneration with Olfactory Ensheathing Cell Inoculated PLGA Scaffolds in Spinal Cord Injury Adult Rats. Neurosignals. 2017;25(1):1-14. [13] GENSEL JC, ZHANG B. Macrophage activation and its role in repair and pathology after spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2015;1619:1-11. [14] 武作龙,达朝明,赵光海,等.小胶质细胞极化在脊髓损伤中的作用与机制研究进展[J].重庆医科大学学报,2021,46(3):268-272. [15] AKHMETZYANOVA E, KLETENKOV K, MUKHAMEDSHINA Y, et al. Different Approaches to Modulation of Microglia Phenotypes After Spinal Cord Injury. Front Syst Neurosci. 2019;13:37. [16] DONG H, ZHANG X, DAI X, et al. Lithium ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial activation via inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 expression by activating the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2014;11:140. [17] YUAN X, YUAN W, DING L, et al. Cell-adaptable dynamic hydrogel reinforced with stem cells improves the functional repair of spinal cord injury by alleviating neuroinflammation. Biomaterials. 2021; 279:121190. [18] TARASSISHIN L, SUH HS, LEE SC. Interferon regulatory factor 3 plays an anti-inflammatory role in microglia by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2011;8:187. [19] LI H, ZHANG X, QI X, et al. Icariin Inhibits Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-induced Neuronal Apoptosis after Spinal Cord Injury through Modulating the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(2):277-286. [20] LI WC, YAO SP, ZHANG J, et al. Low-dose lipopolysaccharide protects nerve cells against spinal cord injury via regulating the PI3K-AKT-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Biochem Cell Biol. 2021;99(5):527-535. [21] LIU AH, CHU M, WANG YP. Up-Regulation of Trem2 Inhibits Hippocampal Neuronal Apoptosis and Alleviates Oxidative Stress in Epilepsy via the PI3K/Akt Pathway in Mice. Neurosci Bull. 2019;35(3):471-485. [22] CHEN S, PENG J, SHERCHAN P, et al. TREM2 activation attenuates neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis via PI3K/Akt pathway after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2020; 17(1):168. [23] KHAN T, HAVEY RM, SAYERS ST, et al. Animal models of spinal cord contusion injuries. Lab Anim Sci. 1999;49(2):161-172. [24] BASSO DM, FISHER LC, ANDERSON AJ, et al. Basso Mouse Scale for locomotion detects differences in recovery after spinal cord injury in five common mouse strains. J Neurotrauma. 2006;23(5):635-659. [25] HACHEM LD, AHUJA CS, FEHLINGS MG. Assessment and management of acute spinal cord injury: From point of injury to rehabilitation. J Spinal Cord Med. 2017;40(6):665-675. [26] 王晓丹,冯晓东,刘承梅,等.脐灸治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱30例临床观察[J].中医杂志,2014,55(1):45-47. [27] 余芳菲,贾新燕,李雯昕,等.电针对不完全性脊髓损伤患者运动功能和大脑皮层运动区兴奋性的影响[J].中医杂志,2018,59(21): 1848-1852. [28] 宋颖军,李旭,刘小舟,等.补阳还五汤通过调控PI3K/Akt、JAK2/STAT3信号促进BMSC趋化迁移对外伤性脊髓损伤大鼠神经元活性及认知功能的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2023,43(17):4206-4213. [29] DE ALMEIDA FM, MARQUES SA, DOS SANTOS ACR, et al. Molecular approaches for spinal cord injury treatment. Neural Regen Res. 2023; 18(1):23-30. [30] HE X, LI Y, DENG B, et al. The PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in inflammation, cell death and glial scar formation after traumatic spinal cord injury: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Prolif. 2022;55(9):e13275. [31] CHEN Y, WANG B, ZHAO H. Thymoquinone reduces spinal cord injury by inhibiting inflammatory response, oxidative stress and apoptosis via PPAR-gamma and PI3K/Akt pathways. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(6): 4987-4994. [32] XIAO CL, YIN WC, ZHONG YC, et al. The role of PI3K/Akt signalling pathway in spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;156:113881. [33] MAN HY, WANG Q, LU WY, et al. Activation of PI3-kinase is required for AMPA receptor insertion during LTP of mEPSCs in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 2003;38(4):611-624. [34] CHU E, MYCHASIUK R, HIBBS ML, et al. Dysregulated phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling in microglia: shaping chronic neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):276. [35] GAUDET AD, FONKEN LK. Glial Cells Shape Pathology and Repair After Spinal Cord Injury. Neurotherapeutics. 2018;15(3):554-577. [36] 冉江霞,石胜良,王成志.TREM2基因过表达慢病毒载体的构建及其表达的研究[J].广西医科大学学报,2018,35(4):436-440. [37] ORTEGA-CUBERO S, LORENZO-BETANCOR O, LORENZO E, et al. TREM2 R47H variant and risk of essential tremor: a cross-sectional international multicenter study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2015;21(3):306-309. [38] JIANG T, TAN L, ZHU XC, et al. Upregulation of TREM2 ameliorates neuropathology and rescues spatial cognitive impairment in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014;39(13):2949-2962. [39] JAY TR, MILLER CM, CHENG PJ, et al. TREM2 deficiency eliminates TREM2+ inflammatory macrophages and ameliorates pathology in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. J Exp Med. 2015;212(3):287-295. [40] 王雪,代朝,方坚松.