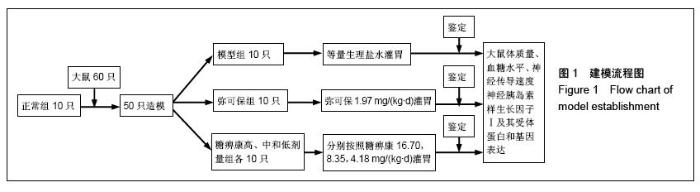
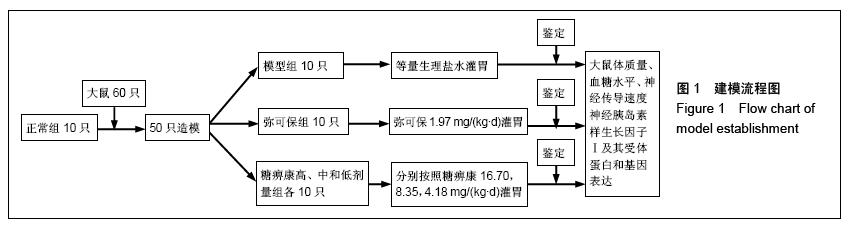
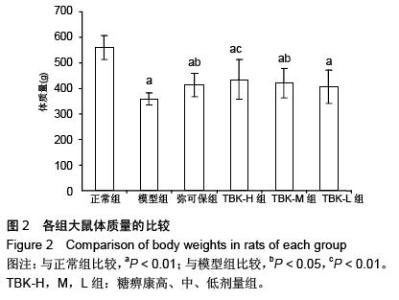
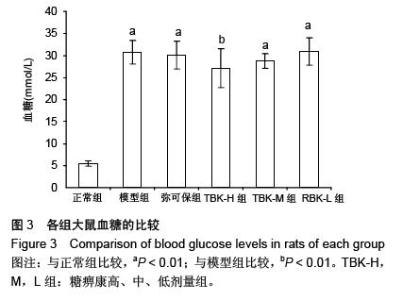
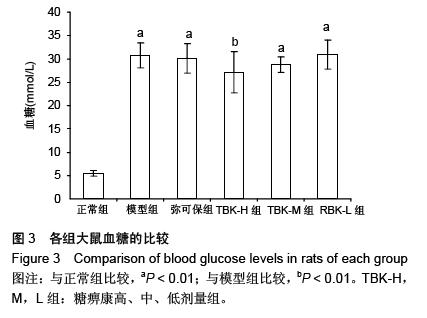
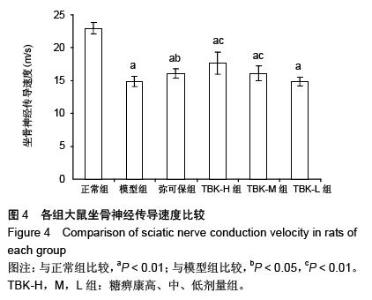
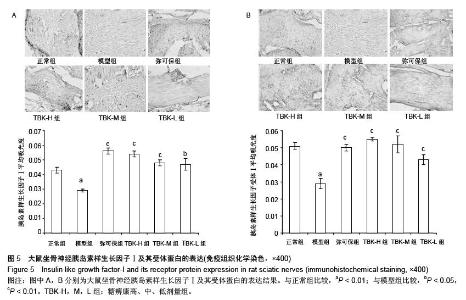
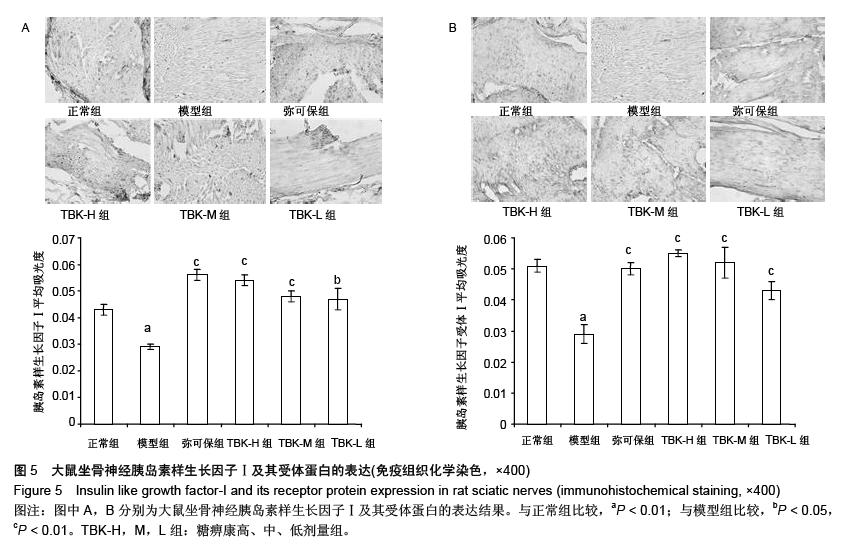
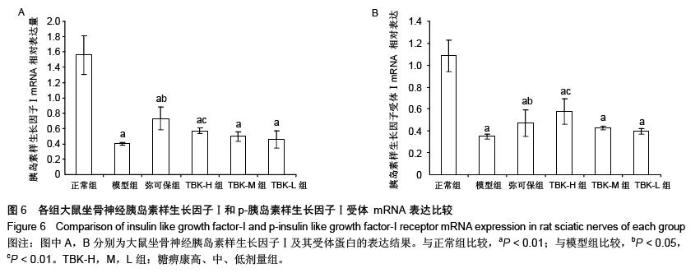
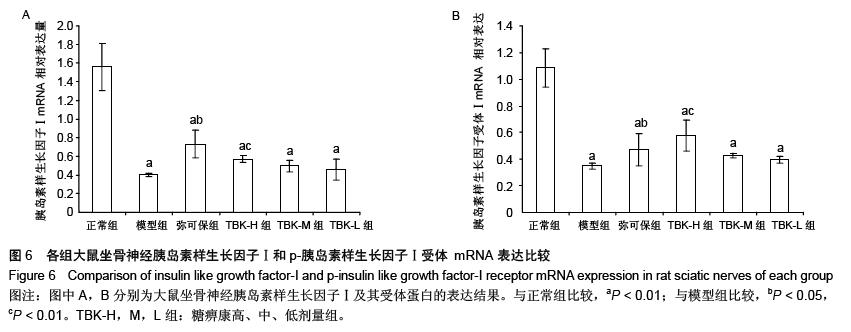
| [1] Russell JW, Zilliox LA. Diabetic neuropathies. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2014;20(5 Peripheral Nervous System Disorders):1226-1240.[2] Callaghan BC, Cheng HT, Stables CL, et al. Diabetic neuropathy: clinical manifestations and current treatments. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11(6):521-534.[3] Lupachyk S, Watcho P, Obrosov AA, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to prediabetic peripheral neuropathy. Exp Neurol.2013;247:342-348.[4] 穆晓红,刘铜华,秦灵灵,等.从血液流变学和坐骨神经传导速度评价中药糖痹康对大鼠糖尿病周围神经病变的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2012,27(2):378-381[5] Yang XW, Liu FQ, Guo JJ, et al. Antioxidation and anti-inflammatory activity of Tang Bi Kang in rats with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015; 15:66.[6] Sima AA, Li ZG, Zhang W. The insulin-like growth factor system and neurological complications in diabetes. Exp Diabesity Res. 2003;4(4):235-256.[7] Yu J, Zhang Y, Sun S, et al. Inhibitory effects of astragaloside IV on diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2006;84(6):579-587.[8] 庞国明,闫镛,朱璞,等.糖尿病周围神经病变中医诊疗规范初稿[J].中华中医药杂志,2010,25(2):260-264.[9] 王志强,庞国明,闫镛,等.糖尿病周围神经病变的中医证型分布规律研究[J].中医学报,2011,26(4):487-489.[10] 苏玉珂.中医药治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的Meta分析[J].