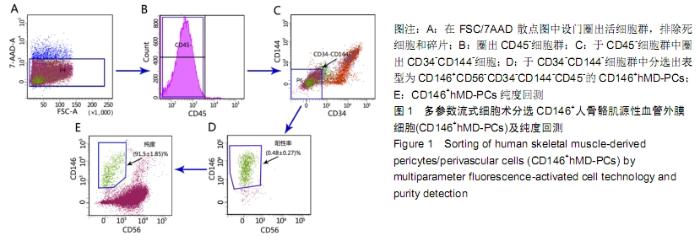
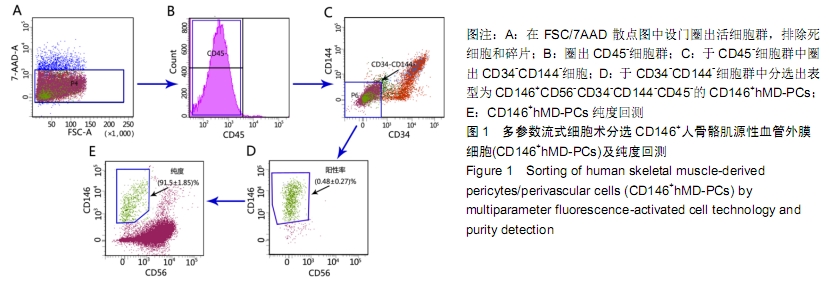
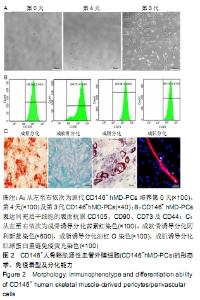
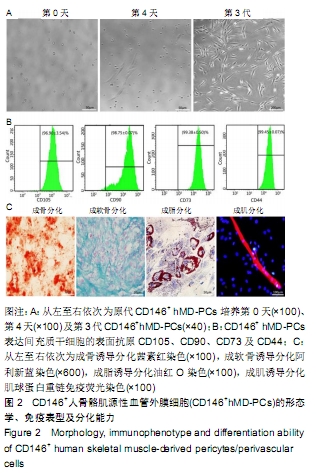
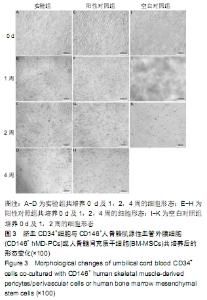
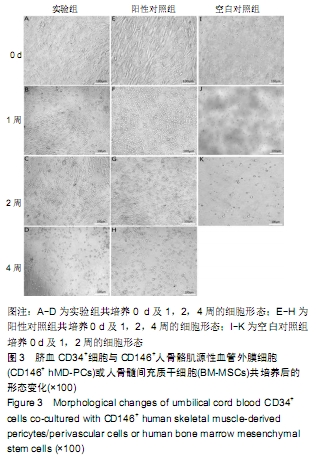
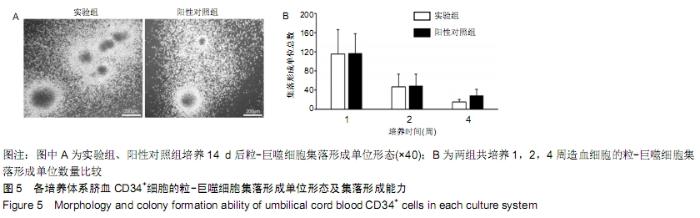
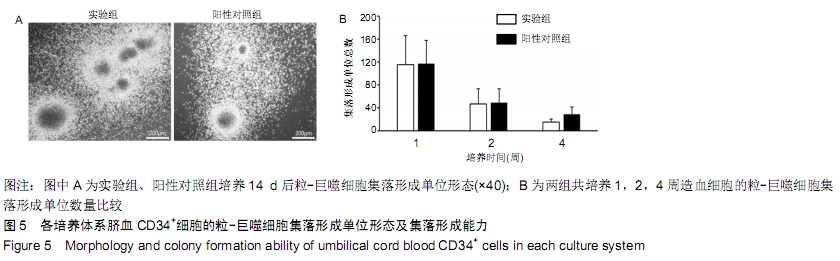
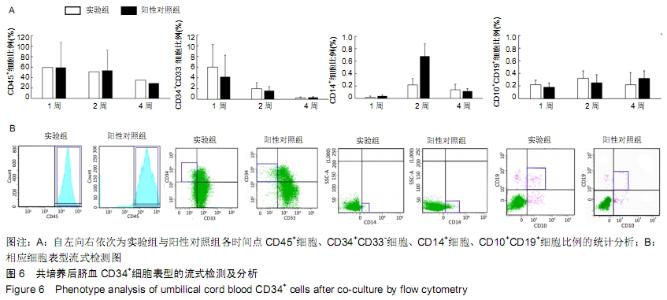
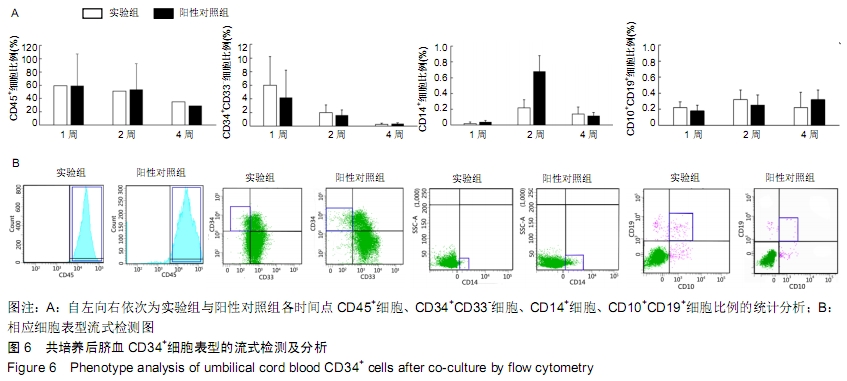
[1] 张哲,曾宪卓,鲁菲,等.基质细胞共培养造血干细胞的应用[J].医药前沿, 2016,6(4):12.
[2] ASADA N, KUNISAKI Y, PIERCE H, et al Differential cytokine contributions of perivascular haematopoietic stem cell niches. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(3):214-223.
[3] SÁ DA BANDEIRA D, CASAMITJANA J, CRISAN M. Pericytes, integral components of adult hematopoietic stem cell niches. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;171:104-113.
[4] LUCAS D. The Bone Marrow Microenvironment for Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1041: 5-18.
[5] LI ZY, WANG CQ, LU G, et al. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on hematopoietic recovery and acute graft-versus-host disease in murine allogeneic umbilical cord blood transplantation model. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;70(1):115-122.
[6] 蒋曲,张红宾.间充质干细胞在造血干细胞移植中的作用[J].重庆医学, 2015,44(36):5164-5167.
[7] KADEKAR D, KALE V, LIMAYE L. Differential ability of MSCs isolated from placenta and cord as feeders for supporting ex vivo expansion of umbilical cord blood derived CD34(+) cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:201.
