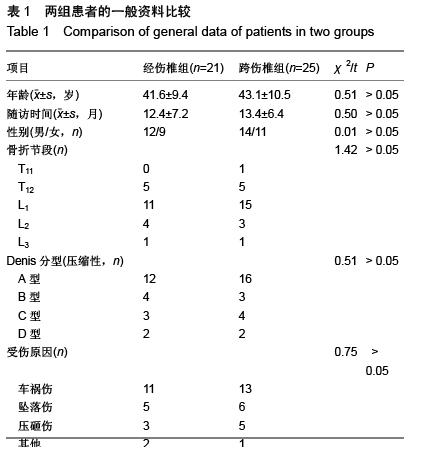
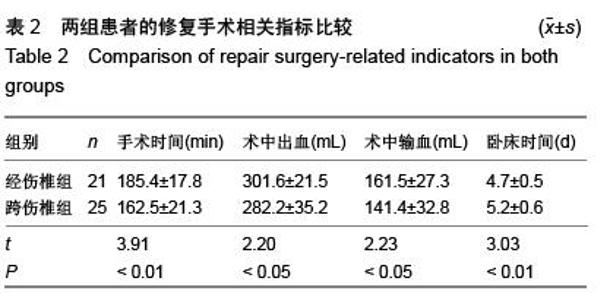
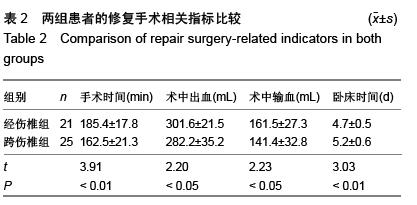
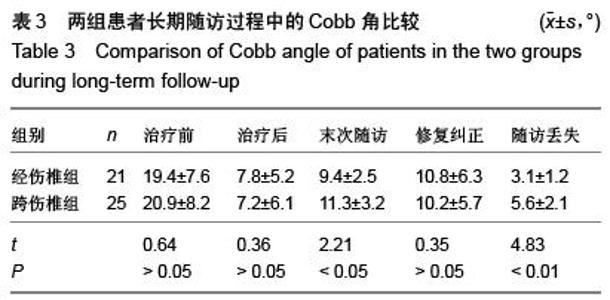
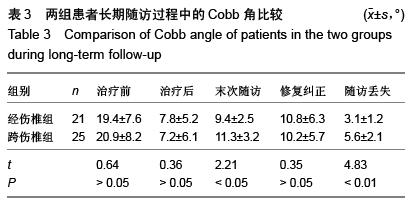
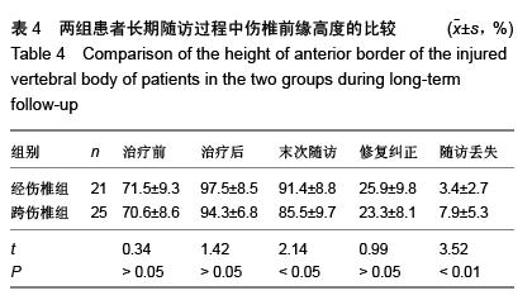
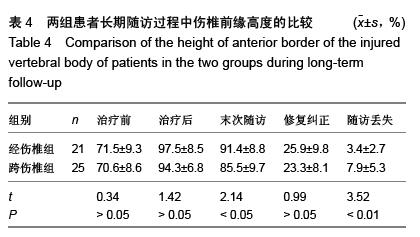
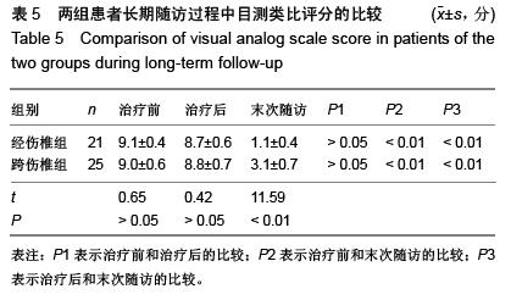
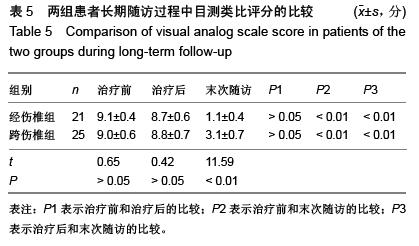
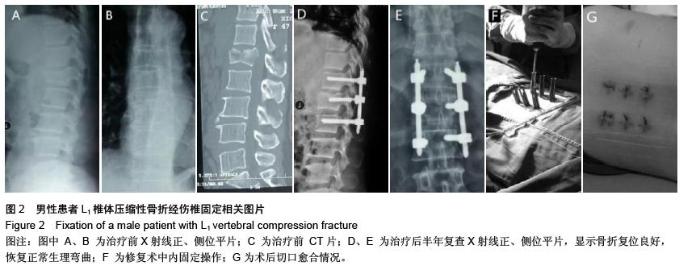
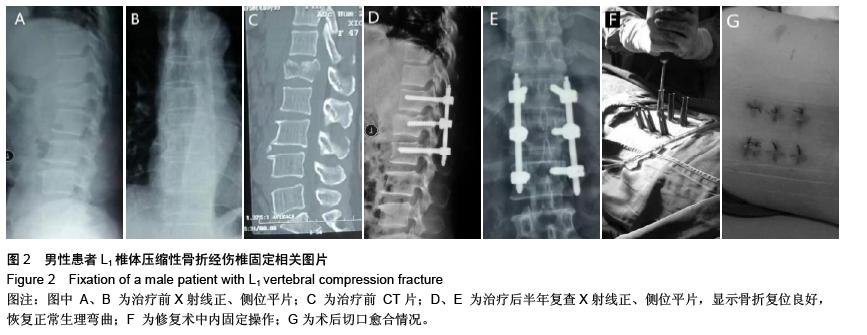
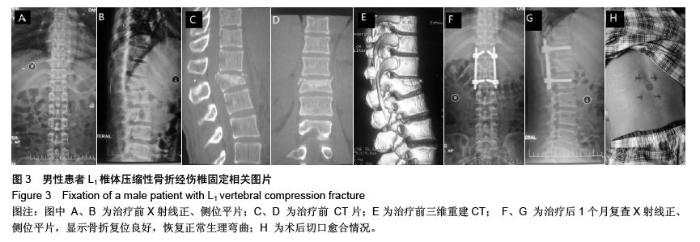
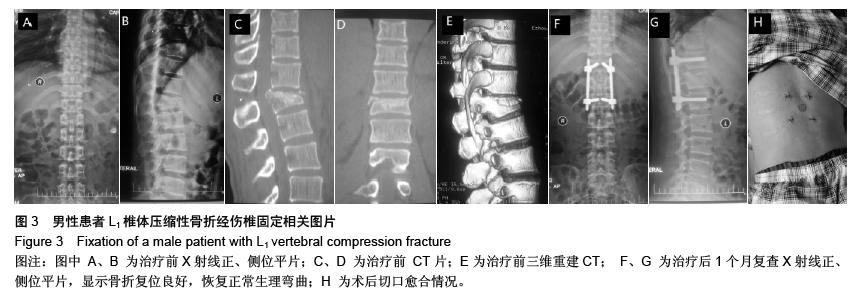
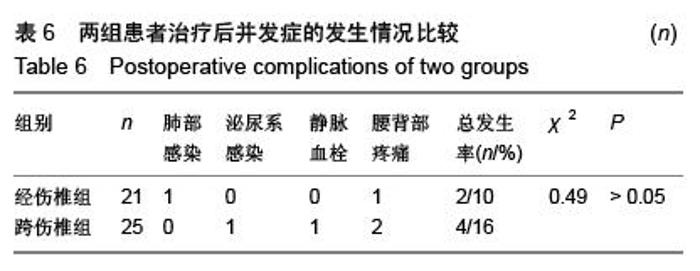
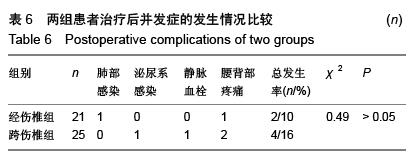
| [1] Kifune M, Panjabi MM, Liu W, et al. Functional morphology of the spinal canal after endplate,wedge,and bumt fractures.J Spine Disord. 1997;(6):457-466.[2] Frangen TM, Ruppert S, Muhr G, et al. The beneficial effects of early stabilization of thoracic spine fractures depend on trauma severity. J Trauma. 2010;68(5): 1208-1212.[3] Aebi M. Classification of thoracolumbar fractures and dislocations. Eur Spine J. 2010;19 (Suppl 1):S2-7.[4] Liao JC,Fan KF,Keorochana G,et al.Transpedicular grafting after short-segment pedicle instrumentation for thoracolumbar burst fracture:calcium sulfate cement versus autogenous iliac bone graft. Spine. 2010;35(15):1482-1488.[5] 李际才,刘平均,贺用礼,等.胸腰椎压缩性骨折单椎体内植入器的初步研制及其生物力学[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(9): 1350-1355.[6] 孙家元,崔蕴威,刘磊,等. 2010年至2011年新疆地区成人胸腰椎骨折的流行病学分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2015, 17(3):248-250.[7] 张奎渤,詹鸿锐,黄丽娟,等. 2种胸腰椎骨折分型在不同专业医师中应用的可信度和可重复性研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014,29(11):1087-1089.[8] 李飞,蒋煜文,黄明光,等.后路椎板减压螺钉置入修复胸腰椎骨折合并脊髓损伤:神经功能评价[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19 (17): 2694-2698.[9] 赵红卫,方煌.脊髓损伤患者神经功能评定标准[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2004,14(5):306-309.[10] 叶启彬,邱贵兴.脊柱外科新手术[M].2版.北京:中国协和医科大学出版社, 2001:79.[11] 谢学义,李金生,吉赵勇,等.后路短节段固定结合椎弓根植骨治疗胸腰段骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2012, 14(4):357-359.[12] 沈华,郑春京,杨文芳,等. 