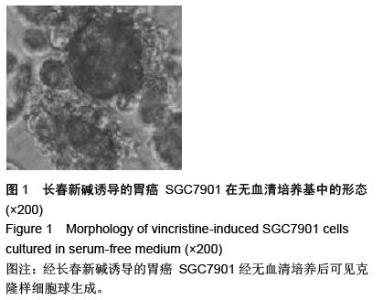
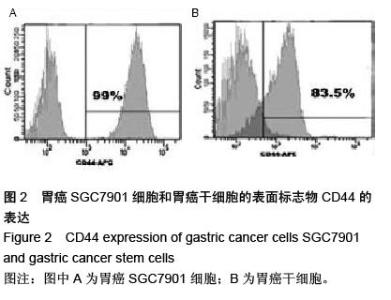
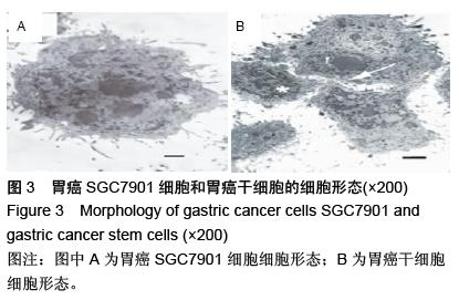
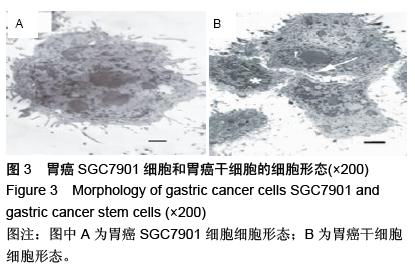
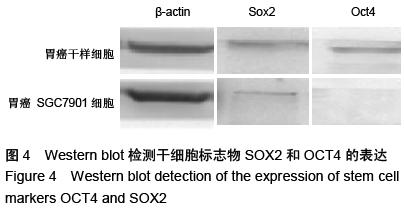
| [1] 邹小农,孙喜斌,陈万青,等.2003-2007年中国胃癌发病与死亡情况分析[J].肿瘤,2012,32(2):109-114.[2] Putney J, O'Grady G, Angeli TR, et al. Determining the efficient inter-electrode distance for high-resolution mapping using a mathematical model of human gastric dysrhythmias. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2015; 2015:1448-1451. [3] 郑朝旭,郑荣寿,陈万青.中国2009年胃癌发病与死亡分析[J].中国肿瘤,2013,22(5):327-332.[4] Tang X, Zhang J, Che X, et al. The Clinicopathological Features and Long-Term Survival Outcomes of Mucinous Gastric Carcinoma: a Consecutive Series of 244 Cases from a Single Institute. J Gastrointest Surg. 2016. in press.[5] Boskovi? T, Zivojinov M, Sabo JI, et al. Rare solitary fibrous tumor of the stomach: A case report. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2015;72(11):1035-1038.[6] 季加孚.我国胃癌防治研究三十年回顾[J].中国肿瘤临床, 2013,(22):1345-1351.[7] 张学伟,郑安斌,石炜,等.胃癌根治术后复发转移的影响因素及其对预后的影响[J].实用癌症杂志,2015,(7): 1062-1064.[8] Barchi LC, Yagi OK, Jacob CE, et al. Predicting recurrence after curative resection for gastric cancer: External validation of the Italian Research Group for Gastric Cancer (GIRCG) prognostic scoring system. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2016;42(1):123-131. [9] Lee JW, Jo K, Cho A, et al. Relationship Between 18F-FDG Uptake on PET and Recurrence Patterns After Curative Surgical Resection in Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer. J Nucl Med. 2015;56(10): 1494-1500. [10] 朱正纲.胃癌复发、转移诊治难点与对策[J].中国实用外科杂志,2015,(10):1037-1039,1045.[11] Squires MH 3rd, Kooby DA, Poultsides GA, et al. Effect of Perioperative Transfusion on Recurrence and Survival after Gastric Cancer Resection: A 7-Institution Analysis of 765 Patients from the US Gastric Cancer Collaborative. J Am Coll Surg. 2015; 221(3):767-777. [12] 胡建昆,赵林勇,陈心足.胃癌术后复发、转移的随访与监测[J].中国实用外科杂志,2015,(10):1082-1085.[13] 杨浪.胃癌干细胞的分离鉴定及其在胃癌侵袭转移中的作用与分子机制[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2013.[14] Choi YJ, Kim N, Chang H, et al. Helicobacter pylori-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition, a potential role of gastric cancer initiation and an emergence of stem cells. Carcinogenesis. 2015;36(5): 553-563. [15] Wang J, Yu J, Wu J, et al. Experimental study of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on regulating the biological characteristics of gastric cancer cells. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015;18(2):159-165.[16] 牛磊,郗洪庆,陈凛.Lgr5-Wnt/β-catenin信号通路与胃癌干细胞的研究进展[J].解放军医学院学报,2014, 35(12): 1268-1272.[17] 查郎. HMGA2促进胃癌上皮细胞间质转化分子机制研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2013.[18] Boyle MJ, Williams B, Ross L. Assessing student paramedic visual and verbal checks for defibrillation safety-an observational study. Springerplus. 2015;4: 773. [19] 庄铭锴,陈丰霖.上皮间质转化相关的生物标志在胃癌中的研究进展[J].世界华人消化杂志,2013,(30):3204- 3210.[20] 印凡,徐霞,赵东宝.上皮间质转化与肿瘤干细胞在肿瘤转移中的作用[J].第二军医大学学报,2011,32(12): 1357-1360.[21] 吴楠蝶,魏嘉,刘宝瑞.胃癌分子靶向治疗的研究进展[J].医学研究生学报,2014,(12):1318-1322.[22] Jung JH, Kim BJ, Choi CH, et al. Second-look endoscopy with prophylactic hemostasis is still effective after endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric neoplasm. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(48): 13518-13523. [23] Kim HS, Kim SO, Kim BS. Use of a clinical pathway in laparoscopic gastrectomy for gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(48):13507-13517. [24] 李一鑫,李秀明,张楠,等.