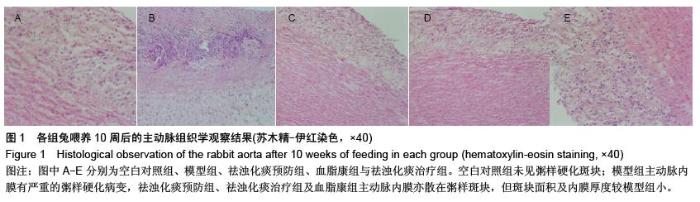
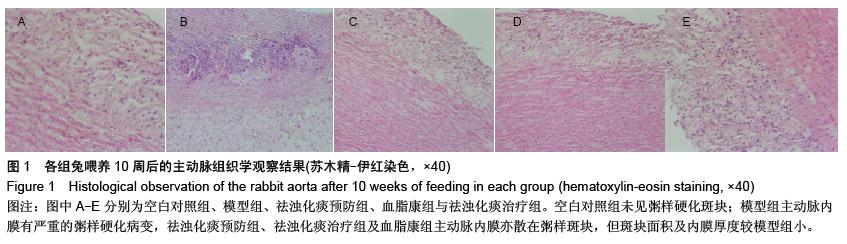
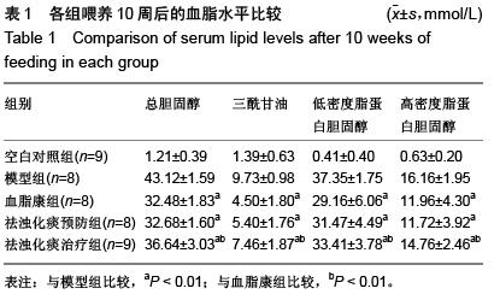
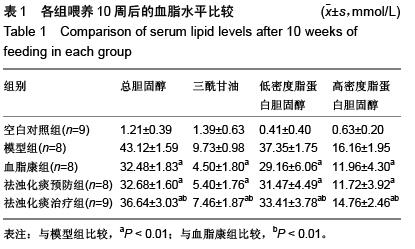
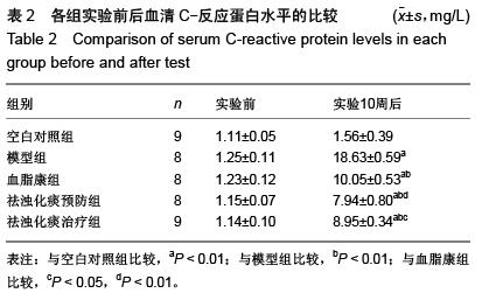
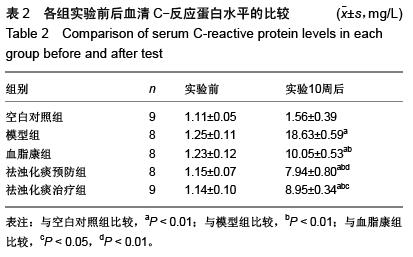
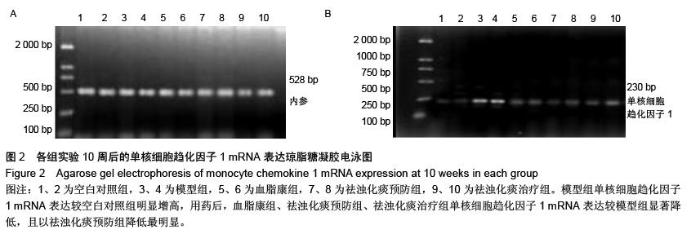
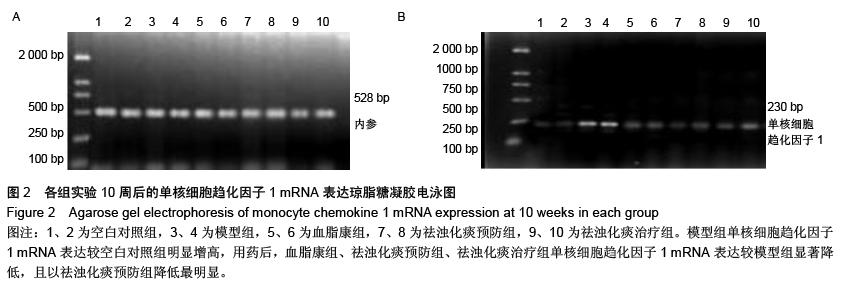
| [1] Das UN.Clinical laboratory tools to diagnose inflammation. Adv Clin Chem.2006;41:189-229.
[2] Libby P.Current concepts of the pathogenesis of the acute coronary syndrome.Circulation.2001;104:365-372.
[3] Calkin AC,Giunti S,Sheehy KJ,et al.The HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor rosuvastatin and the angiotensin receptor antagonist candesartan attenuate atherosclerosis. Diabetologia. 2008; 51(9):1731.
