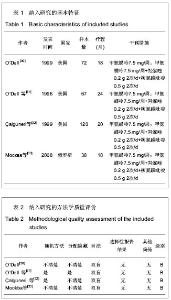
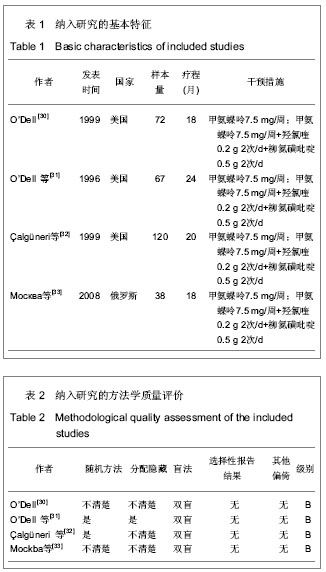
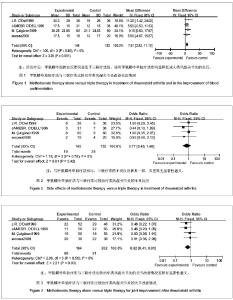
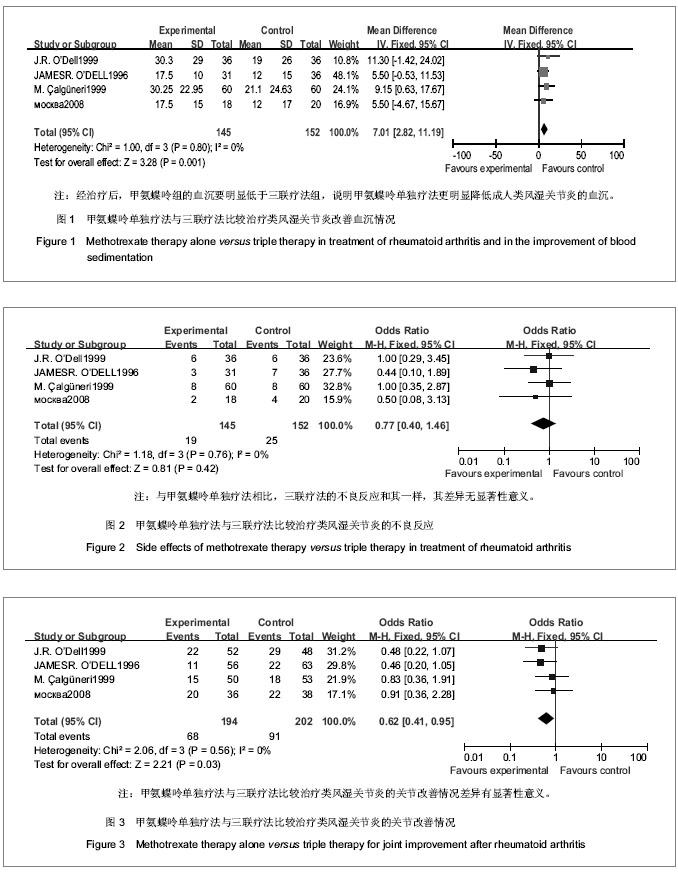
| [1] American College ofRheumatology Subcommittee on Rheumatoid Arthri-tis Guidelines. Guidelines for the management of rheumatoid arthritis2002 update.Arthritis Rheum.2002;46(2):328-346.[2] 覃泱,吕祥威,朱芳晓.来氟米特联合甲氨蝶呤治疗90例类风湿关节炎的疗效及分类研究[J].航空航天医学杂志,2013,24(5): 597-599. [3] 王建明,陶庆文,张英泽,等.补肾祛寒治尪汤联合甲氨喋呤治疗类风湿关节炎肾虚寒盛证的疗效与安全性评价[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2013,33(5):614-618. [4] 陈江艳.英夫利昔单抗联合甲氨喋呤治疗类风湿关节炎的观察与护理[J].当代护士(中旬刊),2013,(3): 24-25. [5] 石宇红,周润华,许佳,等. 亚甲基四氢叶酸还原酶基因多态性对小剂量甲氨喋呤治疗类风湿关节炎不良反应的影响[J]. 中国临床新医学,2013,6(3): 211-214. [6] 李绍华. 尪痹片联合甲氨喋呤治疗类风湿关节炎疗效观察[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2013,10(2):297-298. [7] 王军,祖比亚,林德帅,等.小剂量来氟米特联合甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎的临床分析[J].重庆医学,2012,41(35):3704-3706.[8] 万红建,刘军,徐军英,等.痹祺胶囊联合小剂量甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎的疗效观察[J].中国生化药物杂志,2012,33(5): 669- 671. [9] 夏玉坤,涂胜豪,胡永红,等.正痹关节片联合甲氨喋呤治疗活动期类风湿关节炎临床观察[J].湖北中医药大学学报,2012,14(4): 18-21. [10] 李瑞昌,李娟.正清风痛宁联合甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎的系统评价[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2012,18(11): 1-4.[11] 赵颖,王贯虹,孟力平.甲氨喋呤联合来氟米特治疗活动性类风湿关节炎疗效观察[J].山西大同大学学报:自然科学版,2012,28(1): 61. [12] 接红宇,吴启富,丁朝霞,等.痹祺胶囊联合甲氨喋呤治疗类风湿关节炎的临床研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2012,32(2): 195-198. [13] 王妤,李军霞,李小峰.白芍总苷联合甲氨蝶呤与来氟米特治疗类风湿关节炎疗效及安全性的研究[J].中国医疗前沿,2011, 6(19): 16.[14] 何浩,杨慧琴.补肾蠲痹汤联合甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎临床观察[J].湖北中医杂志,2011,33(6):27-28. [15] 苏冉,魏丽,陈艳春,等.来氟米特和甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎的Meta分析[J].中国循证医学杂志,2011,11(9): 1062-1069. [16] 王银山,苏雅莉,吴云虎,等.龙蚁清风抗风湿浓缩颗粒结合小剂量甲氨喋呤治疗类风湿关节炎的临床疗效优势的对比研究[J].四川中医,2010,28(12):63-65. [17] 李宏艳,张勇,刘爱武.