天津中医药,2014,31(6):335-339.[11] 李娟娥,刘铜华,杨丽霞.中药复方治疗糖尿病周围神经病变随机对照试验的Meta分析[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2009,15(11): 847-850.[12] Piao Y, Liang X. Chinese medicine in diabetic peripheral neuropathy: experimental research on nerve repair and regeneration. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012; 2012:191632.[13] 张敬一,史国兵,徐博,等.黄芪桂枝五物汤治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的Meta分析[J].沈阳药科大学学报,2014,31(8):643-648.[14] 黄勇,顾静,李应东.黄芪桂枝五物汤干预糖尿病周围神经病变临床RCT文献的Meta分析[J].甘肃中医学院学报,2013,30(2): 65-68.[15] 王佳,刘铜华.糖痹康对糖尿病周围神经病变大鼠坐骨神经传导速度的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2010,16(3):209-211.[16] Sima AA, Robertson DM. Peripheral neuropathy in mutant diabetic mouse [C57BL/Ks (db/db)]. Acta Neuropathol. 1978; 41(2):85-89.[17] Drel VR, Mashtalir N, Ilnytska O, et al. The leptin-deficient (ob/ob) mouse: a new animal model of peripheral neuropathy of type 2 diabetes and obesity. Diabetes. 2006;55(12): 3335-3343.[18] 朱志强,吴鹏,张兰.糖尿病早期大鼠坐骨神经形态学的实验研究[J].沈阳医学院学报,2007,9(4):197-199.[19] Yagihashi S, Kamijo M, Watanabe K. Reduced myelinated fiber size correlates with loss of axonal neurofilaments in peripheral nerve of chronically streptozotocin diabetic rats. Am J Pathol. 1990;136(6):1365-1373.[20] Jian-Bo L, Cheng-Ya W, Jia-Wei C, et al. The preventive efficacy of methylcobalamin on rat peripheral neuropathy influenced by diabetes via neural IGF-1 levels. Nutr Neurosci. 2010;13(2):79-86.[21] Mizukami H, Ogasawara S, Yamagishi S, et al. Methylcobalamin effects on diabetic neuropathy and nerve protein kinase C in rats. Eur J Clin Invest. 2011;41(4): 442-450.[22] Apfel SC. Neurotrophic factors and diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Eur Neurol. 