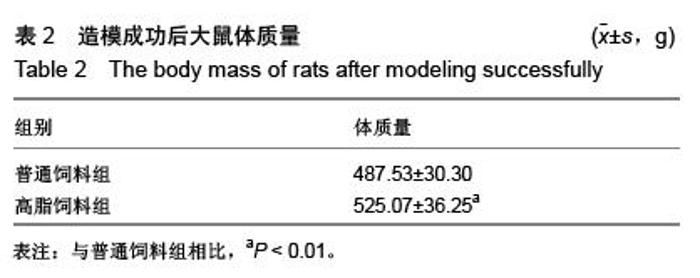
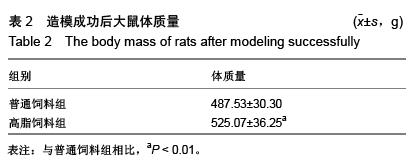
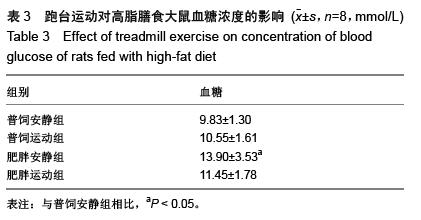
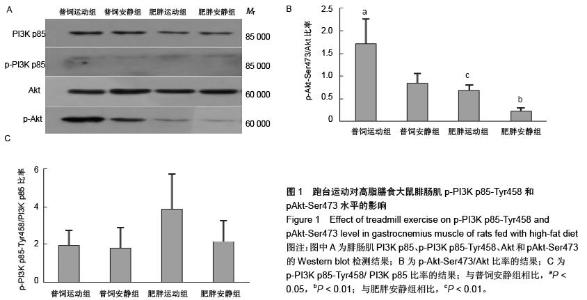
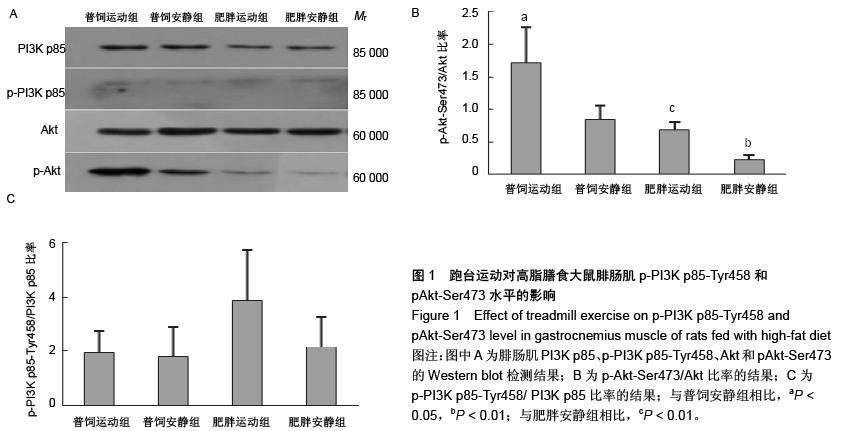
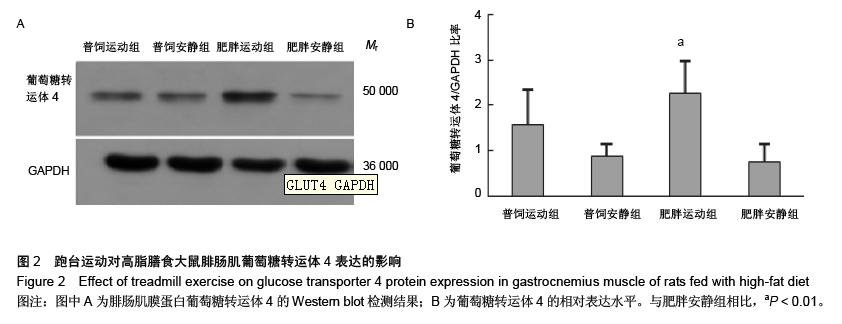
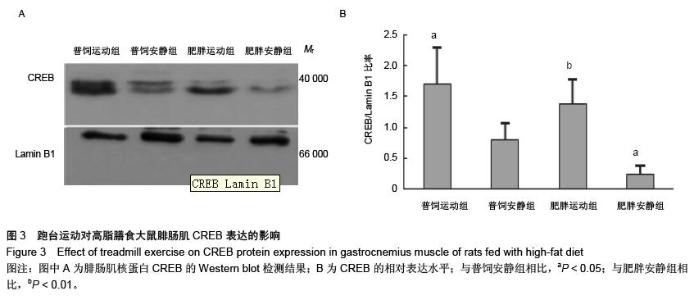
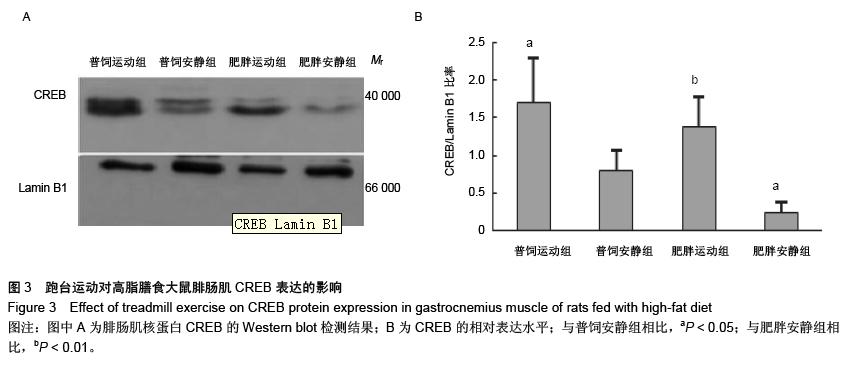
| [1] Huang S, Czech MP. The GLUT4 glucose transporter. Cell Metab. 2007;5(4):237-252.[2] Larance M, Ramm G, James DE. The GLUT4 code. Mol Endocrinol. 2008;22(2):226-233. [3] 曾玉,顾平清,刘康生,等.葡萄糖转运蛋白4在宫内发育迟缓大鼠骨骼肌中的表达和转位[J].中国现代医学杂志,2015,25(9): 14-20.[4] 董坤,方启晨,贾伟平. Rab5在胰岛素抵抗机制中的作用[J].上海医学, 2012,35(1):80-83.[5] Krook A, Wallberg-Henriksson H, Zierath JR. Sending the signal: molecular mechanisms regulating glucose uptake. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36(7):1212-1217.[6] Bernard JR, Crain AM, Rivas DA, et al. Chronic aerobic exercise enhances components of the classical and novel insulin signalling cascades in Sprague-Dawley rat skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 2005;183(4):357-366.[7] 李慧阁,牛燕媚,刘彦辉,等.小鼠骨骼肌细胞蛋白激酶B底物160在有氧运动促进葡萄糖转运体4转运中的作用[J].中国康复医学杂志,2010,25(6):501-506.[8] Iacobazzi V, Infantino V, Costanzo P, et al. Functional analysis of the promoter of the mitochondrial phosphate carrier human gene: identification of activator and repressor elements and their transcription factors. Biochem J. 2005;391(Pt 3):613-621.[9] Altarejos JY, Montminy M. CREB and the CRTC co-activators: sensors for hormonal and metabolic signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12(3):141-151. [10] Wu Z, Huang X, Feng Y, et al. Transducer of regulated CREB-binding proteins (TORCs) induce PGC-1alpha transcription and mitochondrial biogenesis in muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(39):14379-14384. [11] Stewart R, Flechner L, Montminy M, et al. CREB is activated by muscle injury and promotes muscle regeneration. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24714. [12] Phuong NT, Lim SC, Kim YM, et al. Aromatase induction in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer: Role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent CREB activation. Cancer Lett. 2014; 351(1):91-99. [13] 张荷香,毛丽梅,刘烈刚,等.饮食诱导肥胖和肥胖抵抗大鼠脂联素水平研究[J].营养学报,2010,32(4):316-319.[14] Bedford TG, Tipton CM, Wilson NC, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979;47(6):1278-1283.[15] Sasidharan SR, Joseph JA, Anandakumar S, et al. An experimental approach for selecting appropriate rodent diets for research studies on metabolic disorders. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:752870. [16] Buettner R, Schölmerich J, Bollheimer LC. High-fat diets: modeling the metabolic disorders of human obesity in rodents. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2007;15(4):798-808.[17] 仇利红,高静,牛文彦.C2C12-GLUT4HA骨骼肌细胞株的筛选[J].天津医药,2013,41(6):580-582.[18] 李凡,黄慧,宋立功,等.坎地沙坦改善C2C12细胞胰岛素敏感性的机制研究[J].中华保健医学杂志,2015,17(1):21-23.[19] 汤諹,李树清,李凡,等.缺血后适应对树鼩海马CA1区神经元Akt信号转导调控的机制研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2011,27(3): 560-565.[20] 刘伟,陈明卫,童俊露,等.丹蛭降糖胶囊改善肥胖大鼠骨骼肌胰岛素抵抗机制的初步研究[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2014,20(22): 151-156.[21] 童俊露.生活方式对胰岛素抵抗大鼠骨骼肌脂联素、APPL1及GLUT4表达的影响[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2013.[22] Lee SH, Lee HJ, Lee YH, et al. Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) improves insulin sensitivity in high fat fed Sprague-Dawley rats. Phytother Res. 2012;26(1):142-147. [23] 赵海燕,王勇,马永平,等.胰岛素信号转导障碍与胰岛素抵抗[J].新医学,2010,41(4):267-271.[24] 刘树欣,刘玉倩,王海涛,等.运动对葡萄糖转运蛋白4介导的骨骼肌糖摄取调节机制的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2010, 25(6): 592-594.[25] 刘杰,蔡颖,冯彦景,等.运动对胰岛素抵抗小鼠PPAR-γ、Glut-4表达的影响[J].心血管康复医学杂志,2012,21(6):566-571.[26] Chibalin AV, Yu M, Ryder JW, et al. Exercise-induced changes in expression and activity of proteins involved in insulin signal transduction in skeletal muscle: differential effects on insulin-receptor substrates 1 and 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(1):38-43.[27] Huang H, Cheville JC, Pan Y, et al. PTEN induces chemosensitivity in PTEN-mutated prostate cancer cells by suppression of Bcl-2 expression. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(42): 38830-38836.[28] Pugazhenthi S, Nesterova A, Sable C, et al. Akt/protein kinase B up-regulates Bcl-2 expression through cAMP-response element-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(15):10761-10766.[29] Calvo JA, Daniels TG, Wang X, et al. Muscle-specific expression of PPARgamma coactivator-1alpha improves exercise performance and increases peak oxygen uptake. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008;104(5):1304-1312. [30] Wu H, Kanatous SB, Thurmond FA, et al. Regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle by CaMK. Science. 2002;296(5566):349-352.[31] Teodoro BG, Baraldi FG, Sampaio IH, et al. Melatonin prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and insulin resistance in rat skeletal muscle. J Pineal Res. 2014;57(2):155-167.[32] Bruno NE, Kelly KA, Hawkins R, et al. Creb coactivators direct anabolic responses and enhance performance of skeletal muscle. EMBO J. 2014;33(9):1027-1043. |