寄生仙灵汤合甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎临床观察[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2010,5(9):772-775. [18] 李俊巧,王卫力.复方倍他米松关节腔注射与甲氨蝶呤联合治疗类风湿关节炎临床研究[J].河北医药,2010,32(23): 3306-3307. [19] 尉世同,孙永华,邹巧菲,等.双醋瑞因联合甲氨喋呤治疗类风湿关节炎的临床研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2010,32(19): 2112- 2114. [20] 马武开,钟琴,姚血明,等.金乌健骨汤对甲氨喋呤耐药类风湿关节炎患者的影响[J].中医杂志,2010,51(11): 993-995. [21] 马杰.甲氨蝶呤和白芍总苷联用治疗类风湿关节炎的疗效观察[J].吉林医学,2010,31(28): 4934-4935. [22] 庞捷,余克强.加味宣痹汤联合甲氨喋呤治疗活动性类风湿关节炎近期疗效观察[J].中国民间疗法,2010,18(8):58-59. [23] 邓辉,王成芳.甲氨喋呤加来氟米特联合药物治疗类风湿关节炎疗效分析[J].中国民康医学,2010,22(13): 1684,1726. [24] 胡谦,官晓红,练颖,等. 益肾活血通络中药联合来氟米特和甲氨喋呤治疗类风湿关节炎30例疗效观察[J]. 四川中医,2010,28(7): 52-54. [25] 蔡辉,姚茹冰,高佩芳. 甲氨蝶呤对类风湿关节炎环瓜氨酸肽抗原特异性T细胞体外增殖的影响[J].安徽医药,2010,14(7): 829-831. [26] 苏晓,张娜,马青海.补肾通络方联合甲氨喋呤治疗类风湿关节炎临床研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2010,(5). [27] 彭剑虹,叶雪英. 补肾养阴通络方联合甲氨喋呤治疗类风湿关节炎20例[J].中医研究,2010,(3):934. [28] 左川,陈永涛,王忠明,等.复方夏天无联合甲氨喋呤治疗类风湿关节炎的临床研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2009,29(11): 1023- 1025.[29] Arnett FC,Edwothy SM, Bloch DA, et al. TheAmerican Rheumatism As-sociation 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthri-tis.Arthritis Rheum.1988; 31(3): 315-324.[30] O’Dell JR. Combination DMARD therapy with hydroxychloroquine, sulfasalazine, and methotrexate.Clin Exp Rheumatol.1999; 17(Suppl. 18):S53-S58.[31] O'Dell JR, Haire CE, Erikson N,et al.Treatment Of Rheumatoid Arthritis With Methotrexate Alone, Sulfasalazineand Hydroxychloroquline, Or a combination Of allThree medications.N Engl J Med.1996;334(20):1287-1291.[32] Calgüneri M, Pay S, Cali?kaner Z,et al. Combination therapy versus monotherapy for the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis.1999; 17: 699-704.[33] Москва, Ииститу, Tревматологии. РАМН СРАВНЕНИ ЕЭФФЕКТИВНО СТИИЛ ЕРЕНО СИМОСТИ ТРОЙ НОЙБА (МЕТОТРЕКСАТ + СулАэИН + ГИДРОКСИХПОР) СМОНОТЕРАПИЕЙ МЕТОТРЕКСА ТОМу БОПЪНЫХРЕВМА ТОИДНТерале Bтическийархив. 2008,No 5,C.30-37 |