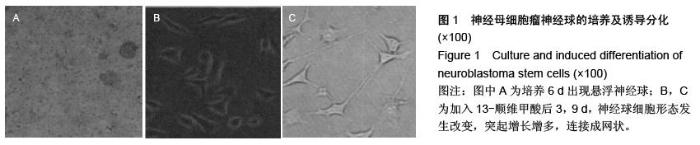
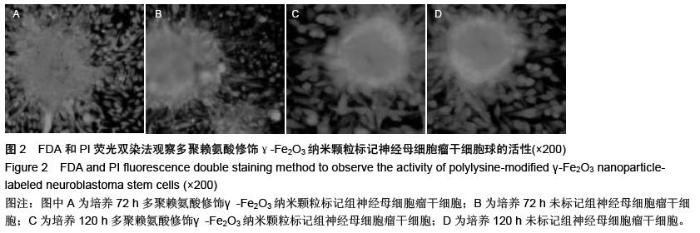
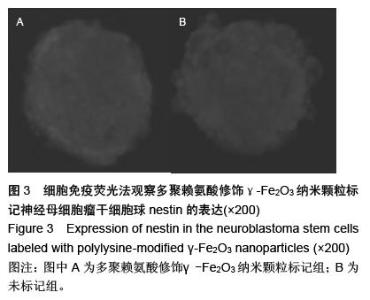
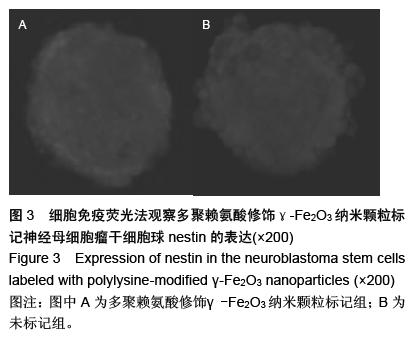
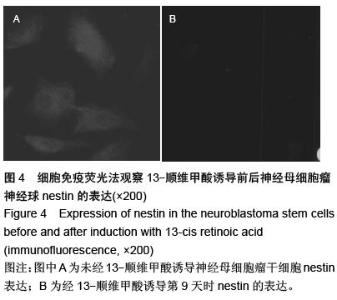
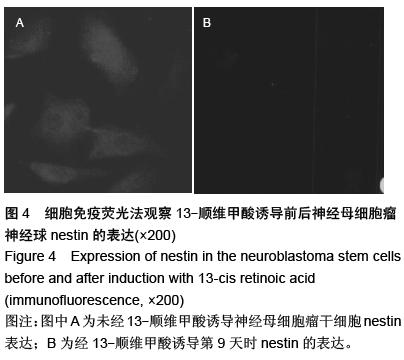
| [1] 郭海霞,黎阳,薛红漫,等.儿童神经母细胞瘤的临床分析[J].中华妇幼临床医学杂志:电子版,2010,5(1):50.[2] Cohen LE, Gordon JH, Popovsky EY, et al. Late effects in children treated with intensive multimodal therapy for high-risk neuroblastoma: high incidence of endocrine and growth problems.Bone Marrow Transplant. 201449(4):502-508.[3] 张大伟,周春菊,金眉,等.儿童神经母细胞瘤临床病理分析[J].中国肿瘤,2009,18(7):70.[4] Vogelzang NJ, Benowitz SI, Adams S, et al. Clinical cancer advances 2011: Annual Report on Progress Against Cancer from the American Society of Clinical Oncology.J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(1):88-109. [5] Gaze MN, Gains JE, Walker C, et al. Optimization of molecular radiotherapy with [131I]-meta Iodobenzylguanidine for high-risk neuroblastoma.Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;57(1):66-78.[6] 江贤萍,周家秀,王国兵,等.神经母细胞瘤24 例临床和病理特点[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2010,18(1):55.[7] 钟丽,陈艳霞,邹杰,等.儿童神经母细胞瘤肺转移的临床影像分析[J].放射学实践,2011,26(8):883-885.[8] Kreissman SG, Seeger RC, Matthay KK,et al. Purged versus non-purged peripheral blood stem-cell transplantation for high-risk neuroblastoma (COG A3973): a randomised phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(10):999-1008.[9] 胡荣兵,周文明.儿童神经母细胞瘤的CT 诊断[J].中国现代医药杂志,2011,10(1):50-52.[10] 刘平,吴惧,张辉韵,等.儿童神经母细胞瘤合并眼球阵挛-肌阵挛综合征1例[J].中国实用儿科杂志,2011, 26(11): 875-876.[11] Morgenstern DA, Baruchel S, Irwin MS. Current and future strategies for relapsed neuroblastoma: challenges on the road to precision therapy.J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2013;35(5):337-347.[12] 李彦格,管玉洁,邹旭凤,等.儿童神经母细胞瘤26 例临床分析[J].中国现代药物应用,2012,6(11):15-16.[13] 吴鑫,何大维,张永波,等.粒细胞集落刺激因子及其受体在儿童神经母细胞瘤中的表达研究[J].解放军医学杂志, 2012,37(12):1103-1106.[14] 黄帆,刘映孜,杨秋珺,等.全反式维甲酸增强骨形态蛋白9 诱导间充质干细胞成骨分化作用[J].第三军医大学报, 2013,35(4):328-331.[15] 严昉,陈连军.维甲酸类药物在皮肤科疾病治疗中的应用[J].上海医药,2010,31(4):156-159.[16] 孙宇强,王雪,关兴芳,等.维甲酸及其受体与肿瘤关系的研究进展[J].生命科学,2014,26(3):295-301.[17] 张斌.核激素受体在皮肤主要构成细胞和表皮鳞癌A431细胞中的表达及其部分配体的调节效应[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2013.[18] Alizadeh F, Bolhassani A, Khavari A, et al. Retinoids and their biological effects against cancer.Int Immunopharmacol. 201418(1):43-49.[19] Das BC, Thapa P, Karki R,et al.Retinoic acid signaling pathways in development and diseases.Bioorg Med Chem. 2014;22(2):673-683.[20] Samarut E, Fraher D, Laudet V, et al. ZebRA: An overview of retinoic acid signaling during zebrafish development.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1849(2): 73-83.[21] Álvarez R, Vaz B, Gronemeyer H,et al.Functions, therapeutic applications, and synthesis of retinoids and carotenoids.Chem Rev. 2014;114(1):1-125.