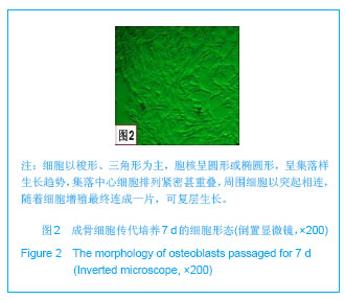
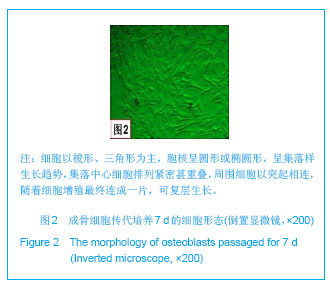
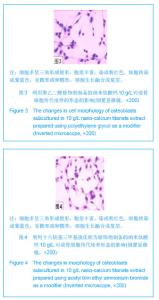
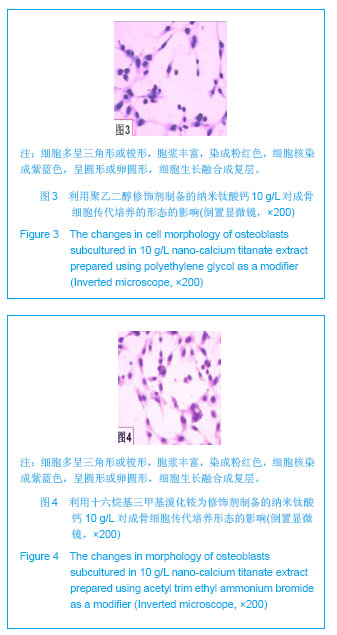
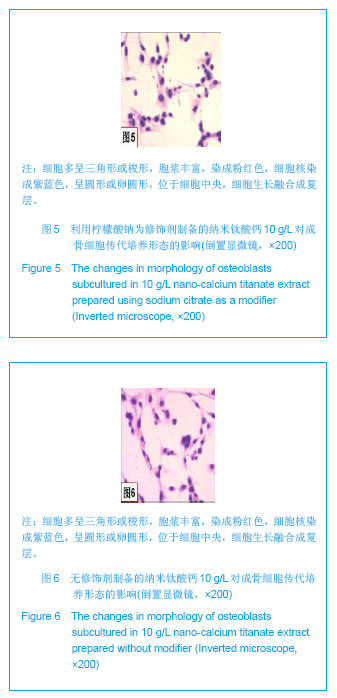
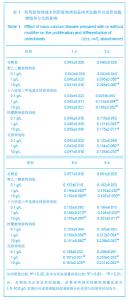
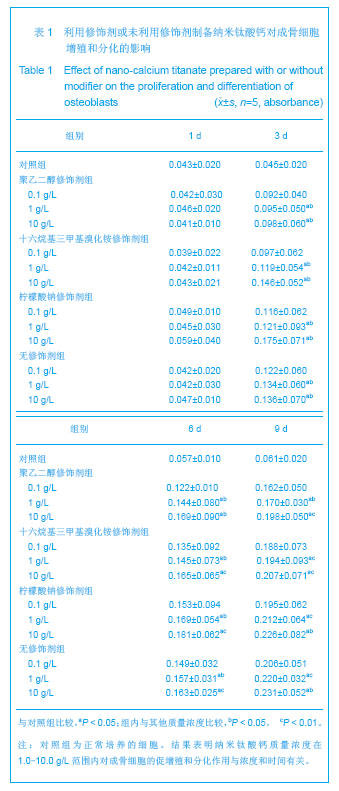
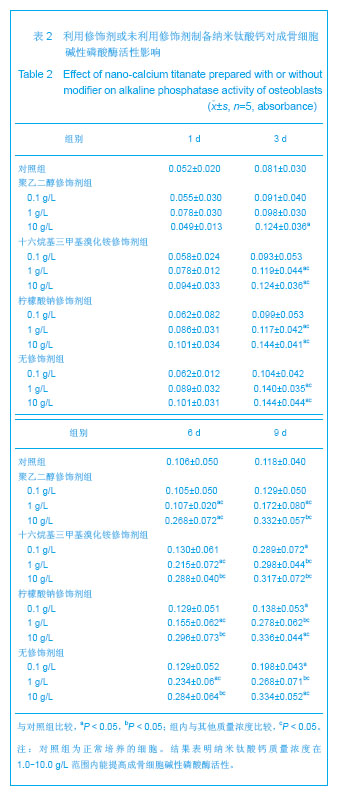
| [1]Macocinschi D,Filip D,Vlad S, et al.Segmented biopolyurethanes for medical applications.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2009;20(8):1659-1668.[2]Kütting M,Roggenkamp J,Urban U,et al.Polyurethane heart valves: past, present and future.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2011;8(2):227-233.[3]Ma Y,Cai ZB.Bionic design of human bone microstructure based on fractal t-heory.J Clin Rehabil Tissue Eng Res. 2007;14:2784-2786.[4]刘琳,包广洁.牙髓牙本质组织工程生物支架材料的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(8):1455-1460.[5]黄晶,蓝琳,肖东琴,等.热化学法制备CaTiO3涂层及涂层的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(16): 2901-2904.[6]Comesaña R,Quintero F,Lusquiños F,et al.Laser cladding of bioactive glass coatings.Acta Biomater.2010;6(3):953-961.[7]Ueda M,Ikeda M,Ogawa M.Chemical-hydrothermal combined surface modification of titanium for improvement of osteointegration.Mater Sci Eng C. 2009;29(3):994-1000.[8]Sugiyama N,Xu H,Onoki T,et al.Bioactive titanate nanomesh layer on the Ti-based bulk metallic glass by hydrothermal- electrochemical technique. Acta Biomater.2009;5(4): 1367-1373.[9]Inoue M,Rodriguez AP,Takagi T,et al.Effect of a new titanium coating material CaTiO3-aC) prepared by thermal decomposition method on osteoblastic cell response.J Biomater Appl.2010;24(7):657-672.[10]严洪海,胡玲华,黄海蓉.不同粗糙表面的纯钛种植体的耐腐蚀性评价[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2008,13(4):175-179.[11]李先安,雷光华,刘文和,等.大鼠成骨细胞的体外培养和鉴定[J].湖南学院学报:医学版,2007,9(1):23-26.[12]傅德皓,杨述华,马德彰,等.鼠胚成骨细胞的原代培养与鉴定[J].创伤外科杂志, 2006,8(2):157-160.[13]Morra M.Biochemical modification of titanium surfaces peptides and ECM proteins.Eur Cell Mater.2006;12:1-15.[14]Morra M,Cassinelli C,Meda L,et al.Surface analysis and effects oninterfacial bone microhardness of collagen-coated titanium implants:Arabbit model.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2005;20(1):23-30.