[8] 章守琴,李维佳,史明霞,等.人羊膜间充质干细胞支持造血的体外实验[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(49): 9235-9238.
[9] MRAVIC M, ASATRIAN G, SOO C, et al. From pericytes to perivascular tumours: correlation between pathology, stem cell biology, and tissue engineering. Int Orthop. 2014;38(9): 1819-1824.
[10] CAPLAN AI. New MSC: MSCs as pericytes are Sentinels and gatekeepers. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(6):1151-1159.
[11] CRISAN M, YAP S, CASTEILLA L, et al. A perivascular origin for mesenchymal stem cells in multiple human organs. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3(3):301-313.
[12] CORSELLI M, CHIN CJ, PAREKH C, et al. Perivascular support of human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Blood. 2013;121(15):2891-2901.
[13] SÁ DA BANDEIRA D, CASAMITJANA J, CRISAN M. Pericytes, integral components of adult hematopoietic stem cell niches. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;171:104-113.
[14] PAKULA A, SPINAZZOLA JM, GUSSONI E. Purification of Myogenic Progenitors from Human Muscle Using Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS). Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1889:1-15.
[15] CHEN WC, SAPAROV A, CORSELLI M, et al. Isolation of blood-vessel-derived multipotent precursors from human skeletal muscle. J Vis Exp. 2014;(90):e51195.