[22] Mendoza-Parra MA, Gronemeyer H.Genome-wide studies of nuclear receptors in cell fate decisions. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013;24(10-12):706-715.[23] Al Tanoury Z, Piskunov A, Rochette-Egly C.Vitamin A and retinoid signaling: genomic and nongenomic effects.J Lipid Res. 2013;54(7):1761-1775.[24] Zhang Y, Maksimovic J, Naselli G,et al.Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis identifies hypomethylated genes regulated by FOXP3 in human regulatory T cells.Blood. 2013;122(16):2823-2836.[25] 王忠永,邱会芬,蒋延伟.阿维A 对寻常型银屑病患者外周血Th17 /Treg 细胞转录因子RORγt 和Foxp3 表达影响的研究[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2012,6(24): 8156-8159.[26] 王沪凯.维甲酸药物对皮肤病的治疗探讨[J].中国药物经济学,2012,7(3):24-25.[27] 陈辉,房晶晶,吴海娟,等.痤疮患者经异维A 酸系统治疗后外周血CD14 + 单核细胞TLR2 的表达变化[J].皮肤性病诊疗学杂志,2013,20(2):77-79.[28] 王忠永,李侃,邱盼盼,等.寻常痤疮患者外周血单核细胞TLR2 的表达及其与IL-8 和TNF-α 的相关性研究[J].中华皮肤科杂志,2011,44(2):121-123.[29] Leyssens C, Verlinden L, Verstuyf A.Antineoplastic effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 and its analogs in breast, prostate and colorectal cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2013;20(2):R31-47.[30] Wang H, Liu K, Geng M,et al.RXRα inhibits the NRF2-ARE signaling pathway through a direct interaction with the Neh7 domain of NRF2.Cancer Res. 2013;73(10):3097-3108.[31] 黄敏,许洪志,隋潇徽,等.急性早幼粒细胞白血病治疗的研究[J].临床血液学杂志,2011,24(11):426-428.[32] 郑琼波.ATRA联合三氧化二砷在急性早幼粒细胞白血病治疗中的临床应用研究[J].中国现代医生,2011,49(20): 73-74.[33] 贺甜甜,史伟,赵万红,等.维甲酸与急性早幼粒细胞白血病(APL)[J].现代肿瘤医学,2011,18(10):2081-2084.[34] 马清君,李伟平,张怀东.亚砷酸、维甲酸联合小剂量化疗治疗骨髓增生异常综合征的临床疗效[J].现代肿瘤医学, 2005,13(4):517-518.[35] 李波,窦芳.利度胺联合司坦唑醇和维A 酸治疗低危骨髓增生异常综合征[J].中国实用医药,2012,12(7):192-193.[36] 孔荣,邱宏春,吴鹏飞,等.小剂量沙利度胺联合十一酸睾酮和维A 酸治疗低危骨髓增生异常综合征[J].临床荟萃, 2010,25(2):158-160.[37] 董志高,陈旭艳.难治性ITP 的发病机制和现代免疫治疗[J].中国老年保健医学,2010,8(5):60-62.[38] 邹乐兰,黄瑞滨.难治性特发性血小板减少性紫癜的治疗进展[J].实用临床医学,2011,16(5):232-234.[39] 刘文宾,王兆钺,曹丽娟,等.全反式维甲酸对于难治性ITP的疗效观察及其机理探讨[J].血栓与止血学,2010,16(1): 15-17.[40] 刘文宾,王兆钺,曹丽娟,等.全反式维甲酸治疗难治性特发性血小板减少性紫癜疗效观察及其机制探讨[J].苏州大学学报:医学版,2009,29(3):476-479.[41] 施锐,张素梅,桂淑玉,等.全反式维甲酸对人胃癌细胞株caveolin-1 表达和定位的影响[J].安徽医科大学学报, 2012,47(3):249-252.[42] 邓玉洁,张强,王慧,等.全反式维甲酸对肝癌HepG2 细胞chemerin 基因表达的调控[J].江苏大学学报:医学版, 2012,22(2):198-200. [43] 李佳鑫,海广范,贾岩龙,等.全反式维甲酸对人胚肺成纤维细胞增殖及a-SMA表达的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2011,27(4):787-790. [44] 钟德君,康敏,王高举,等.全反式维甲酸促大鼠胚胎神经干细胞向神经元分化中β连环蛋白的表达及意义[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(4):305-310. [45] 梁晨,郭世文.全反式维甲酸对NT2细胞系胶质瘤趋向性的影响[J].西安交通大学学报:医学版,2012,33(4): 470-473.[46] 刘燕雄,单振潮,杜勇.全反式维甲酸诱导大鼠肠神经系统发育异常的实验研究[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2012, 34(3): 234-236.[47] 李芳华,谢晓丽,刘静,等.全反式维甲酸对实验性自身免疫性重症肌无力的治疗效果[J].国际免疫学杂志,2013, 36(1):49-53.[48] 王育盛.全反式维甲酸对血管粥样硬化病变作用的研究进展[J].心血管病学进展,2012,33(3):375-378. |