[15]Parfitt AM.Skeletal heterogeneity and the purposes of bone remodeling implications for the understanding of osteoporosis//Marcus R,Feldman D,Kelsey J,Eds. Osteoporosis. San Diego,CA:Academic,1996:315-329.[16]Jayakumar P,Di Silvio L.Osteoblasts in bone tissue engineering. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers.Part H.J Eng Med.2010;224(12):1415-1417. [17]Liao H,Andersson AS,Sutherland D,et al.Response of rat osteoblast-like cells to microstructured model surfaces in vitro.Biomaterials. 2003;24(4):649-654.[18]Gordjestani M,Dermaut L,De Ridder L,et al.Osteopontin and bone metabolism:a histology and scintigraphy study in rats.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2005;34(7):794-799.[19]吕晶,柯杰,王琳,等.与软骨细胞共培养和条件培养液诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(19):3421-3426.[20]Keeney M,Pandit A.The osteochondral junction and its repairvia bi-phasic tissue engineering scaffolds.Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2009;15(1):55-73.[21]Matsusaki M,Kadowaki K,Tateishi K,et al.Scaffold-free tissue-engineered construct-hydroxyapatite composites generated by an alternate soaking process: potential for repair of bone defects.Tissue Eng Part A.2009;15(1):55-63.[22]Getgood AM,Kew SJ,Brooks R et al.Evaluation of early-stage osteochondral defect repair using a biphasic scaffold based on a collagen-glycosaminoglycan biopolymer in a caprine model.Knee.2012;19(4):422-430.[23]Filová E,Jelínek F,Handl M,et al.Novel composite hyaluronan/ type I collagen/fibrin scaffold enhances repair of osteochondral defect in rabbit knee.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2008;87(2):415-424.[24]Khanarian NT,Jiang J,Wan LQ,et al.A hydrogel-mineral composite scaffold for osteochondral interface tissue engineering.Tissue Eng Part A.2012; 18(5-6):533-545.[25]Sundelacruz S,Kaplan DL.Stem cell- and scaffold-based tissue engineering approaches to osteochondral regenerative medicine.Semin Cell Dev Biol.2009; 20(6):646-655.[26]Brady MA,Sivananthan S,Mudera V,et al.The primordium of a biological joint replacement: Coupling of two stem cell pathways in biphasic ultrarapid compressed gel niches. Craniomaxillofac Surg.2011;39(5):380-386. |