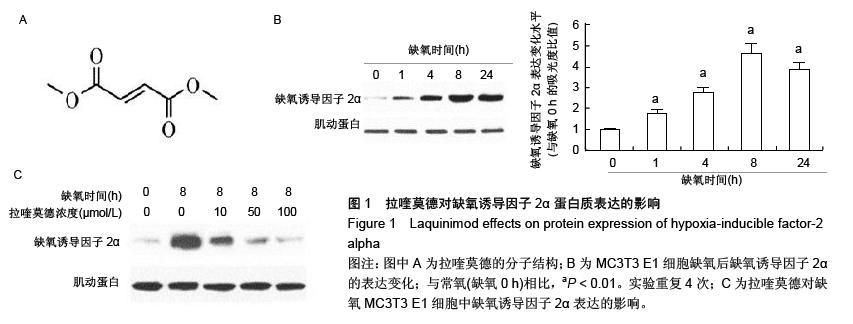
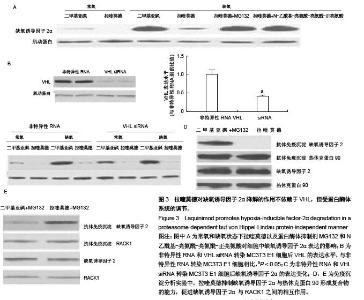
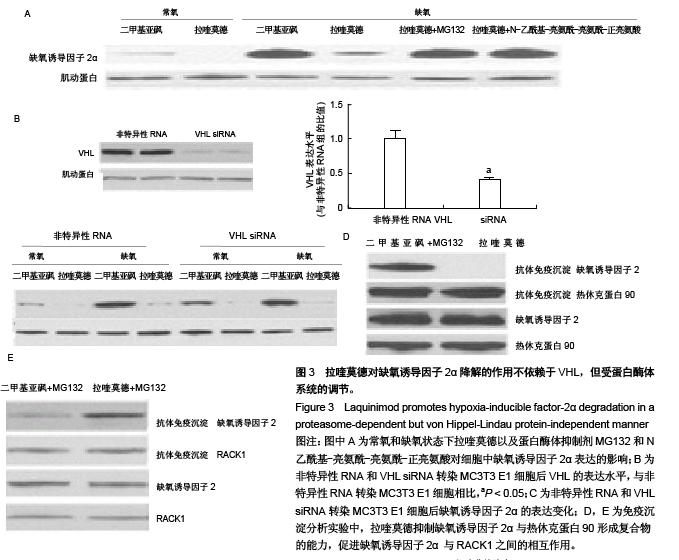
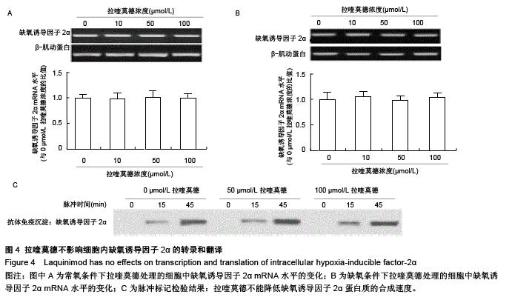
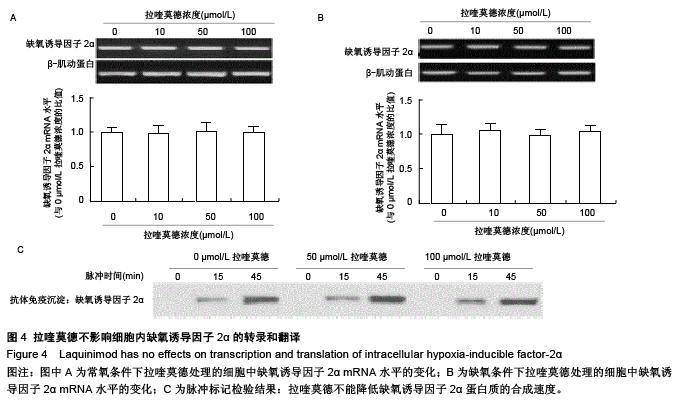
| [1] Auxenfans C, Lequeux C, Perrusel E, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) as a source of endothelial cells in the reconstruction of endothelialized skin equivalents. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012;6(7):512-518.
[2] Bae D, Mondragon-Teran P, Hernandez D, et al. Hypoxia enhances the generation of retinal progenitor cells from human induced pluripotent and embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(8): 1344-1355.
[3] Xu L, Xie K, Mukaida N, et al. Hypoxia-induced elevation in interleukin-8 expression by human ovarian carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1999;59(22): 5822-5829.
[4] Salceda S, Caro J. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) protein is rapidly degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system under normoxic conditions. Its stabilization by hypoxia depends on redox-induced changes. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(36): 22642-22647.
[5] Miyauchi Y, Sato Y, Kobayashi T, et al. HIF1α is required for osteoclast activation by estrogen deficiency in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(41):16568-16573.
[6] Isaacs JS, Jung YJ, Mimnaugh EG, et al. Hsp90 regulates a von Hippel Lindau-independent hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha-degradative pathway. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(33):29936-29944.
[7] Jolivel V, Luessi F, Masri J, et al. Modulation of dendritic cell properties by laquinimod as a mechanism for modulating multiple sclerosis. Brain. 2013;136(Pt 4): 1048-1066.
[8] Aharoni R, Saada R, Eilam R, et al. Oral treatment with laquinimod augments regulatory T-cells and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression and reduces injury in the CNS of mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 2012;251(1-2):14-24.
