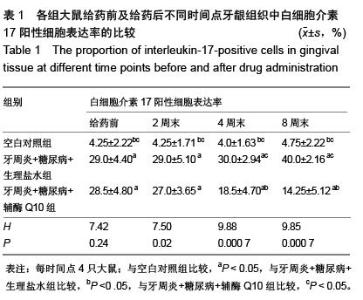
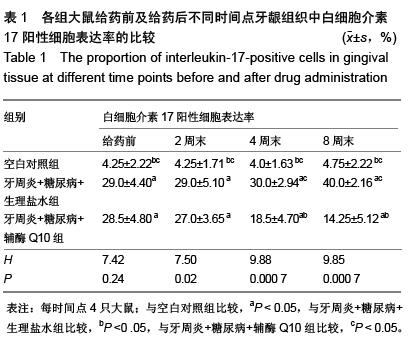
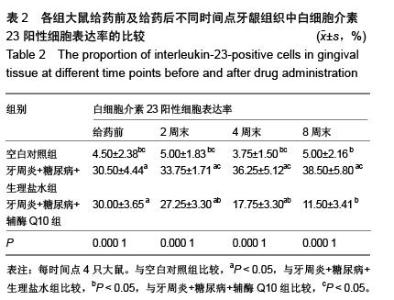
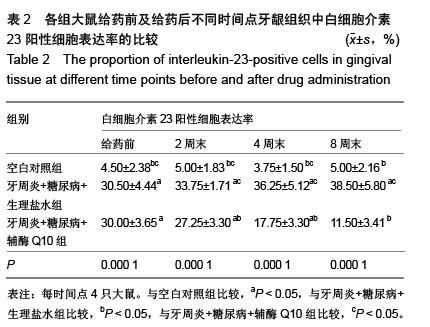
| [1] Darveau RP. Periodontitis: a polymicrobial disruption of host homeostasis. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010;8(7):481-490. [2] Farquharson D, Butcher JP, Culshaw S. Periodontitis, Porphyromonas, and the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Mucosal Immunol. 2012;5(2):112-120.[3] Emrich LJ, Shlossman M, Genco RJ. Periodontal disease in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Periodontol. 1991; 62(2):123-131.[4] Soni S, Agrawal PK, Sharma N, et al. Coenzyme Q10 and periodontal health: A review. Int J Oral and Maxillofac Pathol. 2012;3:21-26.[5] Hans M, Prakash S, Gupta S. Clinical evaluation of topical application of perio-Q gel (Coenzyme Q(10)) in chronic periodontitis patients. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2012;16(2): 193-199.[6] Brandmeyer EA, Shen Q, Thimmesch AR, et al. Using coenzyme Q10 in clinical practice. Nursing. 2014;44(3):63-66.[7] Lee D, Kim KY, Shim MS, et al. Coenzyme Q10 ameliorates oxidative stress and prevents mitochondrial alteration in ischemic retinal injury. Apoptosis. 2014;19(4):603-614.[8] Noh YH, Kim KY, Shim MS, et al. Inhibition of oxidative stress by coenzyme Q10 increases mitochondrial mass and improves bioenergetic function in optic nerve head astrocytes. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e820.[9] Tiano L, Belardinelli R, Carnevali P, et al. Effect of coenzyme Q10 administration on endothelial function and extracellular superoxide dismutase in patients with ischaemic heart disease: a double-blind, randomized controlled study. Eur Heart J. 2007;28(18):2249-2255.[10] Moreira PI, Zhu X, Wang X, et al. Mitochondria: a therapeutic target in neurodegeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010; 1802(1): 212-220.[11] Sourris KC, Harcourt BE, Tang PH, et al. Ubiquinone (coenzyme Q10) prevents renal mitochondrial dysfunction in an experimental model of type 2 diabetes. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012;52(3):716-723.[12] Holzhausen M, Rossa Júnior C, Marcantonio Júnior E, et al. Effect of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition on the development of ligature-induced periodontitis in rats. J Periodontol. 2002;73(9):1030-36.[13] 穆松牛,高云,万福生,等.链尿佐菌素加高糖高脂饮食复制大鼠2型糖尿病模型[J].中国比较医学杂志,2008,18(2):19-22.[14] 徐菁玲,高津福,赵静.牙周病与肺感染相关性实验动物模型的建立[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2006,16(2):93-97.[15] 蒋朝晖,吕玉晶,赵芳,等.高脂高糖饮食结合链脲佐菌素建立2型糖尿病大鼠模型的改良[J].中国比较医学杂志,2011,21(1): 33-36.[16] 于德民,吴锐,尹潍,等. 实验性链脲佐菌素糖尿病动物模型的研究[J].中华糖尿病杂志,1995,2:105-109.[17] Maríková Z, Kindlová M, Mrklas L, et al. Effect of changes in oral conditions on periodontal health in rats. III. Effect of sialoadenectomy on ligature-induced periodontal changes. Cesk Stomatol.1979;79(2):92-96.[18] Di Paola R, Marzocco S, Mazzon E, et al. Effect of aminoguanidine in ligature-induced periodontitis in rats. J Dent Res. 2004;83(4):343-348.[19] 邓雨泉,付云,齐刘英,等.糖基化终产物对人牙龈成纤维细胞增殖和基质金属蛋白酶-1合成的影响[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志, 2009,3(3):250-254.[20] 金惠娇,薛毅,陈光,等.辅酶Q10对大鼠实验性牙周炎牙龈组织中肿瘤坏死因子α及白细胞介素10表达的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2013,48(11):660-663.[21] Ohyama H, Kato-Kogoe N, Kuhara A, et al. The involvement of IL-23 and the Th17 pathway in periodontitis. J Dent Res. 2009;88(7):633-638.[22] Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM, et al. IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 2005;201(2):233-240.[23] Kolls JK, Lindén A. Interleukin-17 family members and inflammation. Immunity. 2004;21(4):467-476.[24] Cua DJ, Tato CM. Innate IL-17-producing cells: the sentinels of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10(7): 479-489.[25] Numasaki M, Fukushi J, Ono M, et al. Interleukin-17 promotes angiogenesis and tumor growth. Blood. 2003;101(7): 2620-2627.[26] Patel DD, Lee DM, Kolbinger F, et al. Effect of IL-17A blockade with secukinumab in autoimmune diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72 Suppl 2:ii116-23.[27] Luzza F, Parrello T, Monteleone G, et al. Up-regulation of IL-17 is associated with bioactive IL-8 expression in Helicobacter pylori-infected human gastric mucosa. J Immunol. 2000;165(9):5332-5337.[28] Lester SR, Bain JL, Johnson RB, et al. Gingival concentrations of interleukin-23 and -17 at healthy sites and at sites of clinical attachment loss. J Periodontol. 2007g;78(8):1545-1550.[29] 惠光艳,吴广升.牙周非手术治疗对2型糖尿病伴牙周炎患者白介素-23及代谢指标的影响[J].中国疗养医学,2013,22(8): 686-688. |