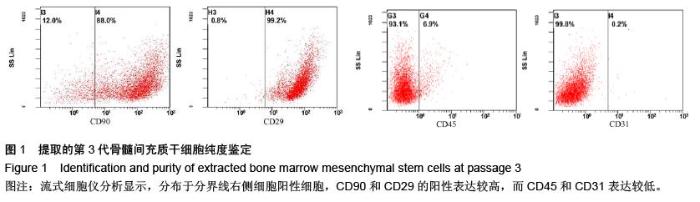
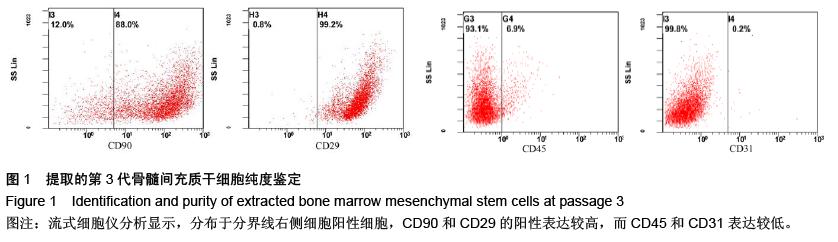
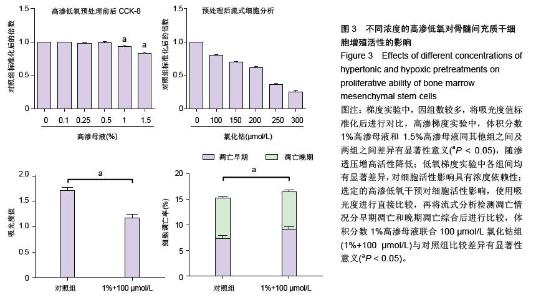
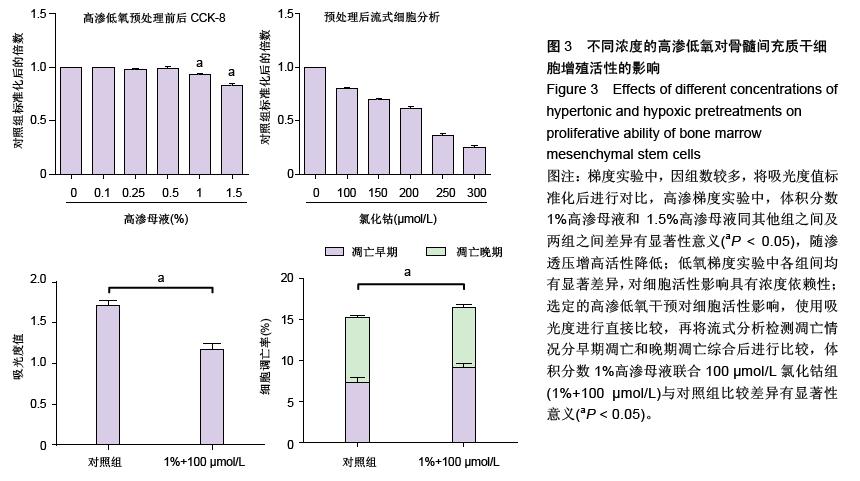
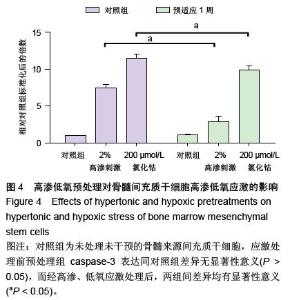
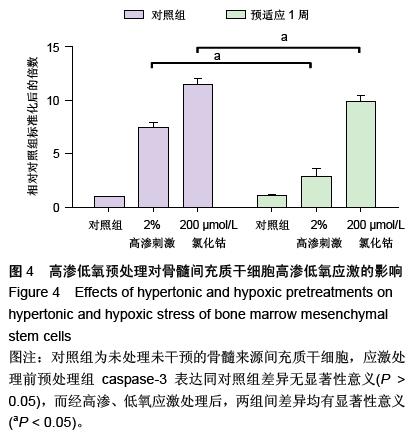
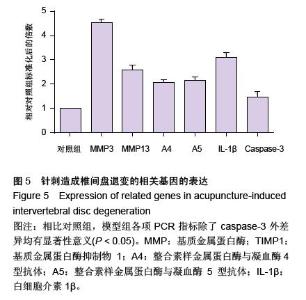
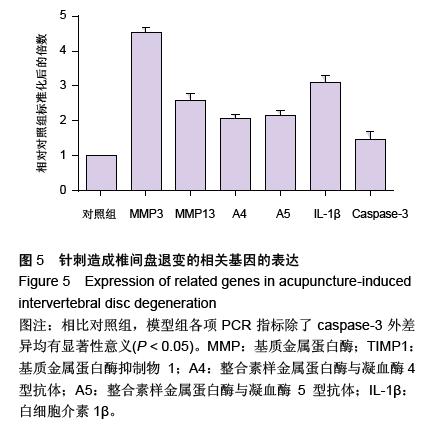
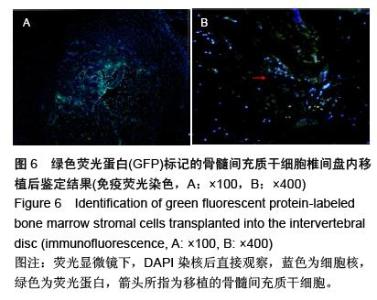
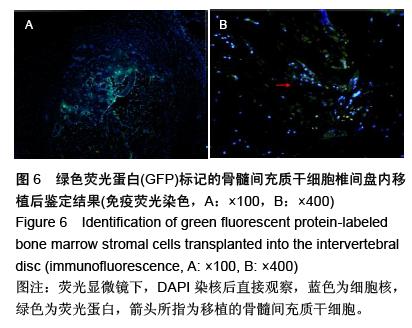
| [1] Raj PP. Intervertebral disc: anatomy-physiology-pathophysiology-treatment. Pain Pract. 2008;8:18-44.[2] Wilkens P, Scheel IB, Grundnes O, et al. Prognostic factors of prolonged disability in patients with chronic low back pain and lumbar degeneration in primary care: a cohort study. Spine. 2013;38:65-74.[3] Bhattacharya A, Leigh JP. Musculoskeletal disorder costs and medical claim filing in the US retail trade sector. Ind Health. 2011;49:517-522.[4] Ding F, Shao ZW, Xiong LM. Cell death in intervertebral disc degeneration. Apoptosis. 2013;18:777-785.[5] Richardson SM, Hughes N, Hunt JA, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation to NP-like cells in chitosan-glycerophosphate hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2008;29:85-93.[6] Cao C, Zou J, Liu X, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells slow intervertebral disc degeneration through the NF-kappaB pathway. Spine J. 2015;15:530-538.[7] Leung VY, Aladin DM, Lv F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells reduce intervertebral disc fibrosis and facilitate repair. Stem cells. 2014;32:2164-2177.[8] Ma CJ, Liu X, Che L, et al. Stem cell therapies for intervertebral disc degeneration: immune privilege reinforcement by Fas/FasL regulating machinery. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;10:285-295.[9] Nachemson A, Lewin T, Maroudas A, et al. In vitro diffusion of dye through the end-plates and the annulus fibrosus of human lumbar inter-vertebral discs. Acta Orthop Scand. 1970;41:589-607.[10] Grunhagen T, Wilde G, Soukane DM, et al. Nutrient supply and intervertebral disc metabolism. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 2:30-35.[11] Urban JP, McMullin JF. Swelling pressure of the inervertebral disc: influence of proteoglycan and collagen contents. Biorheology. 1985;22:145-157.[12] Bartels EM, Fairbank JC, Winlove CP, et al. Oxygen and lactate concentrations measured in vivo in the intervertebral discs of patients with scoliosis and back pain. Spine. 1998;23:1-7.[13] Buchmaier BS, Bibi A, Muller GA, et al. Renal cells express different forms of vimentin: the independent expression alteration of these forms is important in cell resistance to osmotic stress and apoptosis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e68301.[14] Li C, Guo Z, Guo B, et al. Inhibition of the endogenous CSE/H(2)S system contributes to hypoxia and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9:2467-2472.