刺五加防治神经退行性疾病的药理研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2022,47(16):4314-4321. [41] BEATTIE MS, FAROOQUI AA, BRESNAHAN JC. Review of current evidence for apoptosis after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2000;17(10):915-925. [42] HELLENBRAND DJ, QUINN CM, PIPER ZJ, et al. Inflammation after spinal cord injury: a review of the critical timeline of signaling cues and cellular infiltration. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):284. [43] LI C, WU Z, ZHOU L, et al. Temporal and spatial cellular and molecular pathological alterations with single-cell resolution in the adult spinal cord after injury. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):65. [44] 杨光露,马勇,郭杨,等.基于16S rDNA分析脊髓康对脊髓损伤小鼠肠道菌群的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2023,38(3):1009-1014. [45] 杨泽霖,黄鑫,刘俊杰,等.红景天苷调控PI3K/Akt信号通路对LPS诱导的BV2小胶质细胞的抗炎作用[J].中国药理学通报,2019, 35(8):1145-1149. [46] 林嘉楠,阚默,刘晓冉,等.基于PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路人参皂苷CK抑制Aβ诱导小胶质细胞活化和炎症反应的作用机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(8):4652-4657. |
| [1] | Yin Yongcheng, Zhao Xiangrui, Yang Zhijie, Li Zheng, Li Fang, Ning Bin. Effect and mechanism of peroxiredoxin 1 in microglial inflammation after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1106-1113. |
| [2] | He Longcai, Song Wenxue, Ming Jiang, Chen Guangtang, Wang Junhao, Liao Yidong, Cui Junshuan, Xu Kaya. An experimental method for simultaneous extraction and culture of primary cortical neurons and microglial cells from SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1395-1400. |
| [3] | Chi Wenxin, Zhang Cunxin, Gao Kai, Lyu Chaoliang, Zhang Kefeng. Mechanism by which nobiletin inhibits inflammatory response of BV2 microglia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1321-1327. |
| [4] | Wang Rongrong, Huang Yushan, Li Xiangmiao, Bai Jinzhu. Prostaglandin E1 regulates vascular-related factors and protects microcirculatory function during the acute phase of traumatic spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 958-967. |
| [5] | Guo Jia, Ren Yafeng, Li Bing, Huang Jing, Shang Wenya, Yang Yike, Liu Huiyao. Action mechanism of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying miRNAs in improving spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7827-7838. |
| [6] | Zheng Yitong, Wang Yongxin, Liu Wen, Amujite, Qin Hu. Action mechanism of intrathecal transplantation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for repair of spinal cord injury under neuroendoscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7743-7751. |
| [7] | Xu Biao, Dong Yuzhen, Lu Tan. Effect of dihydroquercetin on the expression of inflammatory response markers in rats with spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6843-6850. |
| [8] | Wang Ziheng, Wu Shuang. Oxidative stress-related genes and molecular mechanisms after spinal cord injury: data analysis and verification based on GEO database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6893-6904. |
| [9] | Zhang Songjiang, Li Longyang, Zhou Chunguang, Gao Jianfeng. Central anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of tea polyphenols in exercise fatigue model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6474-6481. |
| [10] | Xu Zhenhua, Li Yanjie, Qin Hewei, Liu Haoyuan, Zhu Bochao, Wang Yupu. Traditional Chinese medicine monomer in treatment of neuroinflammation after spinal cord injury: effects of nuclear transcription factor kappa B signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 590-598. |
| [11] | Liu Ruojing, Zhao Xue, Zhu Yizhen, Fu Lingling, Zhu Junde. Ginsenoside Rb1 alleviates cerebral ischemic injury in mice by regulating microglial polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6219-6227. |
| [12] | Du Juan, Zhang Yi, Hao Quanshui. Effects of exercise on activation of microglia and astrocytes and neuronal apoptosis in depressed rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6243-6248. |
| [13] | Chen Ying, Liu Jian, Liang Yajie, Li Yanqing, Song Lijuan, Huang Jianjun, Yu Jiezhong, Wang Qing, Ma Cungen . Mechanism by which hydroxysafflor yellow A alleviates demyelination in cuprizone mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5311-5319. |
| [14] | Fang Jun, Wei Wei, Xue Yating, Cui Chenlong, Wei Jiasheng, Shi Xiao, Yang Lijuan, Yang Baozhong. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes promote microglia M2-type polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5320-5327. |
| [15] | Guan Mengya, Ren Binbin, Wang Jingying. Major histocompatibility complex regulates immune responses in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5469-5477. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||