联合用药治疗晚期癌痛的临床观察[J].中国医刊,2012,47(5):68-70.[13] 全莉妮,杨慧芳,杜晓蓉,等.静注硫酸镁对腰硬联合麻醉患者术后疼痛和寒战反应的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2015, 15(8): 1522-1524.[14] Wood KB, Li W, Lebl DS, et al. Management of thoracolumbar spine fractures. Spine J. 2014;14(1):145-164.[15] Bastian L, Schils F, Tillman JB,et al. A randomized trial comparing 2 techniques of balloon kyphoplasty and curette use for obtaining vertebral body height restoration and angular-deformity correction in vertebral compression fractures due to osteoporosis. Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34(3): 666-675.[16] 刘上楼,徐军,倪卓民,等.经胸腰段伤椎单节段椎弓根螺钉固定后的生物力学特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(39): 6908- 6913.[17] 王树海,付国权,王桂华,等.后路短节段钉棒系统结合伤椎椎弓根固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2011,26(1):36-38.[18] Derek TC, Michael A, Seamus M.Multifidus innervation and muscle assessment post-spinal surgery.Eur Spine J.2014; 22(2):320-327.[19] Albrecht W, Christin H, Jan W, et al. Denervation and atrophy of paraspinal muscles after open lumbar interbody fusion is associated with clinical outcome-electromyographic and CT-volumetric investigation of 30 patients. Acta Neurochir. 2014;156(2):235-244.[20] Svedbom A, Alvares L, Cooper C, et al. Balloon kyphoplasty compared to vertebroplasty and nonsurgical management in patients hospitalized with acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a UK cost-effectiveness analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(1):355-367.[21] Jan VM, Leonard B,Steven B, et al. A Randomized Trial of Balloon Kyphoplasty and Nonsurgical Management for Treating Acute Vertebral Compression Fractures. Spine. 2013;38(12):971-983.[22] 刘程俊,顾祖超,张宇.Sextant内固定系统修复腰椎骨折:伤椎前后缘高度比及后凸Cobb角变化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(4):548-553.[23] Ray WZ,Krisht KM,Dailey AT,et al. Clinical outcomes of an stable thoraeolumbar junction burst fractures:combined posterior short-segment correction followed by thoracoscopic corpectomy and fusion. Acta Neurochir(Wien). 