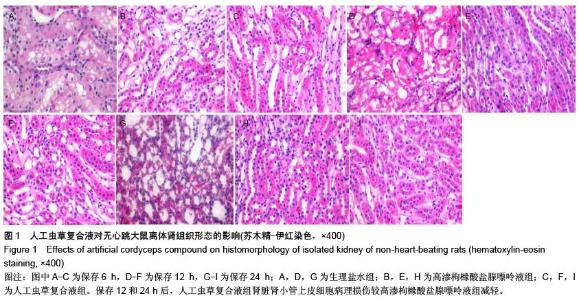
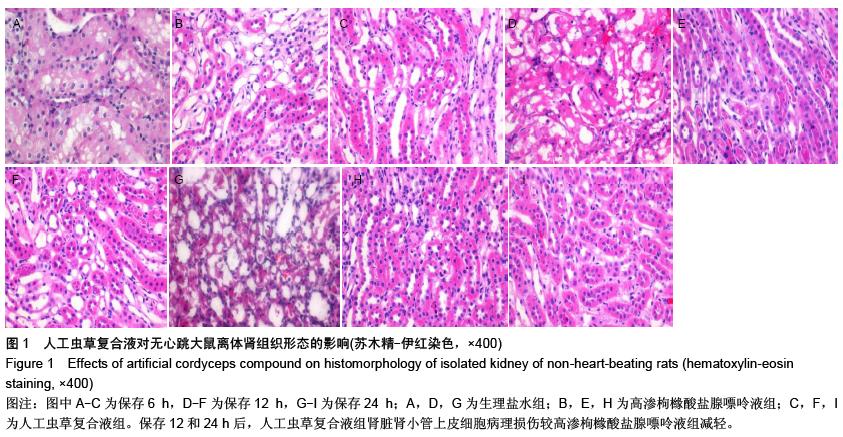
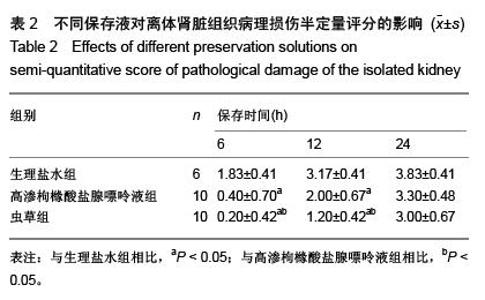
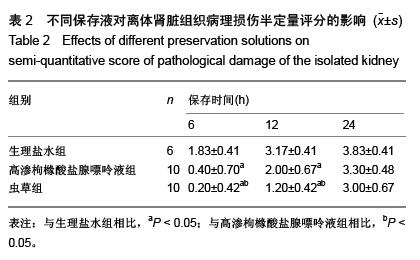
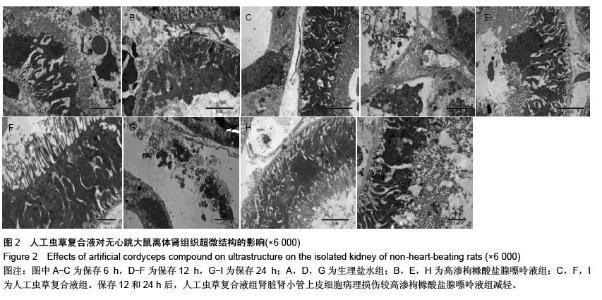
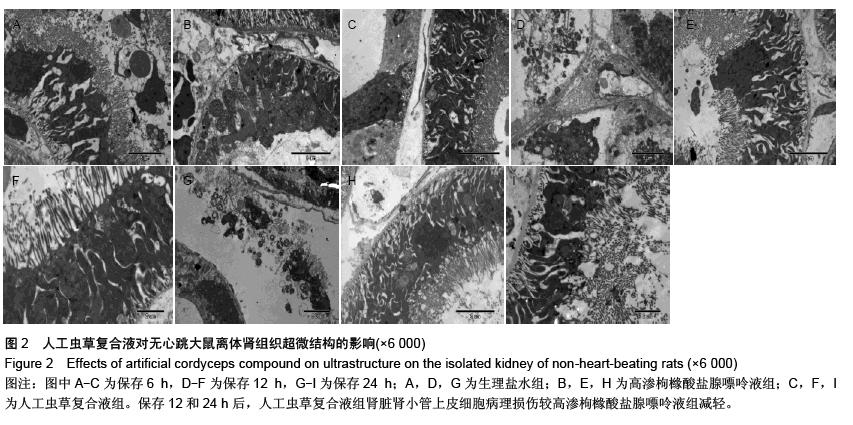
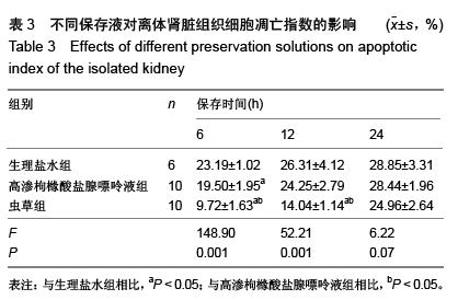
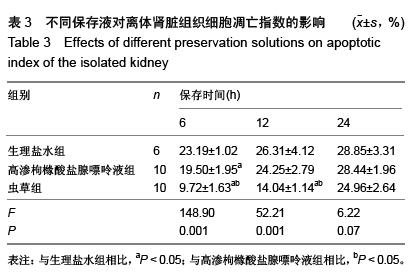
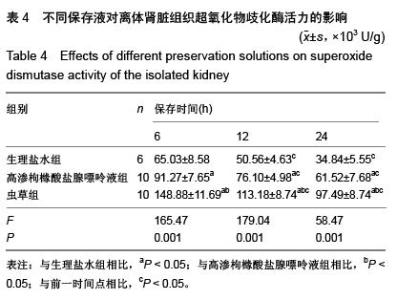
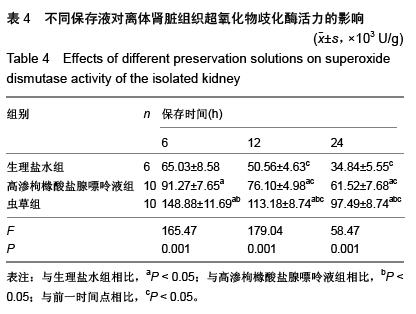
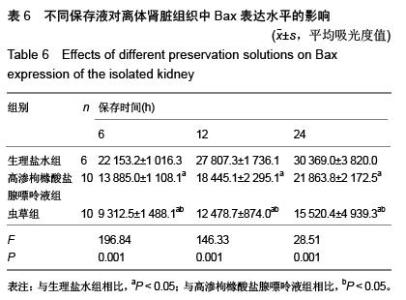
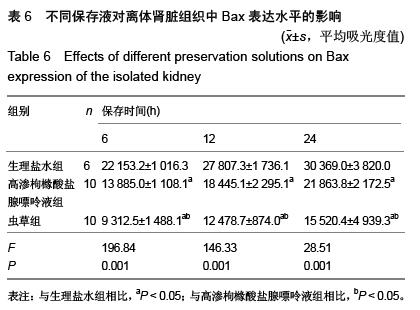
| [1] 鲁可权,朱有华,张纯,等.改良HCA肾保存液对肾脏低温保存效果的动物实验研究[J].山东医药,2004,44(29):7-9.
[2] Dong JZ, Liu MR, Lei C, et al. Effects of selenium and light wavelengths on liquid culture of Cordyceps militaris Link. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2012;166(8):2030-2036.
[3] 刘少静,杨黎彬,王小宁,等.高效液相色谱法定量分析冬虫夏草中尿苷和腺嘌呤[J].中国药业,2013,22(16):19-20.
[4] 杨爽,逯城宇,杨雪薇,等.蛹虫草多糖降糖活性的研究[J].时珍国医国药,2013,24(9):2134-2136.
[5] 于斌,梁留科,李湘豫,等.青海省冬虫夏草资源特征分析[J].植物分类与资源学报,2012,34(5):478-482.
[6] 严冬,梁举春.冬虫夏草化学成分研究综述[J].黑龙江科技信息, 2013,(5):96.