幽门螺杆菌感染与胃癌发生发展及预后的相关性研究[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志,2015, 22(2): 91-94,108.[25] 王为忠,康振华.胃癌复发转移的再手术问题[J].中国实用外科杂志,2008,(9):770-772.[26] Marrelli D, Morgagni P, de Manzoni G, et al. External Validation of a Score Predictive of Recurrence after Radical Surgery for Non-Cardia Gastric Cancer: Results of a Follow-Up Study. J Am Coll Surg. 2015; 221(2):280-290. [27] Kang WM, Meng QB, Yu JC, et al. Factors associated with early recurrence after curative surgery for gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(19): 5934-5940. [28] 张燕平,李宁,邓文英,等.干细胞标志物SOX-2、β-catenin表达与胃癌术后复发转移关系[J].中国癌症杂志,2014, (9):684-689.[29] Zhao Y, Feng F, Zhou YN. Stem cells in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(1):112-123. [30] Wang M, Cai J, Huang F, et al. Pre-treatment of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells with interleukin-6 abolishes their growth-promoting effect on gastric cancer cells. Int J Mol Med. 2015;35(2): 367-375. [31] Morisaki T, Yashiro M, Kakehashi A, et al. Comparative proteomics analysis of gastric cancer stem cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e110736.[32] 李阳,赵永福.胃癌干细胞的分离、鉴定及其特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(32):5188-5192.[33] 杨燕,邹晓平.上皮间质转化与胃癌的研究进展[J].国际消化病杂志,2014,34(5):334-337.[34] Rahimi A, Vazini H, Alhani F, et al. Relationship Between Low Back Pain With Quality of Life, Depression, Anxiety and Stress Among Emergency Medical Technicians. Trauma Mon. 2015;20(2): e18686.[35] 朱登峰,姜波健.胃癌转移中上皮间质转化的作用及其调控机理[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2015,(10):1284- 1288.[36] Kim CH, Kim GW, Cha WC, et al. For how long can two emergency medical technicians perform high-quality cardiopulmonary resuscitation? J Int Med Res. 2015;43(6):841-850.[37] 马飞,张明迪,王雅杰.IL-6与上皮-间质转化因子胃癌组织表达相关性及其临床意义研究[J].中国实用外科杂志, 2014,(3):259-263.[38] Knox S, Dunne S, Cullen W, et al. A qualitative assessment of practitioner perspectives post-introduction of the first continuous professional competence (CPC) guidelines for emergency medical technicians in Ireland. BMC Emerg Med. 2015;15:11.[39] 徐晶钰,张璇,秦志丰,等.从细胞上皮-间质转化角度探讨从痰论治胃癌侵袭转移[J].中华中医药学刊,2014,(9): 2076-2078.[40] Wood D, Kalinowski EJ, Miller DR, et al. Pediatric continuing education for EMTs: recommendations for content, method, and frequency. The National Council of State Emergency Medical Services Training Coordinators. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2004;20(4): 269-272. [41] Dwyer D. Experiences of registered nurses as managers and leaders in residential aged care facilities: a systematic review. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2011;9(4):388-402.[42] Buckley S, Coleman J, Davison I, et al. The educational effects of portfolios on undergraduate student learning: a Best Evidence Medical Education (BEME) systematic review. BEME Guide No. 11. Med Teach. 2009;31(4):282-298.[43] Hwang JY, Kim KY, Lee KH. Factors that influence the acceptance of telemetry by emergency medical technicians in ambulances: an application of the extended technology acceptance model. Telemed J E Health. 2014;20(12):1127-1134.[44] 张翠.上皮-间质转化(EMT)与胃癌耐药和转移关系的初步研究[D].延安:延安大学,2012. [45] Boudreaux E, Jones GN, Mandry C, et al. Patient care and daily stress among emergency medical technicians. Prehosp Disaster Med. 1996;11(3): 188-193; discussion 193-194. [46] Boudreaux E, Mandry C. Sources of stress among emergency medical technicians (Part I): What does the research say? Prehosp Disaster Med. 1996;11(4): 296-301. |