[16] 古晶晶,杨继辉,杨婷婷,等.多参数流式细胞术分选人骨骼肌源性血管内皮细胞和血管外膜细胞的方法[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(21):3357-3364.
[17] WANG L, GU ZY, LIU SF, et al. Single- Versus Double-Unit Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation for Hematologic Diseases: A Systematic Review. Transfus Med Rev. 2019;33(1):51-60.
[18] KUMAR S, GEIGER H. HSC Niche Biology and HSC Expansion Ex Vivo. Trends Mol Med. 2017;23(9):799-819.
[19] TAJER P, PIKE-OVERZET K, ARIAS S, et al. Ex Vivo Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells for Therapeutic Purposes: Lessons from Development and the Niche. Cells. 2019;8(2): E169.
[20] PINEAULT N, ABU-KHADER A. Advances in umbilical cord blood stem cell expansion and clinical translation. Exp Hematol. 2015;43(7):498-513.
[21] 蒋析文,刘悦,马光丽.造血干细胞研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志, 2017,37(19):4935-4936.
[22] GUO B, HUANG X, BROXMEYER HE. Enhancing human cord blood hematopoietic stem cell engraftment by targeting nuclear hormone receptors. Curr Opin Hematol. 2018;25(4): 245-252.
[23] BARI S, ZHONG Q, FAN X, et al. Ex Vivo Expansion of CD34+ CD90+ CD49f+ Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells from Non-Enriched Umbilical Cord Blood with Azole Compounds. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018;7(5):376-393.
[24] 李猛,盛宏霞,张斌,等.脐血来源造血干细胞体外培养扩增技术研究进展[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版), 2016,6(2): 127-133.
[25] COSTA MHG, DE SOURE AM, CABRAL JMS, et al. Hematopoietic Niche - Exploring Biomimetic Cues to Improve the Functionality of Hematopoietic Stem/Progenitor Cells. Biotechnol J. 2018;13(2):1700088.
[26] ZHANG Y. New techniques for umbilical cord blood transplantation.Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2013;33(12):1839-1843.
[27] MEHRASA R, VAZIRI H, OODI A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells as a feeder layer can prevent apoptosis of expanded hematopoietic stem cells derived from cord blood. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2014;3(1):1-10.
[28] 董忱,赵龙,张斌,等.人脐带血来源造血干细胞体外扩增的研究进展[J]. 中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版),2019,9(1):44-49.
[29] 刘禄斌,刘畅,张华,等.人胎盘提取物对脐带血造血干细胞的体外扩增实验研究[J].重庆医学,2010,39(11):1342-1343, 1346.
[30] JING D, FONSECA AV, ALAKEL N, et al. Hematopoietic stem cells in co-culture with mesenchymal stromal cells--modeling the niche compartments in vitro. Haematologica. 2010;95(4):542-550.
[31] ZHANG Y, LI C, JIANG X, et al. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells support culture expansion of long-term culture-initiating cells from cord blood CD34+ cells. Exp Hematol. 2004;32(7):657-664.
[32] SONG Y, BAHNSON A, HALL N, et al. Stem cell traits in long-term co-culture revealed by time-lapse imaging. Leukemia. 2010;24(1):153-161.
[33] WAGNER W, SAFFRICH R, HO AD. The Stromal Activity of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Transfus Med Hemother. 2008;35(3):185-193.
[34] XU ZJ, SHENG LX, LOU YR, et al. Supporting Effect of Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on CD34+ Cell Proliferation and Its Mechanism. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2015;23(3):802-808.
[35] DE SOUZA LE, MALTA TM, KASHIMA HADDAD S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Pericytes: To What Extent Are They Related? Stem Cells Dev. 2016;25(24):1843-1852.
[36] SÁ DA BANDEIRA D, CASAMITJANA J, CRISAN M. Pericytes, integral components of adult hematopoietic stem cell niches. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;171:104-113.
[37] DARVISH M, PAYANDEH Z, SOLEIMANIFAR F, et al. Umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells application in hematopoietic stem cells expansion on nanofiber three-dimensional scaffold. J Cell Biochem. 2019. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28487. [Epub ahead of print]
|