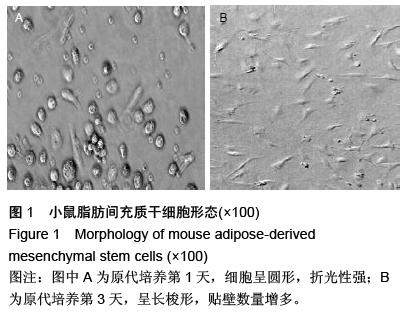
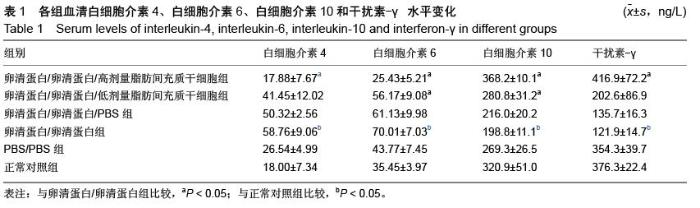
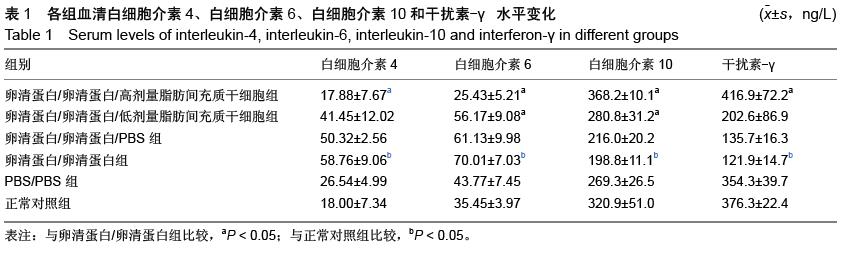
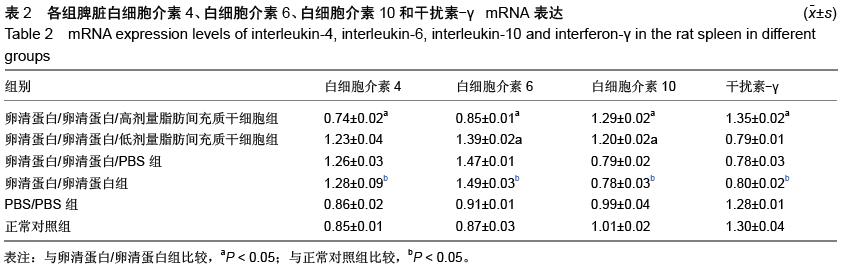
| [1] Li X, Wang J, Cao J, et al. Immunoregulation of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on the Chronic Cigarette Smoking-Induced Lung Inflammation in Rats. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015: 932923.[2] James S, Fox J, Afsari F, et al. Multiparameter Analysis of Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Identifies Distinct Immunomodulatory and Differentiation- Competent Subtypes. Stem Cell Reports. 2015;4(6): 1004-1015. [3] Fan L, Yu Z, Li J, et al. Immunoregulation effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in xenogeneic acellular nerve grafts transplant. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2014;34(7):999-1010. [4] Dorronsoro A, Fernández-Rueda J, Fechter K, et al. Human mesenchymal stromal cell-mediated immunoregulation: mechanisms of action and clinical applications. Bone Marrow Res. 2013;2013:203643. [5] Akiyama K, Chen C, Wang D, et al. Mesenchymal- stem-cell-induced immunoregulation involves FAS-ligand-/FAS-mediated T cell apoptosis. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10(5):544-555. [6] Fan FQ, Li D. Progression of relationship between mesenchymal stem cell and immunoregulation. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2011;32(5): 355-358.[7] Pradier A, Passweg J, Villard J, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells and skin fibroblasts inhibit natural killer cell proliferation and cytotoxic activity. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(5):681-691.[8] Sa YL, Shen XM, Shi KQ, et al. Effects of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on cytokines secretion from allogeneic dendritic cell activated cytokine-induced killer cells. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010;26(10):988-991. [9] Chen X, Armstrong MA, Li G. Mesenchymal stem cells in immunoregulation.Immunol Cell Biol. 2006;84(5): 413-421. [10] Jin JG, Hu JW, Ning HM, et al.The effect of MSC on cytokine production by naive T cell differentiated in vitro.Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2005;26(6):339-341.[11] Chang HY, Seo JH, Kim HY, et al. Allergic diseases in preschoolers are associated with psychological and behavioural problems.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2013;5(5):315-321.[12] Chen MH, Su TP, Chen YS,et al.Allergic rhinitis in adolescence increases the risk of depression in later life: a nationwide population-based prospective cohort study.J Affect Disord. 2013;145(1):49-53.[13] Monticelli LA, Sonnenberg GF, Abt MC, et al. Innate lymphoid cells promote lung-tissue homeostasis after infection with influenza virus. Nat Immunol. 2011; 12(11):1045-1054.[14] Halim TY, Krauss RH, Sun AC, et al. Lung natural helper cells are a critical source of Th2 cell-type cytokines in protease allergen-induced airway inflammation. Immunity. 2012;36(3):451-463.[15] Halim TY, Steer CA, Mathä L, et al. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells are critical for the initiation of adaptive T helper 2 cell-mediated allergic lung inflammation. Immunity. 2014;40(3):425-435.[16] Barrett NA, Boyce JA. Activation of group 2 innate lymphoid cells: a new role for cysteinyl leukotrienes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132(1):214-216.[17] Ziegler SF, Artis D. Sensing the outside world: TSLP regulates barrier immunity. Nat Immunol. 2010;11(4): 289-293.[18] Harada M, Hirota T, Jodo AI, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin gene promoter polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to bronchial asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011;44(6):787-793.[19] Ziegler SF. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin and allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130(4):845-852.