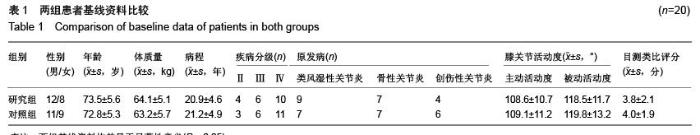
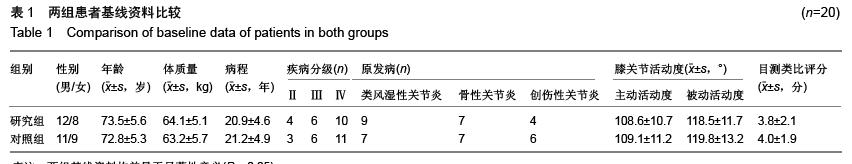
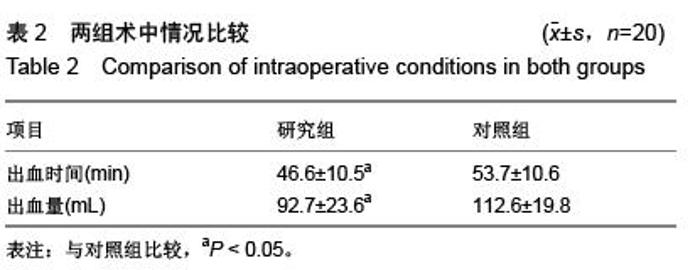
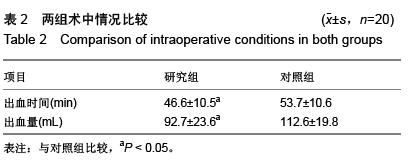
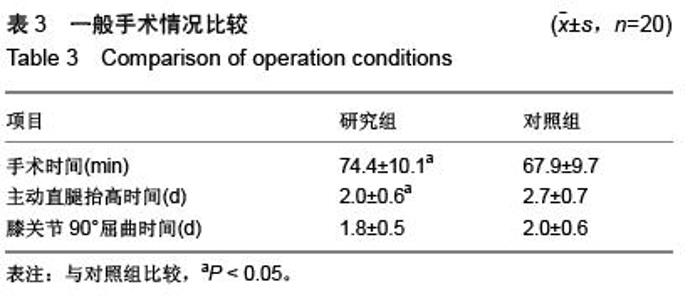
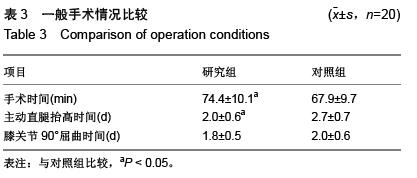
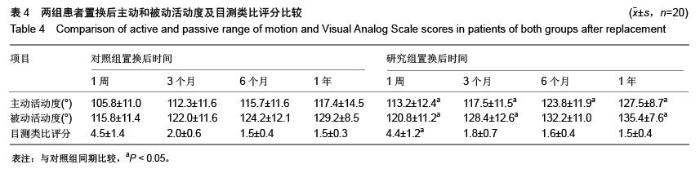
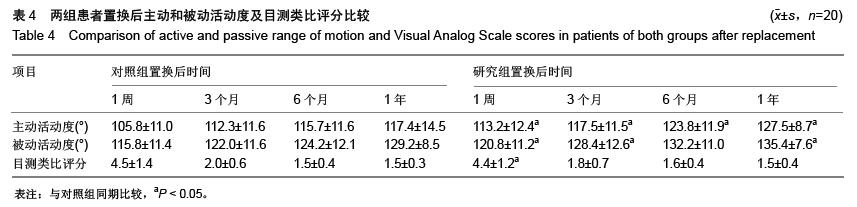
| [1] Poitras S, Wood KE, Savard J, et al. Predicting early clinical function after hip or knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint Res. 2015; 4(9):145-51.
[2] 查国春,孙俊英,田家祥,等.髌骨软骨退变分级对保留髌骨型全膝关节置换疗效的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2013,33(3):226-233.
[3] 陈钢,李文武,辜辉辉,等.康复训练联合髌骨松动术对膝关节骨性关节炎患者全膝关节置换后膝关节功能的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2011,33(8):629-630.
[4] 成世高,王万春,肖扬,等.全膝关节置换中髌骨置换效果的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(43):8097-8103.
[5] 郑鸿鸣,孙俊英,董圣杰,等.后交叉韧带替代型和保留型全膝关节置换的中期疗效比较[J].中国医师进修杂志,2012,35(5):6-10.