[9] Hung SP, Ho JH, Shih YR, et al. Hypoxia promotes proliferation and osteogenic differentiation potentials of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 2012; 30(2):260-266.
[10] Das R, Jahr H, van Osch GJ, et al. The role of hypoxia in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: considerations for regenerative medicine approaches. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2010;16(2):159-168.
[11] Zuk PA. The adipose-derived stem cell: looking back and looking ahead. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21(11):1783-1787.
[12] She T, Hu DH, Zhang YG, et al. Biological effects of paracrine from insulin stimulated adipose-derived stem cells (ADSC) on human vascular endothelial cells. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2011;27(1):32-36.
[13] Liang J, Zhang Z, Liang L, et al. HIF-1α regulated tongue squamous cell carcinoma cell growth via regulating VEGF expression in a xenograft model. Ann Transl Med. 2014;2(9):92.
[14] Jolivel V, Luessi F, Masri J, et al. Modulation of dendritic cell properties by laquinimod as a mechanism for modulating multiple sclerosis. Brain. 2013;136(Pt 4):1048-1066.
[15] Aharoni R, Saada R, Eilam R, et al. Oral treatment with laquinimod augments regulatory T-cells and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression and reduces injury in the CNS of mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 2012;251(1-2):14-24.
[16] Bassi G, Pacelli L, Carusone R, et al. Adipose-derived stromal cells (ASCs). Transfus Apher Sci. 2012;47(2): 193-198.
[17] Xu F, Li X, Chang CK, et al. Establishment and validation of an updated diagnostic FCM scoring system based on pooled immunophenotyping in CD34+ blasts and its clinical significance for myelodysplastic syndromes. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88706.
[18] Abrisqueta P, Villamor N, Terol MJ, et al. Rituximab maintenance after first-line therapy with rituximab, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and mitoxantrone (R-FCM) for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2013;122(24):3951-3959.
[19] Todorich B, Yiu G, Hahn P. Current and investigational pharmacotherapeutic approaches for modulating retinal angiogenesis. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2014; 7(3):375-391.
[20] Chiu CJ, Taylor A. Dietary hyperglycemia, glycemic index and metabolic retinal diseases. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2011;30(1):18-53.
[21] Jacoby JJ, Erez B, Korshunova MV, et al. Treatment with HIF-1alpha antagonist PX-478 inhibits progression and spread of orthotopic human small cell lung cancer and lung adenocarcinoma in mice. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5(7):940-949.
[22] Liao HY, Wang GP, Gu LJ, et al. HIF-1α siRNA and cisplatin in combination suppress tumor growth in a nude mice model of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(2): 473-477.
[23] Wang L, Zhou W, Gou S, et al. Insulin promotes proliferative vitality and invasive capability of pancreatic cancer cells via hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha pathway. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2010;30(3):349-353.
[24] 邓婷,张俊文.缺氧诱导因子-1α与缺氧状态下胃癌细胞侵袭的相关性[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2010,23(7): 696-699.
[25] Zhang JJ, Wu HS, Wang L, et al. Expression and significance of TLR4 and HIF-1alpha in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16(23):2881-2888.
[26] Hopkins PM, Kermeen F, Duhig E, et al. Oil red O stain of alveolar macrophages is an effective screening test for gastroesophageal reflux disease in lung transplant recipients. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2010;29(8): 859-864.
[27] Zheng M, Chi Y, Yi H, et al. Decolorization of Alizarin Red and other synthetic dyes by a recombinant laccase from Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Lett. 2014; 36(1):39-45.
[28] Tomsho JW, Benkovic SJ. Elucidation of the mechanism of the reaction between phenylboronic acid and a model diol, Alizarin Red S. J Org Chem. 2012;77(5):2098-2106.
[29] Bresson C, Darolles C, Carmona A, et al. Cobalt chloride speciation, mechanisms of cytotoxicity on human pulmonary cells, and synergistic toxicity with zinc. Metallomics. 2013;5(2):133-143.
[30] Kim EH, Won JH, Hwang I, et al. Cobalt Chloride-induced Hypoxia Ameliorates NLRP3-Mediated Caspase-1 Activation in Mixed Glial Cultures. Immune Netw. 2013;13(4):141-147.
[31] Liu Y, Wang C, Wang Y, et al. Cobalt chloride decreases fibroblast growth factor-21 expression dependent on oxidative stress but not hypoxia-inducible factor in Caco-2 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012;264(2):212-221.
[32] Lee ZH, Khoobehi K, Chiu ES. Autologous fat grafting for treatment of facial atrophy in Behcet's disease: a case report. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013; 66(12):1759-1762.
[33] Salim F, Chana J. et al. Fat grafting for overcorrected gynaecomastia. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013; 66(10):e294.
[34] Aoyagi Y, Kuroda M, Asada S, et al. Fibrin glue increases the cell survival and the transduced gene product secretion of the ceiling culture-derived adipocytes transplanted in mice. Exp Mol Med. 2011; 43(3):161-167.
[35] Krumboeck A, Giovanoli P, Plock JA. Fat grafting and stem cell enhanced fat grafting to the breast under oncological aspects--recommendations for patient selection. Breast. 2013;22(5):579-584.
[36] Vinci V, Borbon G, Codolini L, et al. Fat grafting versus adipose-derived stem cell therapy: distinguishing indications, techniques, and outcomes. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2013;37(4):856-857. |