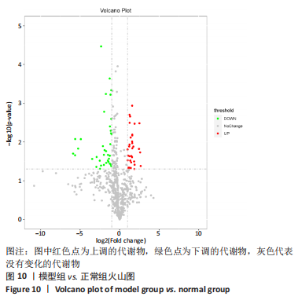
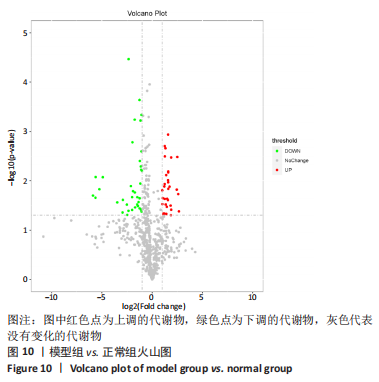
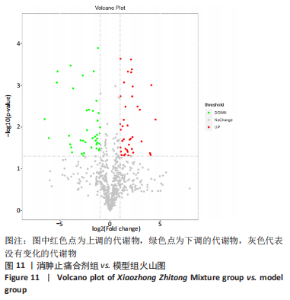
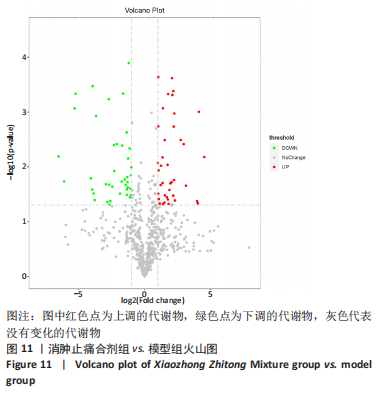
[1] SCHMIDT Y, BANNASCH H, EISENHARDT SU. Ischemia-reperfusion injury leads to significant tissue damage in free flap surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129(1):174e-175e.
[2] BIAN F, XIAO Y, ZAHEER M, et al. Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway by Butyrate Improves Corneal Wound Healing in Corneal Alkali Burn. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3):562.
[3] YIN XF, ZHANG Q, CHEN ZY, et al. NLRP3 in human glioma is correlated with increased WHO grade, and regulates cellular proliferation, apoptosis and metastasis via epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the PTEN/AKT signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 2018;53(3):973-986.
[4] HAN Y, XU X, TANG C, et al. Reactive oxygen species promote tubular injury in diabetic nephropathy: The role of the mitochondrial ros-txnip-nlrp3 biological axis. Redox Biol. 2018;16:32-46.
[5] SHARMA A, TATE M, MATHEW G, et al. Oxidative Stress and NLRP3-Inflammasome Activity as Significant Drivers of Diabetic Cardiovascular Complications: Therapeutic Implications. Front Physiol. 2018;9:114.
[6] 单海民,程春生,马文龙,等.川芎嗪对岛状皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤血液流变学影响的研究[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2012,7(10): 846-849.
[7] HONG P, GU RN, LI FX, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome as a potential treatment in ischemic stroke concomitant with diabetes. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):121.
[8] 毕军伟,李盛华,米仲祥,等.陇中消肿止痛合剂的实验研究与临床应用[J].西部中医药,2016,29(4):51-53.
[9] 王海刚.基于 p38MAPK-PPARγ/NF-κB 信号通路探讨消肿止痛合剂对皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的干预机制研究[D].兰州:甘肃中医药大学,2021.
[10] 姚兴璋,刘涛,何志军,等.消肿止痛合剂对大鼠缺血皮瓣血管再生及VEGF-Dll4/Notch 信号通路的影响[J].暨南大学学报(自然科学与医版),2021,42(2):164-171.
[11] TAN B, MA Y, ZHANG L, et al. The application of metabolomics analysis in the research of gestational diabetes mellitus and preeclampsia. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2020;46(8):1310-1318.
[12] SCHMAUSS D, WEINZIERL A, SCHMAUSS V, et al. Common Rodent Flap Models in Experimental Surgery. Eur Surg Res. 2018;59(3-4):255-264.
[13] CHEN D, ZHONG L, LI Y, et al. Changes in serum inflammatory factor interleukin-6 levels and pathology of carotid vessel walls of rats with chronic periodontitis and diabetes mellitus after the periodontal intervention. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020;27(6):1679-1684.
