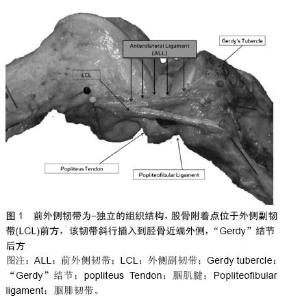
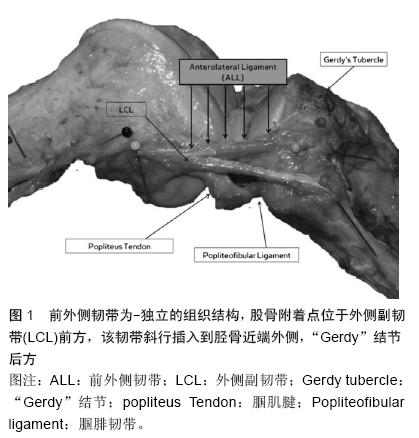
| [1] Segond P. Recherches cliniques et experimentales sur lesepanchements sanguins du genou par entorse. Paris: AuxBureaux du Progrès Médical.1879.[2] Hughston JC, Andrews J, Cross M, et al. Classification of knee ligament instabilities. Part II. The lateral compartment.J Bone Joint Surg Am 1976;58:173-179.[3] Johnson LL.Lateral capsular ligament complex: Anatomical and surgical considerations. Am J Sports Med.1979;7:156-160.[4] Campos JC, Chung CB, Lektrakul N, et al. Pathogenesis of the Segond fracture: Anatomic and MR imaging evidence of an iliotibial tract or anterior oblique band avulsion. Radiology.2001;219:381-386.[5] Terry GC, Norwood LA, Hughston JC,et al. How iliotibial tract injuries of the knee combine with acute anterior cruciate ligament tears to influence abnormal anterior tibial displacement. Am J Sports Med.1993;21: 55-60.[6] Terry GC, LaPrade RF. The posterolateral aspect of the knee. Anatomy and surgical approach. Am J Sports Med.1996;24:732-739.[7] Terry GC, Hughston JC, Norwood LA. The anatomy of the iliopatellar band and iliotibial tract. Am J Sports Med.1986;14:39-45.[8] Terry GC, LaPrade RF. The biceps femoris muscle complex at the knee. Its anatomy and injury patterns associated with acute anterolateral anteromedial rotatory instability. Am J Sports Med.1996;24(1):2-8.[9] Cruells Vieira EL, Vieira EÁ, Teixeira da Silva R, et al. An anatomic study of the iliotibial tract. Arthroscopy. 2007;23:269-274.[10] Dietz GW, Wilcox DM, Montgomery JB. Segond tibial condyle fracture: Lateral capsular ligament avulsion. Radiology. 1986;159:467-469.[11] Davis DS, Post WR. Segond fracture: Lateral capsular ligament avulsion. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther.1997;25: 103-106.[12] Goldman A, Pavlov H, Rubenstein D. The Segond fracture of the proximal tibia: A small avulsion that reflects major ligamentous damage. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1988;151: 1163-1167.[13] Hughston JC, Andrews J, Cross M,et al. Classification of knee ligament instabilities. Part I. The medial compartment and cruciate ligaments. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1976;1:159-172.[14] Woods GW, Stanley RF, Tullos HS. Lateral capsular sign: x-ray clue to a significant knee instability. Am J Sports Med.1979;7:27–33.[15] Hess T, Rupp S, Hopf T, et al. Lateral tibial avulsion fractures and disruptions to the anterior cruciate ligament. A clinical study of their incidence and correlation. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1994;303: 193-197.[16] Irvine G, Dias J, Finlay D. Segond fractures of the lateral tibial condyle: Brief report. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1987;69: 613-614.[17] Haims AH, Medvecky MJ, Pavlovich R Jr, et al. MR imaging of the anatomy of and injuries to the lateral and posterolateral aspects of the knee. Am J Roentgenol.2003;180:647–653.[18] Moorman CT 3rd, LaPrade RF. Anatomy and biomechanics of the posterolateral corner of the knee. J Knee Surg. 2005;18:137–145.[19] Vieira EL, Vieira EA, da Silva RT, et al. An anatomic study of the iliotibial tract. Arthroscopy. 2007;23(3): 269-274.[20] Vincent JP, Magnussen RA, Gezmez F, et al. The anterolateral ligament of the human knee: An anatomic and histologic study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2012;20:147-152.[21] LaPrade RF, Gilbert TJ, Bollom TS,et al. The magnetic resonance imaging appearance of individual structures of the posterolateral knee. A prospective study of normal knees and knees with surgically verified grade III injuries. Am J Sports Med.2000;28:191-199.