1999;41 Suppl 1:27-34.[23] Dupraz S, Grassi D, Karnas D, et al. The insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor is essential for axonal regeneration in adult central nervous system neurons. PLoS One. 2013;8(1): e54462.[24] Rizk NN, Myatt-Jones J, Rafols J, et al. Insulin like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) decreases ischemia-reperfusion induced apoptosis and necrosis in diabetic rats. Endocrine. 2007; 31(1):66-71.[25] Karvestedt L, Martensson E, Grill V, et al. Peripheral sensory neuropathy associates with micro- or macroangiopathy: results from a population-based study of type 2 diabetic patients in Sweden. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(2):317-322.[26] Hao W, Tashiro S, Hasegawa T, et al. Hyperglycemia promotes Schwann cell de-differentiation and de-myelination via sorbitol accumulation and Igf1 protein down-regulation. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(28):17106-17115.[27] Liang G, Cline GW, Macica CM. IGF-1 stimulates de novo fatty acid biosynthesis by Schwann cells during myelination. Glia. 2007;55(6):632-641.[28] Chu Q, Moreland R, Yew NS, et al. Systemic Insulin-like growth factor-1 reverses hypoalgesia and improves mobility in a mouse model of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Mol Ther. 2008;16(8):1400-1408.[29] Singh R, Kishore L, Kaur N. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: current perspective and future directions. Pharmacol Res. 2014;80:21-35.[30] Homs J, Pages G, Ariza L, et al. Intrathecal administration of IGF-I by AAVrh10 improves sensory and motor deficits in a mouse model of diabetic neuropathy. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2014;1:7. |