[20] Siracusa MC, Saenz SA, Wojno ED, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin-mediated extramedullary hematopoiesis promotes allergic inflammation. Immunity. 2013;39(6):1158-1170.[21] Kabata H1, Moro K, Fukunaga K, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin induces corticosteroid resistance in natural helper cells during airway inflammation. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2675.[22] Gauvreau GM, O'Byrne PM, Boulet LP, et al Effects of an anti-TSLP antibody on allergen-induced asthmatic responses. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(22):2102-2110.[23] 齐景翠,赵玉林,李伟亚,等.郑州地区变应性鼻炎患儿变应原谱分析[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015,29(5): 404-406.[24] 李江丽,刘积平,文玉敏.百色市儿童变应性鼻炎过敏原调查与分析[J].右江民族医学院学报,2014,36(6):885-886.[25] 张蕾,艾涛,罗荣华.成都地区1123 例儿童过敏原皮肤点刺结果分析[J].海南医学,2014,25(23):3550-3552.[26] 奚玲.过敏性鼻炎未成年患者常见吸入性变应原分析[J].华西医学,2014,29(4):710-713.[27] 刘保国,李志英,李宗珊,等.抗组胺药临床应用[J].临床合理用药杂志,2015,8(8):85-86.[28] 孔隽.氮卓斯汀喷鼻剂治疗过敏性鼻炎的临床疗效[J].中国药物经济学,2015,(1):62-63.[29] 田卓莎,宋岩.抗组胺鼻喷雾剂与糖皮质激素鼻喷雾剂对于常年性变应性鼻炎的疗效[J].中国医药指南, 2015, 13(1):145-146.[30] 冯韶燕,樊韵平,李磊.白三烯受体拮抗剂联合鼻用激素治疗变应性鼻炎的系统评价[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2015,29(3):207-211.[31] Tintinger GR, Feldman C, Theron AJ, et al. Montelukast: more than a cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonist. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010; 10:2403-2413.[32] Scaife A, Miller D, Spiteri-Cornish D, et al. Inhibitory effects of Montelukast on mediator release by nasal epithelial cells from asthmatic subjects with or without allergic rhinitis Respir Med. 2013;107(12):1859-1865.[33] Goh BS, Ismail MI, Husain S. Quality of life assessment in patients with moderate to severe allergic rhinitis treated with montelukast and/or intranasal steroids: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Laryngol Otol. 2014; 128(3):242-248.[34] 朱和军.变应性鼻炎中西医治疗现状概述[J].光明中医, 2015,30(2):393-395.[35] 黄慧.益气固表中药治疗常年性变应性鼻炎临床研究[J].亚太传统医药,2015,11(6):87-88.[36] 宋建华,杨青.玉屏风散治疗变应性鼻炎56 例疗效观察[J].临床合理用药杂志,2013,6(2):124-125.[37] 赵小慧,周鸿飞.针刺治疗过敏性鼻炎概况[J].实用中医内科杂志,2015,29(1):174-176.[38] 李敏,张勤修,刘洋.针刺联合药物治疗变应性鼻炎患者的临床疗效观察[J].中国民康医学,2015,27(4):81-82.[39] 吴国谦.标准化粉尘瞒变应原疫苗滴剂舌下含服治疗变应性鼻炎的疗效及安全性[J].当代医学, 2015,21(2): 95-96.[40] 张志敏,李国义,陈向军.特异性免疫治疗对变应性鼻炎患者免疫功能的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2015,24(3): 281-283.[41] 葛荣明,余少卿.变应性鼻炎的舌下特异性免疫治疗[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2015,29(9):777-780.[42] 梁美君,徐睿,许庚.变应性鼻炎研究新进展[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科,2015,29(3):202-206.[43] 陈阳静,高建民,赵谦.变应性鼻炎舌下特异性免疫治疗的疗效分析[J].基层医学沦坛,2015,19(4)483-484.[44] 程雷.变应性鼻炎特异性舌下免疫治疗[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2015,29(3):197-198.[45] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编委会鼻科组,中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组.变应性鼻炎诊断和治疗指南[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2009,44(12): 977-978. [46] Fiocchi A, Fox AT. Preventing progression of allergic rhinitis: the role of specific immunotherapy. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed. 2011;96(3):91-100.[47] Hankin CS, Cox L, Bronstone A, et al. Allergy immunotherapy: reduced health care costs in adults and children with allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131(4):1084-1091.[48] Kopp MV. Role of immunmodulators in allergen- specific immunotherapy.Allergy. 2011;66(6): 792-797.[49] Cho KS, Park HK, Park HY, et al. IFATS collection: Immunomodulatory effects of adipose tissue-derived stem cells in an allergic rhinitis mouse model. Stem Cells. 2009;27(1):259-265.[50] Akdis M, Verhagen J, Taylor A, et al. Immune responses in healthy and allergic individuals are characterized by a fine balance between allergen-specific T regulatory 1 and T helper 2 cells.J Exp Med. 2004;199(11):1567-1575. |