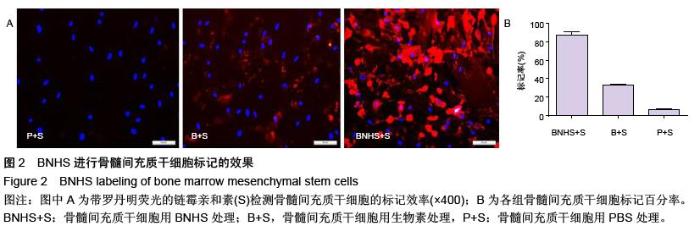
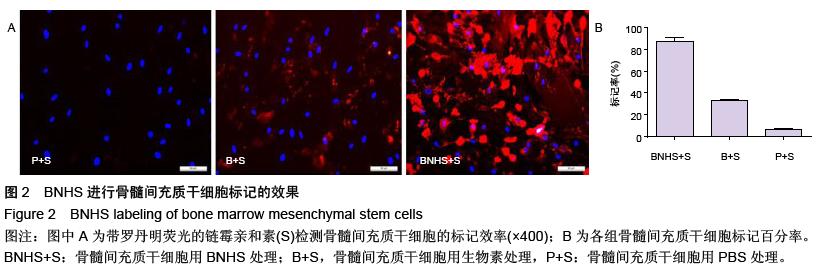
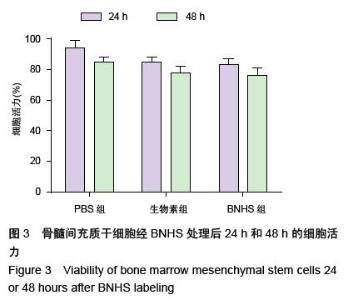
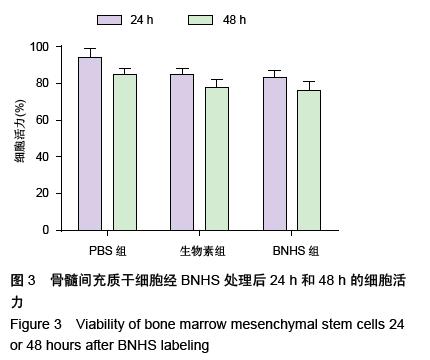
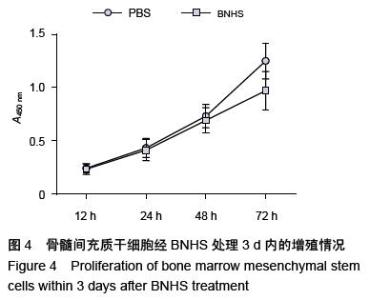
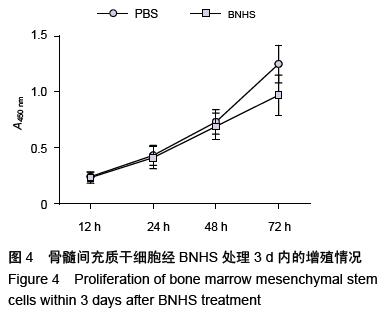
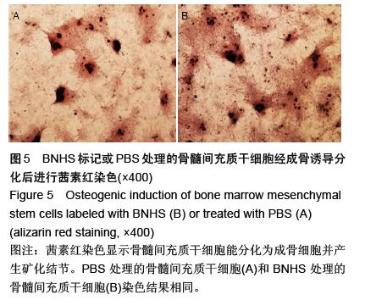
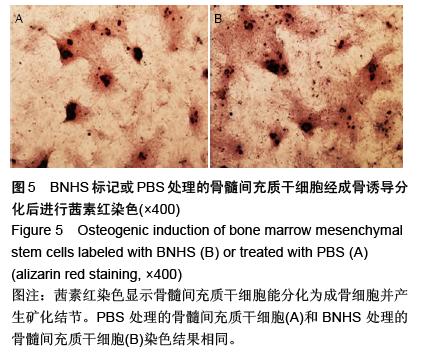
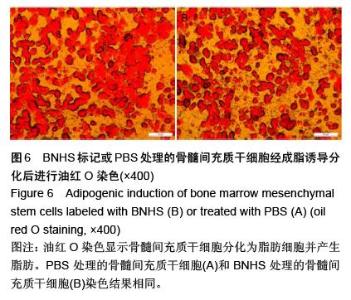
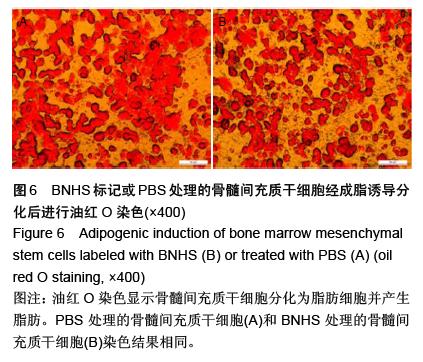
| [1] Volarevic V, Arsenijevic N, Lukic ML, et al. Concise review: Mesenchymal stem cell treatment of the complications of diabetes mellitus. Stem Cells. 2011; 29(1):5-10. [2] Porada CD, Zanjani ED, Almeida-Porad G. Adult mesenchymal stem cells: a pluripotent population with multiple applications. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2006; 1(3): 365-369.[3] Kocher AA, Schuster MD, Szabolcs MJ, et al. Neovascularization of ischemic myocardium by human bone-marrow-derived angioblasts prevents cardiomyocyte apoptosis, reduces remodeling and improves cardiac function. Nat Med. 2001;7(4): 430-436.[4] Lange C, Tögel F, Ittrich H, et al. Administered mesenchymal stem cells enhance recovery from ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute renal failure in rats. Kidney Int. 2005;68(4):1613-1617.[5] Fox JM, Chamberlain G, Ashton BA, et al. Recent advances into the understanding of mesenchymal stem cell trafficking. Br J Haematol. 2007;137(6): 491-502.[6] Tögel F, Zhang P, Hu Z, et al. VEGF is a mediator of the renoprotective effects of multipotent marrow stromal cells in acute kidney injury. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(8B):2109-2114.[7] Morigi M, Introna M, Imberti B, et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells accelerate recovery of acute renal injury and prolong survival in mice. Stem Cells. 2008;26(8):2075-2082.[8] Kale S, Karihaloo A, Clark PR, et al. Bone marrow stem cells contribute to repair of the ischemically injured renal tubule. J Clin Invest. 2003;112(1):42-49.[9] Zhang M, Mal N, Kiedrowski M, et al. SDF-1 expression by mesenchymal stem cells results in trophic support of cardiac myocytes after myocardial infarction. FASEB J. 2007;21(12):3197-3207.[10] Sarkar D, Zhao W, Gupta A, et al. Cell surface engineering of mesenchymal stem cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;698:505-523.[11] Kawada H, Fujita J, Kinjo K, et al. Nonhematopoietic mesenchymal stem cells can be mobilized and differentiate into cardiomyocytes after myocardial infarction. Blood. 2004;104(12):3581-3587.[12] Sarkar D, Vemula PK, Zhao W, et al. Engineered mesenchymal stem cells with self-assembled vesicles for systemic cell targeting. Biomaterials. 2010;31(19): 5266-5274.[13] 熊建文,肖化,张镇西.MTT法和CCK-8法检测细胞活性之测试条件比较[J].激光生物学报,2007,16(5):559-562.[14] Yago T, Leppänen A, Qiu H, et al. Distinct molecular and cellular contributions to stabilizing selectin-mediated rolling under flow. J Cell Biol. 2002; 158(4):787-799. |