[15] Nallamshetty S, Chan SY, Loscalzo J. Hypoxia: a master regulator of microRNA biogenesis and activity. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;64:20-30.[16] Leung Y, Kandyba E, Chen YB, et al. Bifunctional ectodermal stem cells around the nail display dual fate homeostasis and adaptive wounding response toward nail regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111: 15114-15119.[17] Madonna R, Gorbe A, Ferdinandy P, et al. Glucose metabolism, hyperosmotic stress, and reprogramming of somatic cells. Mol Biotechnol. 2013;55:169-178. [18] Zhang H, Ma X, Zhang L, et al. The ability to form cartilage of NPMSC and BMSC in SD rats. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8:4989-4996.[19] Issy AC, Castania V, Castania M, et al. Experimental model of intervertebral disc degeneration by needle puncture in Wistar rats. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2013;46: 235-244.[20] Wei A, Tao H, Chung SA, et al. The fate of transplanted xenogeneic bone marrow-derived stem cells in rat intervertebral discs. J Orthop Res. 2009;27:374-379.[21] Rani A, Prasad S. CoCl2-induced biochemical hypoxia down regulates activities and expression of super oxide dismutase and catalase in cerebral cortex of mice. Neurochem Res. 2014;39:1787-1796.[22] Schumacker PT. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1). Crit Care Med. 2005;33:S423-S425.[23] Adams JM, Difazio LT, Rolandelli RH, et al. HIF-1: a key mediator in hypoxia. Acta Physiol Hung. 2009;96: 19-28.[24] Zhang J, Cao J, Weng Q, et al. Suppression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) by tirapazamine is dependent on eIF2alpha phosphorylation rather than the mTORC1/4E-BP1 pathway. PLoS One. 2010;5:e13910.[25] Clouzeau C, Godefroy D, Riancho L, et al. Hyperosmolarity potentiates toxic effects of benzalkonium chloride on conjunctival epithelial cells in vitro. Mol Vis. 2012;18:851-863.[26] Numata T, Sato K, Christmann J, et al. The DeltaC splice-variant of TRPM2 is the hypertonicity-induced cation channel in HeLa cells, and the ecto-enzyme CD38 mediates its activation. J Physiol. 2012;590: 1121-1138.[27] Tao YQ, Liang CZ, Li H, et al. Potential of co-culture of nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells and nucleus pulposus cells in hyperosmotic microenvironment for intervertebral disc regeneration. Cell Biol Int. 2013;37:826-834.[28] Silva RA, Palladino MV, Cavalheiro RP, et al. Activation of the low molecular weight protein tyrosine phosphatase in keratinocytes exposed to hyperosmotic stress. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0119020.[29] Misheva M, Kaur G, Ngoei KR, et al. Intracellular mobility and nuclear trafficking of the stress-activated kinase JNK1 are impeded by hyperosmotic stress. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1843:253-264. |