[7] 胡敏,皮惠敏,郑元梅.冬虫夏草的化学成分及药理作用[J].时珍国医国药,2008,19(11):2804-2806.
[8] 李风华,刘平,王春树.虫草菌丝逆转二甲基亚硝胺诱导大鼠肝纤维化的有效组分及其作用机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2011, 17(9):164 -168.
[9] Wang Y, Jia H, Li WY, et al. Synergistic effects of bone mesenchymal stem cells and chondroitinase ABC on nerve regeneration after acellular nerve allograft in rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2012;32(3):361-371.
[10] Li SP, Zhao KJ, Ji ZN, et al. A polysaccharide isolated from Cordyceps sinensis, a traditional Chinese medicine, protects PC12 cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced injury. Life Sci. 2003;73(19):2503-2513.
[11] Yamaguchi Y, Kagota S, Nakamura K, et al. Antioxidant activity of the extracts from fruiting bodies of cultured Cordyceps sinensis. Phytother Res. 2000;14(8):647-649.
[12] 张薇薇,胡永君,龚韬,等.北虫草中核苷类成分的含量测定与质量评价[J].北京中医药,2013,32(3):230-232.
[13] 于荣敏,叶斌,宋丽艳.人工培养蛹虫草高效液相色谱指纹图谱的初步研究[J].中草药,2007,38(9):1403-1405.
[14] 雷宁,杜树山,倪雪梅,等.RP-HPLC 测定天然虫草与人工虫草中核苷类成分的含量[J].中国药学杂志,2006,41(12): 948-951.
[15] 宫壮,张晓良,刘必成.冬虫夏草研究现状及治疗进展[J].东南大学学报(医学版),2008,27(2):140-144.
[16] 赵辉.冬虫夏草的抗氧化活性[J].国外医学(中医中药分册), 2001, 23(5):270-271.
[17] 孙岩,申红,刘健,等.人工虫草复合液对大鼠离体肾缺血再灌注损伤的保护效应[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志,2010,19(5):440-444.
[18] Jablonski P, Howden BO, Rae DA, et al. An experimental model for assessment of renal recovery from warm ischemia. Transplantation. 1983;35(3):198-204.
[19] Huang J, Wang H, Fan ST, et al. The national program for deceased organ donation in China. Transplantation. 2013; 96(1):5-9.
[20] 陈劲松,文吉秋,季曙明,等.亲属肾移植供者术后早期肾功能变化的影响因素[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志,2013,22(2):106-111.
[21] 谢轲楠.活体肾移植供者的心理状态及影响因素分析[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志,2013,22(2):180-183.
[22] Nagaraja P, Roberts GW, Stephens M, et al. Influence of delayed graft function and acute rejection on outcomes after kidney transplantation from donors after cardiac death. Transplantation. 2012;94(12):1218-1223.
[23] Meurisse N, Vanden Bussche S, Jochmans I, et al. Outcomes of liver transplantations using donations after circulatory death: a single-center experience. Transplant Proc. 2012; 44(9):2868-2873.
[24] Wadei HM, Heckman MG, Rawal B, et al. Comparison of kidney function between donation after cardiac death and donation after brain death kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2013;96(3):274-281.
[25] Wang C, Fu Q, Liu L, et al. Kidney transplantation from donation after cardiac death donors in China--a single-center experience. Transplant Proc. 2012;44(4):862-864.
[26] 王磊,刘修恒,陈志远,等.臭氧氧化预处理对体外大鼠肾小管上皮细胞缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2014, 31(6):1207-1209.
[27] Quijano C, Castro L, Peluffo G, et al. Enhanced mitochondrial superoxide in hyperglycemic endothelial cells: direct measurements and formation of hydrogen peroxide and peroxynitrite. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;293(6): H3404-3414.
[28] Cuperus R, Leen R, Tytgat GA, et al. Fenretinide induces mitochondrial ROS and inhibits the mitochondrial respiratory chain in neuroblastoma. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010;67(5):807-816.
[29] Mitchell T, Rotaru D, Saba H, et al. The mitochondria-targeted antioxidant mitoquinone protects against cold storage injury of renal tubular cells and rat kidneys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011;336(3):682-692.
