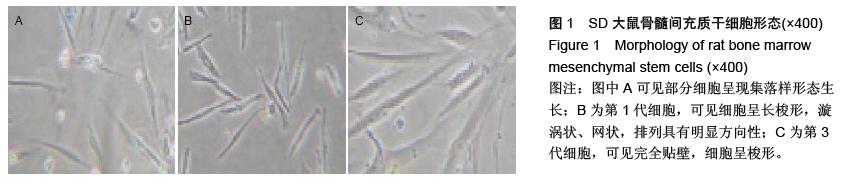
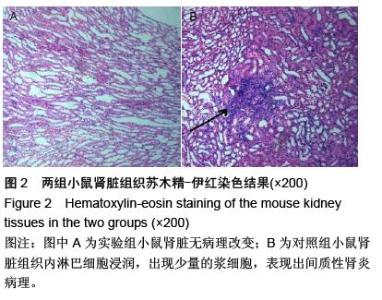
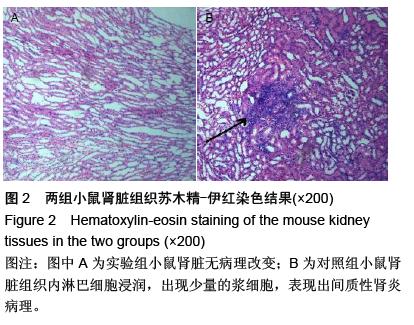
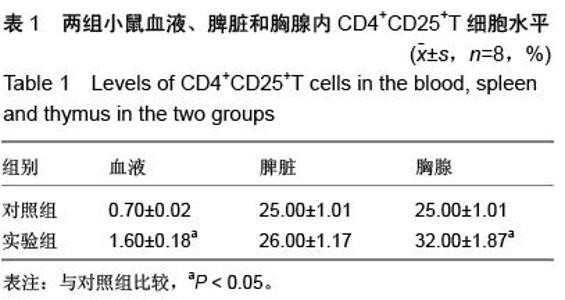
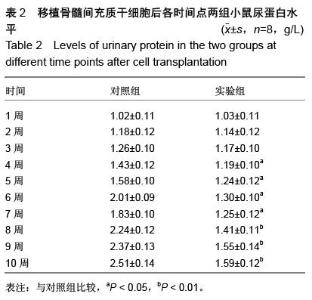
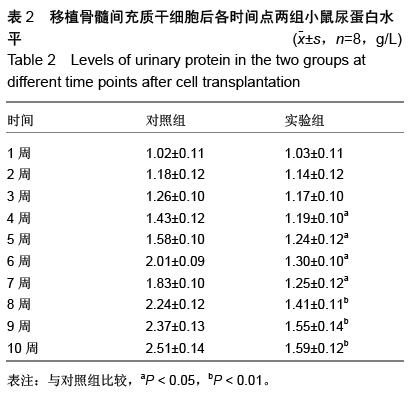
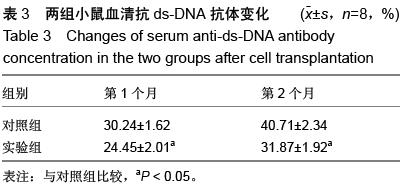
| [1] Prockop DJ. Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 1997;276(5309): 71-74.[2] Friedenstein AJ, Gorskaja JF, Kulagina NN. Fibroblast precursors in normal and irradiated mouse hematopoietic organs. Exp Hematol. 1976;4(5):267-274.[3] Castro-Malaspina H, Gay RE, Resnick G, et al. Characterization of human bone marrow fibroblast colony-forming cells (CFU-F) and their progeny. Blood. 1980;56(2):289-301.[4] Bab I, Ashton BA, Gazit D, et al. Kinetics and differentiation of marrow stromal cells in diffusion chambers in vivo. J Cell Sci. 1986;84:139-151.[5] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见.2006-09-30.[6] Gregory CA, Gunn WG, Peister A, et al. An Alizarin red-based assay of mineralization by adherent cells in culture: comparison with cetylpyridinium chloride extraction. Anal Biochem. 2004;329(1):77-84.[7] Hayashi O, Katsube Y, Hirose M, et al. Comparison of osteogenic ability of rat mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, periosteum, and adipose tissue. Calcif Tissue Int. 2008;82(3):238-247.[8] Planat-Benard V, Silvestre JS, Cousin B, et al. Plasticity of human adipose lineage cells toward endothelial cells: physiological and therapeutic perspectives.Circulation. 2004;109(5):656-663.[9] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies.Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228.[10] Lin CS, Xin ZC, Deng CH, et al. Defining adipose tissue-derived stem cells in tissue and in culture. Histol Histopathol. 2010;25(6):807-815.[11] Shetty P, Cooper K, Viswanathan C. Comparison of proliferative and multilineage differentiation potentials of cord matrix, cord blood, and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Asian J Transfus Sci. 2010; 4(1):14-24.[12] Hiyama A, Mochida J, Iwashina T, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells in a canine disc degeneration model. J Orthop Res. 2008;26(5):589- 600.[13] Richardson SM, Hughes N, Hunt JA, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation to NP-like cells in chitosan-glycerophosphate hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2008;29(1):85-93.[14] Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005;105(4):1815-1822.[15] Wei A, Tao H, Chung SA, et al. The fate of transplanted xenogeneic bone marrow-derived stem cells in rat intervertebral discs. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(3): 374-379.[16] Lepski G, Jannes CE, Strauss B, et al. Survival and neuronal differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells transplanted into the rodent brain are dependent upon microenvironment.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(9): 2769-2782.[17] Yang Z, Li K, Yan X, et al. Amelioration of diabetic retinopathy by engrafted human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in streptozotocin diabetic rats. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010;248(10): 1415-1422.[18] Shainer R, Gaberman E, Levdansky L, et al. Efficient isolation and chondrogenic differentiation of adult mesenchymal stem cells with fibrin microbeads and micronized collagen sponges. Regen Med. 2010;5(2): 255-265.[19] Marongiu F, Gramignoli R, Sun Q, et al. Isolation of amniotic mesenchymal stem cells. Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol. 2010;Chapter 1:Unit 1E.5.