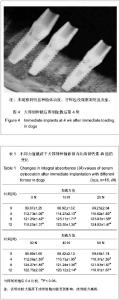
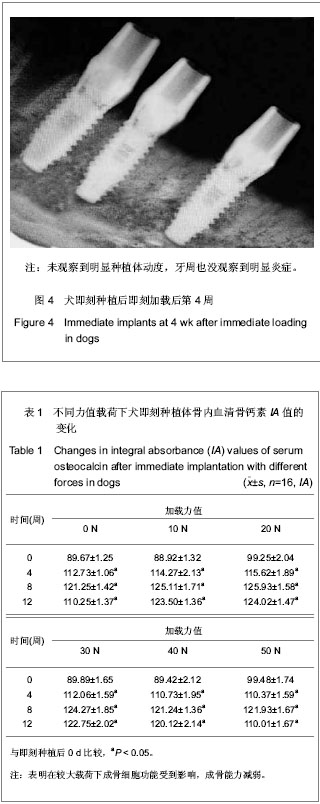
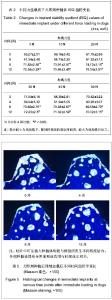
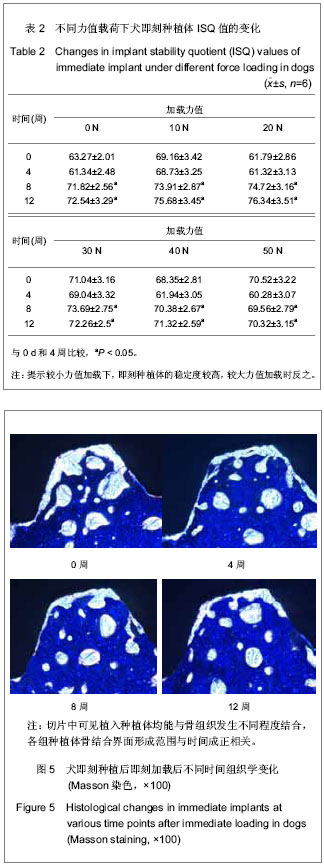
| [1] Branemark PI,Breine U,Adell R,et al.Intraosseous anchorage of dental prosthesis. Experimental studies. Plast Reconstr Surg.l969;3:81-100.[2] Jayme SJ, de Oliveira RR, Muglia VA,et al. The effects of different loading times on the bone response around dental implants: a histomorphometric study in dogs. Oral Maxillofacial Implants.2010;25(3):473-491.[3] Blanco J,Liñares A,Pérez J,et al. Ridge alterations following flapless immediate implant placement with or without immediate loading. Part II: a histometric study in the Beagle dog. Clin Periodontal.2011;38(8):762-770.[4] Moon SY, Kim SG, Lim SC. Histological and histomorphometric evaluation of early and immediately loaded implants in the dog mandible. Biomed Mater Res A.2008; 86(4):112-117.[5] Babbush CA, Kutsko G T, Brokloff, et al. The all-on-four immediate function treatment concept with Nobel Active implants: a retrospective study. Oral Implant.2011;37(4): 431-445.[6] Tealdo T, Bevilacqua M, Menini M.Immediate versus delayed loading of dental implants in edentulous maxillae: a 36-month prospective study. Prosthodontics.2011; 24(4):1294-1302.[7] Ravindran DM, Sudhakar U, Ramakrishnan T, et al. The efficacy of flapless implant surgery on soft-tissue profile comparing immediate loading implants to delayed loading implants: A comparative clinical study. Indian Soc Periodontal. 2010;14(4):245-512.[8] 吴丹,王璐,徐凌,等.即刻种植即刻加载对Beagle犬骨结合界面形成的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2012,12(30):1197-1201.[9] 张欣珂,郑小波.犬股骨骨折髓内针内固定和相关因子的变化研究[D].西南大学,2009[10] 周庆梅,孙健,李亚莉,等.生长因子缓释系统复合纳米支架材料修复犬下颌骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,21(17): 3816- 3822.[11] 崔玉明,冯守诚,王冰封.兔桡骨骨折和骨缺损修复过程中血清骨钙素含量的动态变化[J]兰州医学院学报,1996,22(2):55-58.[12] Akech J,Wixted JJ,Bedard K,et al.Runx2 association with progression of prostate cancer in patients:mechanisms mediating bone osteolysis and osteoblastic metastatic lesions. Oncogene.2010;29(6):811-821.[13] 庄龙飞,张志勇,赖红昌.ITI种植体早期负重与传统负重稳定性的比较[J].上海口腔医学,2007,16(3):1276-1281.[14] 鲍琰,肖立群,施斌,等.Straumann种植体骨愈合期稳定性变化的临床动态监测[J].口腔医学研究,2009,25(6):1321-1326[15] 许尧祥,李亚莉,陈立强,等.壳聚糖微球/纳米羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸复合支架制备及其蛋白缓释效果:与单纯纳米羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸支架、壳聚糖微球的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床复,2010,14(3):452-456.[16] Worthington P.Injury to the inferior alveolar nerve during implant placement: A formula for protection of the patient and clinician Oral Maxillofacial Implants.2004;19(5):731-734.[17] Becker W. Immediate implant placement:Treatment planning and surgical steps for successful outcomes. Br Dent. 2006; 201(4):199-205.[18] Mara CS, Sartori AR, Duarte AS, et al. Periosteum as a source of mesenchymal stem cells:the effects of TGF-beta3 on chondrogenesis.Clinics(Sao Paulo).2011;66(3):487-857.[19] 秋霞,罗南萍,王瑞山.IL-6及骨代谢生化指标对骨吸收和骨形成的影响[J].放射免疫学杂志,2003,16(l):33.[20] Degidi M,Perrotti V,Piattelli A.Immediately loaded titanium implants with a porous anodized surface with at least 36 months of follow-up.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2006;8(4): 169-177.[21] Bischof M, Nedir R, Szmukler-Moncler S, et al. Implant stability measurement of delayed and immediately loaded implants during healing.Clini Oral Implants Res. 2004;15(5): 529-539.[22] Bessa PC,Casal M,Reis RL,et al.Bone morphogenetic proteins in tissue engineering: the road from the laboratory to the clinic, part I (basic concepts) .Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2008;2(1):1-13.[23] Zheng Y, Wu G, Zhao J, et al. rhBMP2/7Heterodimer: An Osteoblasto-genesis Inducer of Not Higher Potency but Lower Effective Concentration Compared with rhBMP2 and rhBMP7 Homodimers.Tissue Eng Part A.2010;16(3):879-887. |