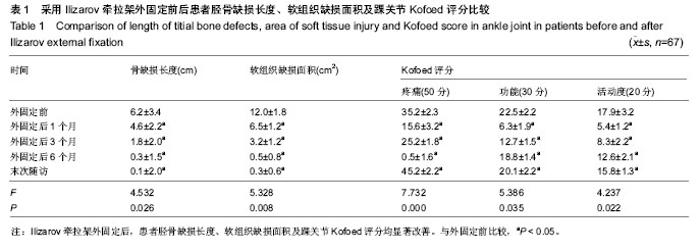
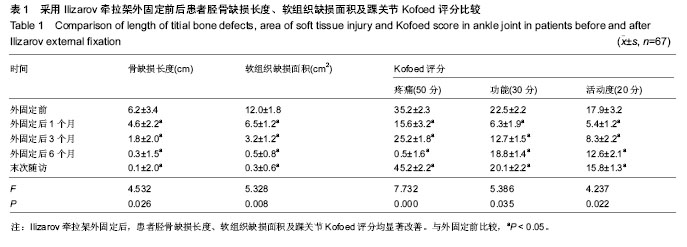
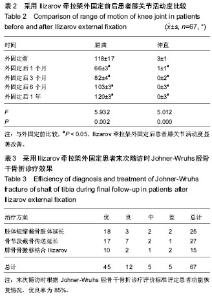
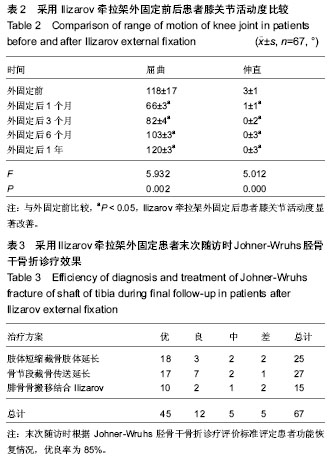
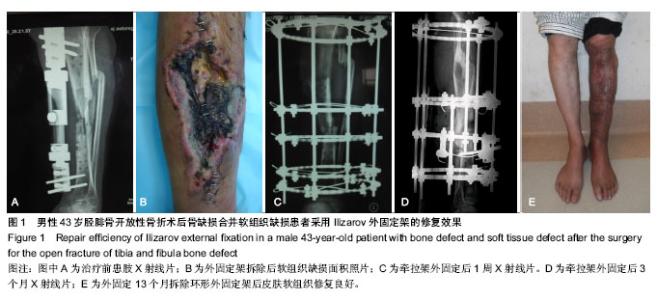
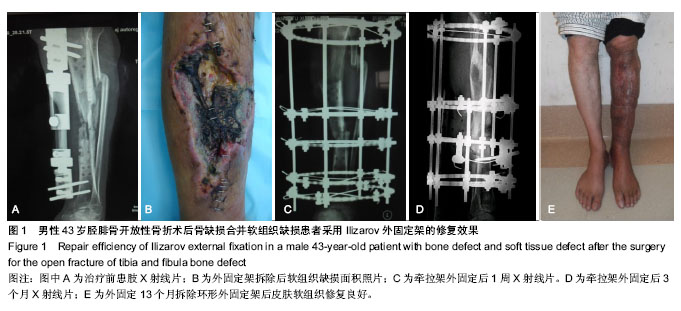
| [1] McKee MD, Yoo DJ, Zdero R, et al.Combined single-stage osseous and soft tissue reconstruction of the tibia with the Ilizarov method and tissue transfer.J Orthop Trauma. 2008; 22(3):183-189. [2] Wu CC.Single-stage surgical treatment of infected nonunion of the distal tibia. J Orthop Trauma. 2011;25(3):156-161.[3] Tuli SM.Tibialization of the fibula: a viable option to salvage limbs with extensive scarring and gap nonunions of the tibia.J Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;(431):80-84.[4] 纪红军,冯琼华.锁定加压钢板联合植骨治疗胫骨下段骨不连38例[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14(6):718.[5] 朱雅龙,吴金平,王永安,等.锁定钢板治疗四肢长管状骨骨不连[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14(6):720.[6] 秦泗河,李刚.Ilizarov理论与技术的起源、发展与传播史[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010,3(5):417-423.[7] 陈建文,秦泗河.Ilizarov技术临床应用的相关问题[J].中国骨与关节外科,2011,4(1):56-59.[8] Tripathy SK,Saini R,Sudes P,et al.Application of the Ponseti principle for deformitv correction in neglected and relapsed club foot using the Ilizarov fixator. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2011; 20(1):26-32.[9] 秦泗河,陈建文,郑学建,等.改良Ilizarov技术救治频临截肢的下肢残缺畸形[J].中国骨科杂志,2010,30(4):423-426.[10] 秦泗河. Ilizarov技术概述[J].中华骨科杂志,2006, 26(9): 642-645.[11] Fischgrund J, Paley D, Suter C. Variables affecting time to bone healing during limb lengthening. J Clin Orthop.1994; 301:31-37.[12] Ullmann Y,Fodor L,Soudry M,et al.The Ilizarov technique in joint contractures and dislocations. J Acta Orthop Belg. 2007;73(1):77-82.[13] Steinwender G,Saraph V,Zwick EB,et al.Complex footdeformities associated with soft-tissue scarring in children. J Foot Ankle Surg.2001;40(1):42-49.[14] Segev E,Wientroub S,Kollender Y,et al.A combined use of a free vascularised flap and an external fixator forreconstruction of lower extremity defects in children.J Orthop Surg(Hong Kong).2007;15(2):207-210.[15] Van Bosse HJ,Feldman DS,Anavian J,et al.Treatment of knee flexion contractures in patients with arthrogryposis.J Pediatr Orthop2007,27(8):930-937.[16] Carmichael KD,Maxwell SC,Calhoun JH.Recurrence rates of burn contracture ankle equinus and other foot deformities in children treated with Ilizarov fixation.J Pediatr Orthop.2005; 25(4):523-528.[17] Ferreira RC,Costa MT,Frizzo GG,et al.Correction of severe recurrent clubfoot using a simplified setting of the Ilizarov device. Foot Ankle Int. 2007;28(5):557-568.[18] Zhao ZY,Shao L,Zhao HM,et al. Osteogenic growth peptide aecelerates bon'e healing during distraction osteogenesis in rabbit tibia.J Int Med Res. 2011;39(2):456-463.[19] Spiro AS,Babin K,Lipovac S,et al. Combined treatment of congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia,including recombinant human bone morphogenetie protein-2:a case series.J Bone Joint Surg. 2011;93(5):695-699.