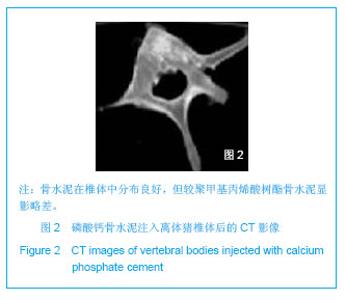
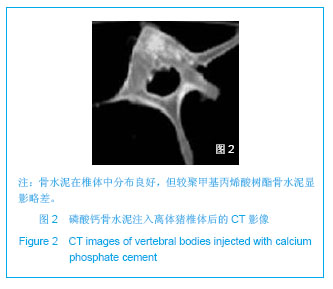
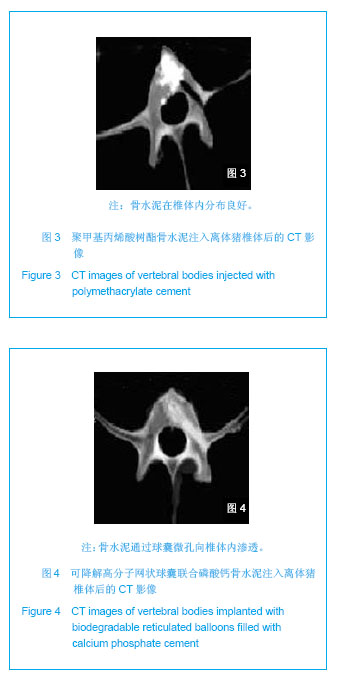
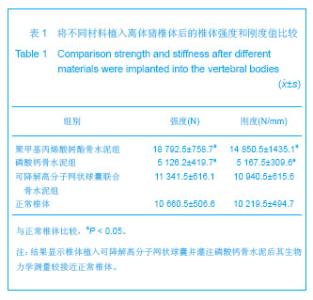
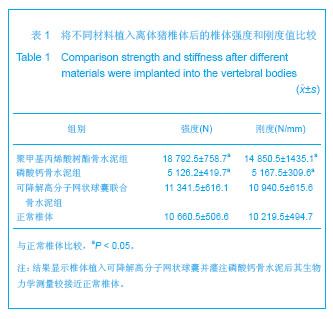
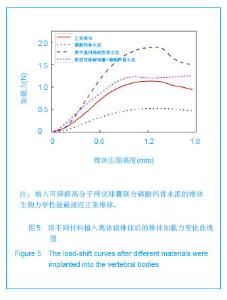
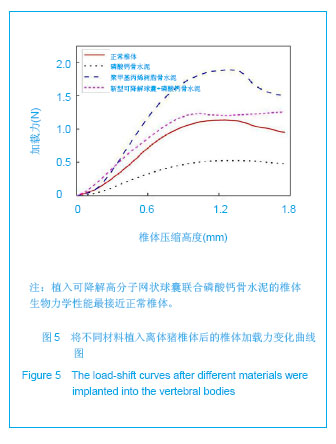
| [1]滕皋军,何仕诚,郭金和,等.经皮椎体成形术治疗椎体良恶性病变的临床技术应用探讨[J].中华放射学杂志,2002,36(4):295-299.[2]倪才方,杨惠林,唐天驷.经皮椎体成形术的初步临床应用[J].介入放射学杂志,2002,1194):275-278. [3]Röllinghoff M,Siewe J,Zarghooni K,et al. Effectiveness,security and height restoration on fresh compression fractures--a comparative prospective study of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty.Minim Invasive Neurosurg.2009;52:233-237.[4]孙钢,金鹏,刘训伟,等.球囊扩张椎体后凸成形术的技术操作及相关问题的探讨[J].中华放射学杂志,2007,41(11):1224. [5]吴春根,程永德.加强脊柱介入放射学的技术研究和临床应用[J].介入放射学杂志,2008,17(2):417-420.[6]Sun G,Wei DX,Liu XW,et al.Novel biodegradable electrospun nanofibrous P(DLLA-CL) balloons for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures. Nanomedicine.2013. pii: S1549-9634(13)00003-8. [7]中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30. [8]Belkoff SM,Mathis JM,Jasper LE,et al.The biomechanics of vertebroplasty. The effect of cement volume on mechanical behavior. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2001;26:1537-1541.[9]Yeom JS,Kim WJ,Choy WS,et al.Leakage of cement in percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic compression fractures.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2003;85:83-89.[10]Phillips FM,Todd Wetzel F,Lieberman I,et al. An in vivo comparsion of the potential for extravertebral cement leak after vertebroplasty snd kyphoplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27:2173-2179.[11]Hulme PA,Krebs J,Ferguson SJ,et al.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: a systematic review of 69 clinical studies. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2006;31:1983-2001.[12]Eck JC,Nachtigall D,Humphreys SC,et al.Comparison of vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a metaanalysis of the literature. Spine J.2008;8:488-497.[13]于金河,孙先泽,任亮,等.“支柱块”置入与球囊扩张椎体后凸成形治疗老年胸腰椎压缩骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(9): 1648-1654.[14]Flors L,Lonjedo E,Leiva-Salinas C,et al.Vesselplasty: a new technical approach to treat symptomatic vertebral compression fractures.AJR Am J Roentgenol.2009; 193: 218-226.[15]Rotter R,Martin H,Fuerderer S,et al.Vertebral body stenting: a new method for vertebral augmentation versus kyphoplasty. Eur Spine J. 2010;19:916-923.[16]Barr JD,Barr MS,Lemley TJ,et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for pain relief and spinal stabilization.Spine. 2000;25:923-928.[17]Tzermiadianos MN,Renner SM,Phillips FM,et al. Altered disc pressure profile after an osteoporotic vertebral fracture is a risk factor for adjacent vertebral body fracture.Eur Spine J. 2008;17:1522-1530. [18]Sun G,Jin P,Li M,et al. Height restoration and wedge anglecorrection effects of percutaneous vertebroplasty: association with intraosseous clefts.Eur Radiol.2011;21: 2597-2603.[19]Wagner AL,Baskurt E. Refracture with cement extrusion following percutaneous vertebroplasty of a large interbody cleft.AJR Am J Roentgenol.2006;27:230-231.[20]Togawa D,Kovacic JJ,Bauer TW,et al.Radiographic and histologic findings of vertebral augmentation using polymethylmethacrylate in the primate spine: percutaneous vertebroplasty versus kyphoplasty.Spine.2006;31:E4-10.[21]周鑫,夏群,苗军,等.磷酸钙骨水泥改性研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(1):55-57.[22]Lieberman IH,Togawa D,et al.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: filler materials .Spine J.2005;11: 305S-316S.[23]van de Watering FC,van den Beucken JJ,Walboomers XF,et al. Calcium phosphate/poly(D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) composite bone substitute materials: evaluation of temporal degradation and bone ingrowth in a rat critical-sized cranial defect. Clin Oral Implants Res.2012;23:151-159.[24]Aberg J,Henriksson HB,Engqvist H,et al. Biocompatibility and resorption of a radiopaque premixed calcium phosphate cement. J Biomed Mater Res A.2012;100:1269-1278. |