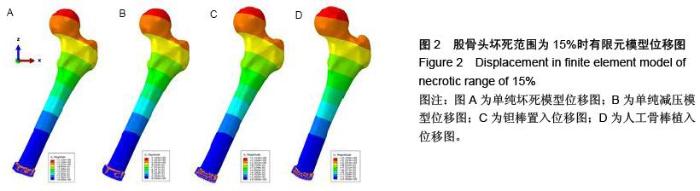
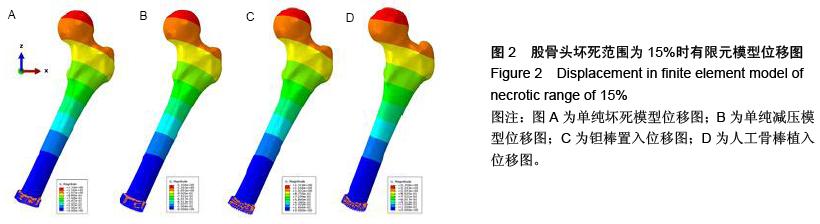
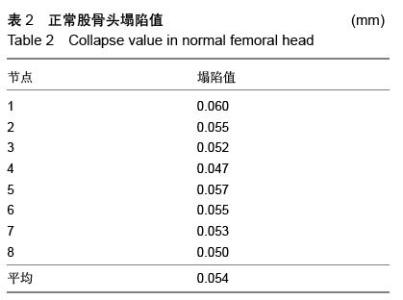
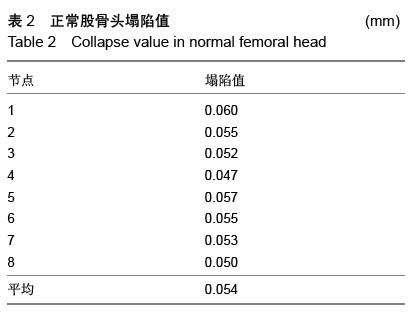
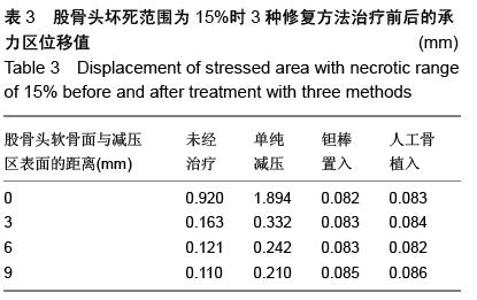
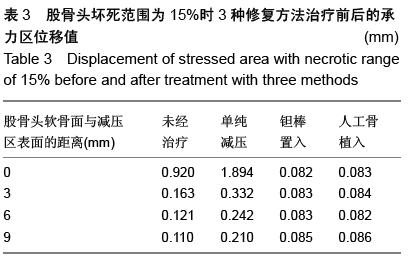
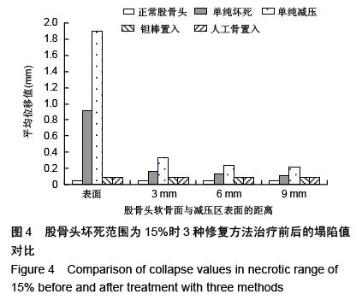
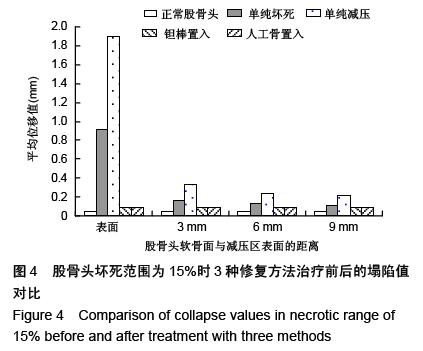
| [1] Varitimidis SE, Dimitroulias AP, Karachalios TS,et al.Outcome after tantalum rod implantation for treatment of femoral head osteonecrosis: 26 hips followed for an average of 3 years.Acta Orthop. 2009; 80(1):20-25.
[2] Floerkemeier T, Lutz A, Nackenhorst U,et al.Core decompression and osteonecrosis intervention rod in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: clinical outcome and finite element analysis.Int Orthop. 2011;35(10): 1461-1466.