[6] Aryal MR, Pandit A, Ghimire S, et al. Thromboprophylaxis with apixaban and the risk of pulmonary embolism in patients undergoing kneereplacement surgery. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2015;5(4):27889.
[7] 杜晋强,王小虎,卫小春,等.全膝关节置换中髌骨处理的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(23):2367-2370.
[8] 郭峰,刘晋平,李正南,等.经髌骨正中入路与内侧髌旁入路行人工膝关节表面置换临床效果分析[J].中国综合临床,2012,28(11): 1204-1207.
[9] 王健,郑少伟,陈国奋,等.全膝关节置换后低位髌骨的处理策略及文献回顾[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2014,32(6):739-742.
[10] 徐建平,徐卫东,林国兵,等.双膝骨关节炎患者行小切口单髁置换与全膝关节置换临床疗效对比分析[J].中华外科杂志,2013, 51(2): 157-160.
[11] 覃小东,李朝健,符俏,等.人工膝关节常用假体材料及其生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(12):2257-2260.
[12] 李伟,张世权,刘安庆,等.双侧一期人工膝关节置换临床疗效分析[J].西部医学,2014,26(8):1011-1013.
[13] 刘文刚,许学猛,吴淮,等.CR假体膝关节置换治疗膝骨关节炎的早期疗效分析[J].中医正骨,2013,25(8):27-29.
[14] 彭周全,张卫,李丽伟,等.下肢神经阻滞联合全麻与全麻下膝关节置换老年患者置换后早期认知功能的比较[J].中华麻醉学杂志, 2014,34(12):1498-1499.
[15] 武晓瑛,刘晓梅,张卫华,等.高龄患者人工膝关节置换的系统化护理及康复训练的效果[J].全科护理,2015,5(20):1950-1952.
[16] 左银龙,李忠,刘俊才.高屈曲后稳定固定平台假体与普通型假体在人工膝关节置换的临床疗效分析[J].中国伤残医学,2015,(9): 2-4.
[17] 牛雪飞,苏辉棠.关节松动术联合物理因子治疗人工全膝关节置换后关节活动受限的临床疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2015,37(5):380-381.
[18] 李洪星,毛新展,吕国华,等.多模式镇痛在髋膝关节置换围手术期的应用[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2014,1(2):228-232.
[19] 刘强,王德国,赵亮.全膝关节置换的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(16):1625-1628.
[20] 李玉安,谷长跃,王佳音,等.膝关节置换及假体的研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2013,33(6):1462-1464.
[21] Goesling J, Moser SE, Zaidi B, et al. Trends and Predictors of Opioid Use Following Total Knee and Total Hip Arthroplasty. Pain. 2016.
[22] Bravo D, Wagner ER, Larson DR, et al. No increased risk of knee arthroplasty failure in patients with positive skin patch testing for metal hypersensitivity: a matched cohort study. J Arthroplasty. 2016.
[23] Jacobs CA, Christensen CP, Karthikeyan T. An Intact Anterior Cruciate Ligament at the Time of Posterior Cruciate Ligament-Retaining Total Knee Arthroplasty Was Associated With Reduced Patient Satisfaction and Inferior Pain and Stair Function. J Arthroplasty. 2016.
[24] Mikkelsen LR, Petersen AK, Mechlenburg I, et al. Description of load progression and pain response during progressive resistance training early after total hip arthroplasty: Secondary analyses from a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2016.
[25] Ruel A, Ortiz P, Westrich G. Five year survivorship of primary non-modular stemless constrained knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2016.
[26] Elmallah RD, Jauregui JJ, Cherian JJ, et al. Effect of Age on Postoperative Outcomes Following Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2016.
[27] Chan IA, Maslany JG, Gorman KJ, et al. Dexmedetomidine during total knee arthroplasty performed under spinal anesthesia decreases opioid use: a randomized-controlled trial. Can J Anaesth. 2016.
[28] Jiang C, Liu Z, Wang Y, et al. Posterior cruciate ligament retention versus posterior stabilization for total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11(1):e0147865.
[29] Nori M, Marupaka SK, Alluri S, et al. MRI Evaluation of Post Core Decompression Changes in Avascular Necrosis of Hip. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9(12):TC04-TC08.
[30] Wilson RA, Watt-Watson J, Hodnett E, et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial of an Individualized Preoperative Education Intervention for Symptom Management After Total Knee Arthroplasty. Orthop Nurs. 2016;35(1):20-29.