2013;155(7): 1179-1186.[24] Lee GW, Jang SJ, Kim JD, et al. The efficacy of percutaneous long-segmental posterior fixation of unstable thoracolumbar fracture with partial neurologic deficit. Asian Spine J. 2013; 7(2): 81-90.[25] Jiang SD, Wu QZ, Lan SH,et al. Reliability of the measurement of thoracolumbar burst fracture kyphosis with Cobb angle, Gardner angle, and sagittal index. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(2): 221-225.[26] 周卓鹏,范建文,植伟宏.经伤椎椎弓根螺钉置入内固定修复胸腰椎骨折:3年随访效果评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(22): 3519-3524.[27] Mahar A, Kim C, Wedemeyer M, et al. Short-segment fixation of lumbar burst fractures using pedicle fixation at the level of the fracture. Spine. 2007;32(23):1503-1507.[28] 刘匆聪,镇万新,高国勇,等.经伤椎与跨伤椎短节段内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效比较[J].广东医学,2013,34(4):590-592.[29] 袁强,田伟,张贵林,等.骨折椎垂直应力螺钉在胸腰椎骨折中的应用[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2006,26(4):217-220.[30] Gelb D, Ludwig S, Karp JE, et al. Successful treatment of thoracolumbar fractures with short-segment pedicle instrumentation. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(5):293-301.[31] Farrokhi MR, Razmkon A, Maghami Z, et al. Inclusion of the fracture level in short segment fixation of thoracolumbar fractures. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(10):1651-1656.[32] 刘匆聪,镇万新,高国勇,等. 经伤椎与跨伤椎短节段内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效比较[J]. 广东医学,2013,34(4):590-592.[33] Kim HS, Kim SW, Ju CI, et al. Short segment fixation for thoracolumbar burst fracture accompanying osteopenia : a comparative study. J Korean Neurosurg Soc.2013;53(1): 26-30.[34] Li X, Ma Y, Dong J, et al. Retrospective analysis of treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture using mono-segment pedicle instrumentation compared with short-segment pedicle instrumentation. Eur Spine J.2012;21(10):2034-2042.[35] 崔尚斌,魏富鑫,刘少喻,等.胸腰椎B型骨折经伤椎单节段与跨伤椎短节段固定的对比研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(17): 2709-2715.[36] 崔尚斌,魏富鑫,刘少喻,等.