[22] Macchi V, Porzionato A, Morra A,et al. The anterolateral ligament of the knee: a radiologic and histotopographic study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2015 Oct 17. [Epub ahead of print][23] Mazzuca SA, Brandt KD, Dieppe PA,et al. Effect of alignment of the medial tibial plateau and x-ray beam on apparent progression of osteoarthritis in the standing anteroposterior knee radiograph. Arthritis Rheum.2001;44(8):1786-1794.[24] Pietrini SD, LaPrade RF, Griffith CJ, et al. Radiographic identification of the primary posterolateral knee structures.Am J Sports Med. 2009;37(3):542-551.[25] Claes S, Vereecke E, Maes M, et al. Anatomy of the anterolateral ligament of the knee. J Anat.2013;223: 321-328. [26] Claes S, Bartholomeeusen S, Bellemans J. High prevalence of anterolateral ligament abnormalities in magnetic resonance images of anterior cruciate ligament-injured knees. Acta Orthop Belg.2014; 80: 45-49.[27] Claes S, Luyckx T, Vereecke E, et al. The Segond fracture: A bony injury of the anterolateral ligament of the knee. Arthroscopy.2014;30:1475-1482.[28] Helito CP, Demange MK, Bonadio MB, et al. Anatomy and histology of the knee anterolateral ligament. Orthop J Sports Med. Orthop J Sports Med. 2013;1(7): 2325967113513546.[29] Helito CP, Bonadio MB, Soares TQ,et al. The meniscal insertion of the knee anterolateral ligament. Surg Radiol Anat. 2015 Aug 6.[30] Helito CP, Demange MK, Bonadio MB, et al. Radiographic landmarks for locating the femoral origin and tibial insertion of the knee anterolateral ligament. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42:2356-2362.[31] Dodds AL, Halewood C, Gupte CM, et al. The anterolateral ligament: Anatomy, length changes and association with the Segond fracture. Bone Joint J.2014;96: 325-331.[32] Milch H. Cortical avulsion fracture of the lateral tibial condyle. J Bone Joint Surg.1936;18:159-164.[33] Vieira EL, Vieira EA, da Silva RT, et al. An anatomic study of the iliotibial tract. Arthroscopy. 2007;23(3): 269-274.[34] Gossner J. The anterolateral ligament of the knee Visibility on magnetic resonance imaging. Rev Bras Ortop.2014;49:98-99.[35] Rezansoff AJ, Caterine S, Spencer L, et al. Radiographic landmarks for surgical reconstruction of the anterolateral ligament of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2015;23(11):3196-201.[36] Caterine S, Litchfield R, Johnson M,et al. A cadaveric study of the anterolateral ligament: re-introducing the lateral capsular ligament.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2015;23(11):3186-3195z.[37] Tavlo M, Eljaja S, Jensen JT,et al. The role of the anterolateral ligament in ACL insufficient and reconstructed knees on rotatory stability: A biomechanical study on human cadavers. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015ug 6. doi: 10.1111/sms.12524.[38] Lutz C, Sonnery-Cottet B, Niglis L, et al. Behavior of the anterolateral structures of the knee during internal rotation. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(5): 523-528.[39] Zens M, Niemeyer P, Ruhhammer J,et al. Length Changes of the Anterolateral Ligament During Passive Knee Motion: A Human Cadaveric Study. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(10):2545-2552.[40] Peltola EK, Mustonen AO, Lindahl J,et al. Segond fracture combined with tibial plateau fracture. AJR Am J Roentgenol.2011;197(6):W1101-4. [41] Falciglia F, Mastantuoni G, Guzzanti V. Segond fracture with anterior cruciate ligament tear in an adolescent.J Orthop Traumatol.2008;9(3):167-169.[42] 喻长纯,王园园,张江涛.膝关节前外侧结构损伤及相关问题探讨[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2008,16(8):20-21. |