[14] LIU X, ZHANG M, CHENG X, et al. LC-MS-Based Plasma Metabolomics and Lipidomics Analyses for Differential Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer and Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2020;10:717.
[15] WEBB JL. Enzyme and metabolism inhibitors. New York: Academic Press, 1966.
[16] BRAND MD. Mitochondrial generation of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide as the source of mitochondrial redox signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;100:14-31.
[17] HAUSENLOY DJ, YELLON DM. Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: a neglected therapeutic target. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(1):92-100.
[18] QUINLAN CL, ORR AL, PEREVOSHCHIKOVA IV, et al. Mitochondrial complex II can generate reactive oxygen species at high rates in both the forward and reverse reactions. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(32):27255-27264.
[19] KONSTAM MA, KIERNAN MS, BERNSTEIN D, et al. Evaluation and Management of Right-Sided Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137(20):e578-e622.
[20] HARJOLA VP, MEBAZAA A, ČELUTKIENĖ J, et al. Contemporary management of acute right ventricular failure: a statement from the Heart Failure Association and the Working Group on Pulmonary Circulation and Right Ventricular Function of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016;18(3):226-241.
[21] MILLS EL, KELLY B, LOGAN A, et al. Succinate Dehydrogenase Supports Metabolic Repurposing of Mitochondria to Drive Inflammatory Macrophages. Cell. 2016;167(2):457-470.e13.
[22] BAILIS W, SHYER JA, ZHAO J, et al. Distinct modes of mitochondrial metabolism uncouple T cell differentiation and function. Nature. 2019;571(7765):403-407.
[23] PELL VR, CHOUCHANI ET, FREZZA C, et al. Succinate metabolism: a new therapeutic target for myocardial reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 2016;111(2):134-141.
[24] CHOUCHANI ET, PELL VR, GAUDE E, et al. Ischaemic accumulation of succinate controls reperfusion injury through mitochondrial ROS. Nature. 2014;515(7527):431-435.
[25] ZHANG J, WANG YT, MILLER JH, et al. Accumulation of Succinate in Cardiac Ischemia Primarily Occurs via Canonical Krebs Cycle Activity. Cell Rep. 2018;23(9):2617-2628.
[26] PELL VR, SPIROSKI AM, MULVEY J, et al. Ischemic preconditioning protects against cardiac ischemia reperfusion injury without affecting succinate accumulation or oxidation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018;123:88-91.
[27] MARTIN JL, COSTA ASH, GRUSZCZYK AV, et al. Succinate accumulation drives ischaemia-reperfusion injury during organ transplantation. Nat Metab. 2019;1:966-974.
[28] KOHLHAUER M, PELL VR, BURGER N, et al. Protection against cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury by hypothermia and by inhibition of succinate accumulation and oxidation is additive. Basic Res Cardiol. 2019;114(3):18.
[29] PRAG HA, PALA L, KULA-ALWAR D, et al. Ester Prodrugs of Malonate with Enhanced Intracellular Delivery Protect Against Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury In Vivo. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2022;36(1):1-13.
[30] CHENG D, SONG Q, DING Y, et al. Comparative Study on the Protective Effect of Chlorogenic Acid and 3-(3-Hydroxyphenyl) Propionic Acid against Cadmium-Induced Erythrocyte Cytotoxicity: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. J Agric Food Chem. 2021;69(13):3859-3870.
[31] WAHYUNI WT, ROHAETI E, SARI DR. Graphene modified screen printed carbon electrode for voltammetric detection of glutathione as oxidative stress biomarker[A]//IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science[C]. Bogor: The 4th International Seminar on Sciences, 2018.
[32] 聂春霞,何盼,郝艳艳,等.基于1H-NMR代谢组学的山楂不同炮制品对高脂血症大鼠模型的影响研究[J].中草药,2019,50(10): 2362-2370.
[33] 彭琳秀,谢彤,单进军.基于气相色谱-质谱联用的抗结核药致肾损伤代谢组学及谷胱甘肽治疗作用研究[J].分析化学,2020,48(9): 1160-1168.
|