[20] Zeddou M, Briquet A, Relic B, et al. The umbilical cord matrix is a better source of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) than the umbilical cord blood. Cell Biol Int. 2010; 34(7):693-701.[21] Baer PC, Griesche N, Luttmann W, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro: evaluation of an optimal expansion medium preserving stemness. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(1):96-106.[22] Vilalta M, Dégano IR, Bagó J, et al. Biodistribution, long-term survival, and safety of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplanted in nude mice by high sensitivity non-invasive bioluminescence imaging. Stem Cells Dev. 2008;17(5): 993-1003.[23] Satija NK, Singh VK, Verma YK, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy: a new paradigm in regenerative medicine. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(11-12): 4385-4402.[24] Morel L.Genetics of SLE: evidence from mouse models. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6(6):348-357.[25] Georgin-Lavialle S, Aouba A, Mouthon L, et al. The telomere/telomerase system in autoimmune and systemic immune-mediated diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2010;9(10):646-651.[26] Hu N, Long H, Zhao M, et al. Aberrant expression pattern of histone acetylation modifiers and mitigation of lupus by SIRT1-siRNA in MRL/lpr mice. Scand J Rheumatol. 2009;38(6):464-471.[27] Sioud M, Mobergslien A, Boudabous A, et al. Evidence for the involvement of galectin-3 in mesenchymal stem cell suppression of allogeneic T-cell proliferation. Scand J Immunol. 2010;71(4):267-274. [28] Spaggiari GM, Abdelrazik H, Becchetti F, et al. MSCs inhibit monocyte-derived DC maturation and function by selectively interfering with the generation of immature DCs: central role of MSC-derived prostaglandin E2. Blood. 2009;113(26):6576-6583.[29] Sioud M, Mobergslien A, Boudabous A, et al. Evidence for the involvement of galectin-3 in mesenchymal stem cell suppression of allogeneic T-cell proliferation. Scand J Immunol. 2010;71(4):267-274.[30] Asari S, Itakura S, Ferreri K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells suppress B-cell terminal differentiation. Exp Hematol. 2009;37(5):604-615.[31] Spaggiari GM, Capobianco A, Becchetti S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-natural killer cell interactions: evidence that activated NK cells are capable of killing MSCs, whereas MSCs can inhibit IL-2-induced NK-cell proliferation. Blood. 2006;107(4):1484-1490.[32] Bochev I, Elmadjian G, Kyurkchiev D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow or adipose tissue differently modulate mitogen-stimulated B-cell immunoglobulin production in vitro. Cell Biol Int. 2008;32(4):384-393.[33] Xinqiang S, Fei L, Nan L, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of experimental rheumatoid arthritis with low-dose methotrexate by increasing partially CD4+CD25+ Treg cells and inducing Th1 to Th2 shift in both cells and cytokines. Biomed Pharmacother. 2010;64(7):463-471.[34] Azab NA, Bassyouni IH, Emad Y, et al. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells (TREG) in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients: the possible influence of treatment with corticosteroids. Clin Immunol. 2008; 127(2):151-157.[35] Kaya TI, Eskandari G, Guvenc U, et al. CD4+CD25+ Treg cells in patients with toenail onychomycosis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2009;301(10):725-729.[36] Jung YJ, Seoh JY. Feedback loop of immune regulation by CD4+CD25+ Treg. Immunobiology. 2009;214(4):291-302.[37] Hu AP, Du JM, Li JY, et al. Oridonin promotes CD4+/CD25+ Treg differentiation, modulates Th1/Th2 balance and induces HO-1 in rat splenic lymphocytes. Inflamm Res. 2008;57(4):163-170. |