[31] Park CN, White PB, Meftah M, et al. Diagnostic Algorithm for Residual Pain After Total Knee Arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2016.
[32] Soltesz S, Meiger D, Milles-Thieme S, et al. Intermittent versus continuous sciatic block combined with femoral block for patients undergoing knee arthroplasty. A randomized controlled trial. Int Orthop. 2016.
[33] Fan L, Yu X, Zan P, et al. Comparison of local infiltration analgesia with femoral nerve block for total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized clinical trial. J Arthroplasty. 2015.
[34] Mammoto T, Fujie K, Mamizuka N, et al. Effects of postoperative administration of celecoxib on pain management in patients after total knee arthroplasty: study protocol for an open-label randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2016;17(1):45.
[35] Moucha CS, Weiser MC, Levin EJ. Current Strategies in Anesthesia and Analgesia for Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(2):60-73.
[36] Hughes AJ, O'hEireamhoin S, Heffernan E, et al. A simple approach to assessment of a total knee replacement's rotationary profile using computed tomography. Orthop Surg. 2015;7(4):350-353.
[37] van de Groes S, van der Ven P, Kremers-van de Hei K, et al. Flexion and anterior knee pain after high flexion posterior stabilized or cruciate retaining knee replacement. Acta Orthop Belg. 2015;81(4):730-737.
[38] Vaishya R, Wani AM, Vijay V. Local Infiltration Analgesia reduces pain and hospital stay after primary TKA: randomized controlled double blind trial. Acta Orthop Belg. 2015;81(4): 720-729.
[39] Johnson RL, Kopp SL, Burkle CM, et al. Neuraxial vs general anaesthesia for total hip and total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review of comparative-effectiveness research. Br J Anaesth. 2016;116(2):163-176.
[40] Wang Y, Klein MS, Mathis S, et al. Adductor canal block with bupivacaine liposome versus ropivacaine pain ball for pain control in total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective cohort study. Ann Pharmacother. 2016;50(3):194-202.
[41] Kuyucu E, Bülbül M, Kara A, et al. Is cold therapy really efficient after knee arthroplasty? Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2015; 4(4):475-478.
[42] Desteli EE, Imren Y, Ayd?n N. Effect of both preoperative andpostoperative cryoceutical treatment on hemostasis and postoperative pain following total knee arthroplasty. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(10):19150-19155.
[43] Wang F, Zhou Y, Sun J, et al. Influences of continuous femoral nerve block on knee function and quality of life in patients following total knee arthroplasty. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8(10):19120-19125.
[44] Calatayud J, Casaña J, Ezzatvar Y, et al. High-intensity preoperative training improves physical and functional recovery in the early post-operative periods after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016.
[45] 张淼,白波,陈艺,等.全膝置换经小切口股内侧肌入路与标准髌旁入路临床疗效比较的META分析[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2014,(3):358-366.
[46] 白国玺,徐小会,段永宏,等.全膝关节置换治疗晚期类风湿性关节炎的早期临床随访研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2014,14(35): 6926-6930.
[47] 苗兵,于建华.全膝关节置换治疗膝骨关节炎膝外翻畸形临床研究[J].山东医药,2008,48(27):53-54.
[48] 李文菁,赵宇,孙志坚,等.手术治疗腰椎退行性疾病合并膝骨关节炎的临床分析[J].中国骨与关节外科,2014,(1):9-14.
[49] 崔鲁霞,焦裕光,王晓锋,等.全膝关节置换治疗膝骨关节炎57膝的临床观察[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2011,5(6):787-790.
[50] 林治平,汤炀炀,谭宏昌,等.同期双侧全膝关节置换治疗膝骨关节炎效果观察[J].海南医学,2015,26(21):3218-3219.
[51] 何仲佳,刘先银,莫新发,等.全膝关节置换在严重老年性膝骨关节炎中的应用[J].中华试验外科杂志,2004,21(7):786.
[52] 李国远,尚希福,胡飞.CR假体全膝关节置换治疗膝骨关节炎的近期疗效[J].临床骨科杂志,2014,(4):415-418.
[53] 叶一林,柴卫兵,卢宏章.伴有关节外畸形的膝骨关节炎行全膝关节置换的治疗体会[J].中国骨与关节外科,2014,(5):399-403.
[54] 马青川,肖丽英,李志昌.单侧全膝关节置换后两下肢受力不对称性的影响因素[J].医用生物力学,2015,30(1):89-93. |