[20] Sashieh S,El Bitar Y,Berjawi G,et al.Distraction histogenesis in ankle burn deformities.J Bum Care Res. 2011;32(1): 160-165.[21] Lee DY, Choi IH, Yoo WJ, et al. Application of the Ilizarov technal to the correction of neurologic equinocavovams foot defor- mity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(3):860-867.[22] Desgrippes Y,Souchet P,Bensahel H.Use of the Ilizarov exter-nal fixator in multioperated,recurrent clubfoot. J Pediatr Orthop Part B. 1992;1(2):181. [23] Segev E, Ezra E, Yaniv M, et al. Vosteotomy and Ilizarov technique for residual idiopathic or neurogenic clubfeet.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2008;16(2):215-219.[24] Andersen LR, Johannsen HG, Ernst C, et al. Tibial pseudoarthrosis. Treatment using the Ilizarov technique. Ugeskr Laeger. 1996;157:2237-2240. [25] Dagher F, Roukoz S. Compound tibial fractures with bone loss treated by the Ilizarov technique. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]. 1991;73:316-321. [26] Dendrinos GK, Kontos S, Lyritsis E. Use of the Ilizarov technique for treatment of non-union of the tibia associated with infection. J Bone Joint Surg [Am]. 1995;77:835-846.[27] 李红宇,才志勇,李玉山,等.Ilizarov外固定架在胫骨截骨延长治疗中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(13):985-987.[28] Bradish CF,Noor S.The Ilizaror method in the management of relapsed club feet.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(3):387-391.[29] Melvin JS,Dahners LE.A technique for correction of equinus contracture using a wire fixator and elastic tension.J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(2):138-142.[30] Cierny G III, Zorn KE. Segmental tibial defects. Comparing conventional and Ilizarov methodologies. Clin Orthop. 1994; 301:118-123. [31] 艾合买提·玉素甫,陈统一,王晓峰,等.应用Ilizarov技术治疗长管状骨缺损性骨不连[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,26(4):247-251.[32] 方广文,吕廷灼,舒衡生,等.Ilizarov技术在治疗骨折并发症中的应用进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(10):825-827. [33] Green SA. A comparison of bone grafting and bone transport for segmental skeletal defects. Clin Orthop. 1994;301:111-117.[34] Brunner UH, Cordey J, Schweiberer L, et al. Force required for bone segment transport in the treatment of large bone defects using medullary nail fixation. Clin Orthop. 1994; 301:147-155. [35] Lovisetti G, Agus MA, Pace F, et al. Management of distal tibial intra-articular fractures with circular external fixation. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2009;4(1):1-6.[36] Steinwender G, Saraph V, Zwick EB, et al.Complex foot defor. mities associated with soft-tissue scarring in children. J Foot An-kle Surg. 2001;40(1):42-49.[37] Gillooly JJ, Tilkeridis K, Simonis RB, et al.The treatment of high tibial osteoto- my non-union with the Ilizarov external fixator. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2012;7(2):93-97.[38] Mccoy TH Jr, Kim HJ, Cross MB,et al.Bone tumor reconstruction with the Ilizarov method.J Surg Oncol. 2013; 107(4):343-352. |