[3] TN Tran, Warwas S, Haversatha M,et al.Experimental and computational studies on the femoral fracture risk for advanced core decompression.Clin Biomech. 2014; 29(4):412-417.
[4] Song WS, Yoo JJ, Kim YM,et al.Results of multiple drilling compared with those of conventional methods of core decompression.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 454(6):139-146 .
[5] Liu WG, Wang SJ, Yin QF, et al. Biomechanical supporting effect of tantalum rods for the femoral head with various sized lesions: a finite-element analysis. Chin Med J. 2012;125(22):4061-4065.
[6] Matsusaki H, Noguchi M, Kawakami T,et al.Use of vascularized pedicle iliac bone graft combined with transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy in the treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005;125(2): 95-101.
[7] Yoon TR, Abbas AA, Hur CI,et al.Modified transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy for femoral head osteonecrosis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(5): 1110-1116.
[8] Zhao D, Xu D, Wang W,et al.Iliac graft vascularization for femoral head osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;442(5):171-179.
[9] Liu F, Williams S, Fisher J,et al. Effect of microseparation on contact mechanics in metal-on- metal hip replacements-A finite element analysis. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(6): 1312-1319.
[10] Zietz C, Fabry C, Baum F,et al. The Divergence of Wear Propagation and Stress at Steep Acetabular Cup Positions Using Ceramic Heads and Sequentially Cross-Linked Polyethylene Liners. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(8):1458-1463.
[11] Yoon TR, Song EK, Rowe SM,et al.Failure after core decompression in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Int Orthop. 2001;24(6):316-318.
[12] Tran TN, Warwas S, Haversath M,et al.Experimental and computational studies on the femoral fracture risk for advanced core decompression.Clin Biomech. 2014; 29(4):412-417.
[13] Derikx LC, van Aken, Janssen D,et al.The assessment of the risk of fracture in femora with metastatic lesions: comparing case-specific finite element analyses with predictions by clinical experts.J Bone Joint Surg. 2012: 94(8):1135-1142.
[14] Stolk J, Verdonschot N, Huiskes R,et al.Hip-joint and abductor-muscle forces adequately represent in vivo loading of a cemented total hip reconstruction.J Biomech. 2001;34(7):917-926.
[15] Park S, Hung CT, Ateshian GA,et al.Mechanical response of bovine articular cartilage under dynamic unconfined compression loading at physiological stress levels.Osteoarthritis Cartilag. 2004;12(1):65-73.
[16] 韦葛堇,李奇,林荔军,等.金属对金属髋关节表面置换后的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 13(17): 3217-3222.
[17] Luo HY, Chen CW.Treatment of adult early femur head necrosis with the tantalum screw. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2011;24(6):482-485.
[18] 马信龙,付鑫,马剑雄,等.股骨头内松质骨空间分布和力学性能变化有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2010,25(6):465-470.
[19] 方斌,何伟,展磊,等.不同坏死范围下股骨头坏死区应力分布的有限元分析[J].中医正骨,2012,24(10):10-15.
[20] Schildhauer TA, Robie B, Muhr G, et al. Bacterial adherence to tantalum versus commonly used orthopedic metallic implant materials. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(7): 476-484.
[21] 林斌.镍钛记忆合金网球治疗股骨头缺血性坏死的生物力学及三维有限元分析[J].中国矫形杂志,2003,11(15):45-48.
[22] 张怡元,冯尔宥,陈日齐等.多孔钽块置入治疗股骨头缺血性坏死的生物力学及 三维有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(12):1113-1116.
[23] 陈凯,蔡郑东.多孔钽金属植入治疗早期股骨头坏死研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2008,29(1):41-42.
[24] 钟务学,张银网,朱海波,等.采用体绘制方法建立人股骨三维有限元模型及其应力分析[J].中国组织工程研究杂志, 2012,16(17):3048-3051.
[25] Pang Z, Wei Q, Zhou G,et al. Establishment and application of subject-specific three-dimensional finite element mesh model for osteonecrosis of femoral head. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2012;29(2):251-255.
[26] Lutz A, Nackenhorst U, von Lewinski G,et al.Numerical studies on alternative therapies for femoral head necrosis: a finite element approach and clinical experience. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2011;10(5): 627-640. |