[30] Ohno K, Ito M, Ichihara M, et al. Molecular hydrogen as an emerging therapeutic medical gas for neurodegenerative and other diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012;2012:353152.
[31] Belzer FO, Southard JH. Principles of solid-organ preservation by cold storage. Transplantation. 1988;45(4): 673-676.
[32] Li SP, Su ZR, Dong TT, et al. The fruiting body and its caterpillar host of Cordyceps sinensis show close resemblance in main constituents and anti-oxidation activity. Phytomedicine. 2002;9(4):319-324.
[33] Zhang J, Yu Y, Zhang Z, et al. Effect of polysaccharide from cultured Cordyceps sinensis on immune function and anti-oxidation activity of mice exposed to 60Co. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011;11(12):2251-2257.
[34] Zhang Y, Yang M, Gong S, et al. Cordyceps sinensis extracts attenuate aortic transplant arteriosclerosis in rats. J Surg Res. 2012;175(1):123-130.
[35] Zhang HW, Lin ZX, Tung YS, et al. Cordyceps sinensis (a traditional Chinese medicine) for treating chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;12:CD008353.
[36] Wu MF, Li PC, Chen CC, et al. Cordyceps sobolifera extract ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced renal dysfunction in the rat. Am J Chin Med. 2011;39(3):523-535.
[37] Wang HP, Liu CW, Chang HW, et al. Cordyceps sinensis protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;40(3):2347-2355.
[38] Rössig L, Haendeler J, Mallat Z, et al. Congestive heart failure induces endothelial cell apoptosis: protective role of carvedilol. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;36(7):2081-2089.
[39] 吕中桥,范钰,张艳涛,等.巴利昔单抗预处理抑制T淋巴细胞增殖对小鼠肾脏缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2014,31(6):1210-1212.
[40] Regner KR, Roman RJ. Role of medullary blood flow in the pathogenesis of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012;21(1):33-38.
[41] Chatauret N, Thuillier R, Hauet T. Preservation strategies to reduce ischemic injury in kidney transplantation: pharmacological and genetic approaches. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2011;16(2):180-187.
[42] Wever KE, Warlé MC, Wagener FA, et al. Remote ischaemic preconditioning by brief hind limb ischaemia protects against renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury: the role of adenosine. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(10):3108-3117.
[43] Leone S, Noera G, Bertolini A. Melanocortins as innovative drugs for ischemic diseases and neurodegenerative disorders: established data and perspectives. Curr Med Chem. 2013; 20(6):735-750.
[44] Denecke C, Tullius SG. Innate and adaptive immune responses subsequent to ischemia-reperfusion injury in the kidney. Prog Urol. 2014;24 Suppl 1:S13-19.
[45] Day YJ, Huang L, McDuffie MJ, et al. Renal protection from ischemia mediated by A2A adenosine receptors on bone marrow-derived cells. J Clin Invest. 2003;112(6):883-891.
[46] Lee HT, Xu H, Nasr SH, et al. A1 adenosine receptor knockout mice exhibit increased renal injury following ischemia and reperfusion. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004; 286(2):F298-306.
[47] Zhu JS, Halpern GM, Jones K. The scientific rediscovery of a precious ancient Chinese herbal regimen: Cordyceps sinensis: part II. J Altern Complement Med. 1998;4(4):429-457.
[48] Lin CY, Ku FM, Kuo YC, et al. Inhibition of activated human mesangial cell proliferation by the natural product of Cordyceps sinensis (H1-A): an implication for treatment of IgA mesangial nephropathy. J Lab Clin Med. 1999;133(1):55-63.
[49] 陈梅英,方凯.百令胶囊对AECOPD 合并ARF 患者肾功能的影响[J].浙江中西医结合杂志,2012,22(6):442-443.
[50] Hashemi M. The study of pentoxifylline drug effects on renal apoptosis and bcl-2 gene expression changes following ischemic reperfusion injury in rat. Iran J Pharm Res. 2014; 13(1):181-189.
[51] Czabotar PE, Westphal D, Dewson G, et al. Bax crystal structures reveal how BH3 domains activate Bax and nucleate its oligomerization to induce apoptosis. Cell. 2013; 152(3):519-531. |