后路经伤椎单节段固定治疗B型胸腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2014,30(10):990-994.[37] 潘俊,王根林,史金辉,等.间接复位治疗胸腰椎爆裂型骨折术后椎管重塑形[J].脊柱外科杂志, 2012, 10(2): 72-75.[38] Scapinelli R, Candiotto S. Spontaneous remodeling of the spinal canal after burst fractures of the low thoracic and lumbar region. J Spinal Disord. 1995;8(6): 486-493.[39] de Klerk LW, Fontijne WP, Stijnen T,et al. Spontaneous remodeling of the spinal canal after conservative management of thoracolumbar burst fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1998;23(9): 1057-1060.[40] 昌耘冰,夏虹,王义生,等伤椎置钉技术在治疗胸腰椎骨折中的即时复位作用[J]中华创伤杂志,2009,25(10):894-897.[41] 吕夫新,黄勇,张强,等.椎弓根钉结合伤椎固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J]中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(1):46-48.[42] 冯睿,马信龙,马剑雄等.伤椎置钉短节段内固定和传统短节段内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折疗效的Meta分析[J].中华创伤杂志, 2014, 30(6):525-529.[43] Liu L, Gan Y, Zhou Q, et al. Improved Monosegment Pedicle Instrumentation for Treatment of Thoracolumbar Incomplete Burst Fractures. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:357206.[44] Moon MS, Kim SS, Yoon MG, et al. Radiographic Assessment of Effect of Congenital Monosegment Synostosis of Lower Cervical Spine between C2-C6 on Adjacent Mobile Segments. Asian Spine J. 2014;8(5):615-623. [45] Ma YQ, Li XL, Dong J, et al. Comparison of percutaneous versus open monosegment instrumentation in the treatment of incomplete thoracolumbar burst fracture. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012;92(13):904-908. [46] Li XL, Zhou XG, Dong J, et al. The treatment of monosegmental fixation and short-segment fixation on thoracolumbar burst fracture a retrospective controlled study. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011;49(4):315-319. [47] Zeng ZY, Zhang JQ, Jin CY, et al. Surgical treatment of thoracolumbar fractures using pedicle screws fixation at the level of the fracture: results for following up more than 2 years. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(2):128-132. |