[4] Arao K,Yasu T,Umemoto T,et al.Effects of pitavastatin on fasting and postprandial endothelial function and blood rheology in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Circ J.2009;73(8):1523.
[5] 倪量,王融冰,郭会军,等.中药治疗HAART相关血脂异常的临床研究[J].中国中药杂志,2013,38(15):2443-2447.
[6] 高敏,王凤荣.通脉降浊方治疗不稳定性心绞痛临床疗效观察[J],辽宁中医药大学学报,2013,15(2):147-149.
[7] 李贵才,刘占军,徐德锌,等.家兔动脉粥样硬化模型稳定性的观察[J].中国比较医学杂志,2004,14(5):294-297.
[8] 施新猷.医用实验动物学[M].西安:陕西科学技术出版社,1989: 235-237.
[9] 韩丽蓓,吴兢,朱爱华,等.原发性血脂异常患者情志证素分布规律及与血脂指标相关性研究[J].北京中医药大学学报:中医临床版, 2013,20(6):20-22.
[10] 韩丽蓓,李小玲,刘金凤,等.原发性血脂异常与2型糖尿病合并血脂异常中医证素及血脂指标对照研究[J].北京中医药大学学报:中医临床版,2011,18(4):1-3.
[11] Hana X,Gross RW. Global analyses of cellular lipdomes directly from crude extracts of biological samples by ESI mass spectrometry:a bridge to lipidomics. J of Lipid Res, 2003,(06):1071-1079.
[12] 丁绍祥.脂质代谢失调作为慢性应激原致动脉粥样硬化的发病机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2011,6(31):2154-2157.
[13] Ross R. Atheroselerosis is an inflammatory disease.Am Heart J.1999;138(5Pt2): S419-420.
[14] 徐也鲁.动脉粥样硬化-一种慢性炎症过程[J].中国动脉硬化杂志, 2001,9(2):93-95.
[15] 刘红彬,籍振国,张源祥,等.炎症因子与冠状动脉病变严重程度的关系探讨[J].临床荟萃, 2005,20(9):487-490.
[16] 范砚超,张国平,唐明,等.从毒论治动脉粥样硬化初探[J].山东中医杂志,2004,23(5): 261-263.
[17] 杨永宗.动脉粥样硬化性心血管病基础与临床[M].北京:科学出版社,2004:51.
[18] 沈彬,吴宗贵.炎症与动脉粥样硬化[J].心血管病学进展杂志, 2004, 25(1):66-69.
[19] 李超林.单核细胞趋化因子-1与糖尿病大血管病变[J].医学综述, 2004,10(11):672-674.
[20] 郑娴,王凤荣.大柴胡汤对动脉粥样硬化家兔血脂及炎性因子表达的影响[J].中医杂志,2013,54(19):1681-1685.
[21] 钱小奇,张敏.大柴胡汤治疗无症状性高脂血症临床研究[J].国医论坛,2001,16(1):11-12.
[22] 丁开科,刘翔.硝酸甘油伍大柴胡汤加减治疗胆绞痛90例临床观察[J].四川中医,2003,21(8):25-26.
[23] Liu JJ,Huang TS,Cheng WF,et al.Baicalein and ba-icalin are potent inhibitors of angiogenesis: Inhibition ofendothelial cell proliferation, migration and differentiation.Int J Cancer. 2003; 106(4):559-565.
[24] 郑虎占,董泽宏,佘靖.中药现代研究与应用[M].4版.北京:学苑出版社,1998:3022.
[25] 尹春萍,吴继洲.泽泻及其活性成分免疫调节作用研究进展[J].中草药,2001,32(12):1132.
[26] 王凤荣,王帅,孙淼.大柴胡汤防治动脉粥样硬化的理论基础与研究依据[J].中华中医药学刊,2010,28(10):2038-2039.
[27] Tohru N,Satoe S,Hideki K,et al.Effects of three Chinese herbal medicines on plasma and liver lipids in mice fed a high-fat diet.J Ethnopharmacol.2007;109(2):236-240.
[28] Fumihiko Y,Akira I,Yasuhiro K,et al.Effects of Dai-saiko-to (Da-Chai-Hu-Tang) on plasma lipids and atherosclerotic lesions in female heterozygous heritable Kurosawa and Kusanagi-hypercholesterolemic (KHC) rabbits.Pharmacol Res.2004;50(3):223-230.
[29] Iizuka A,Iijima OT,Yoshie F,et al.Inhibitory effects of Dai-saiko-to (Da-Chai-Hu-Tang) on the progression of atherosclerotic lesions in Kurosawa and Kusanagi- hypercholesterolemic rabbits.J Ethnopharmacol. 1998;63(3): 209-218. |