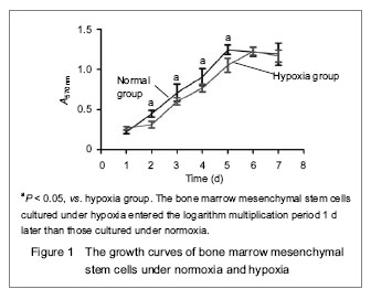
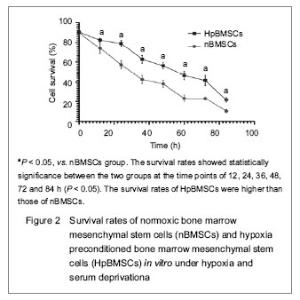
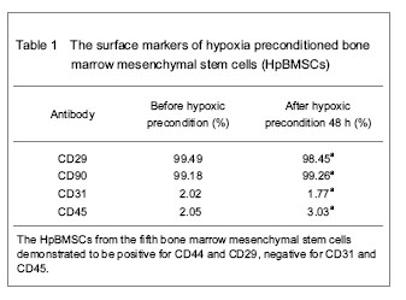
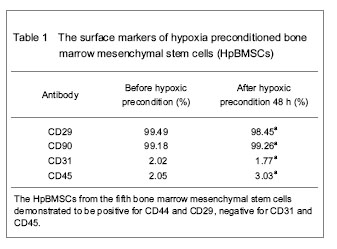
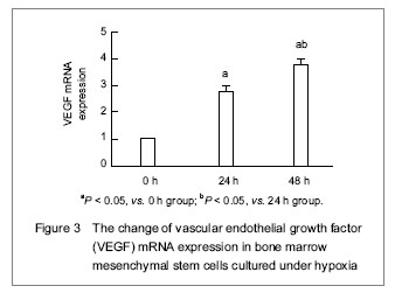
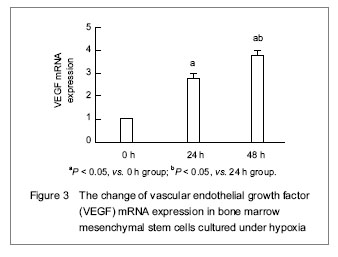
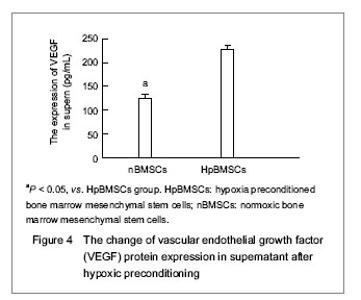
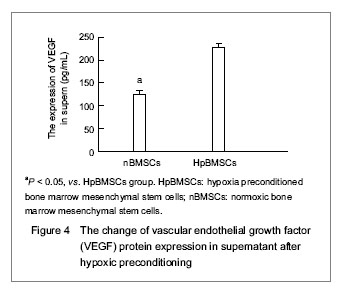
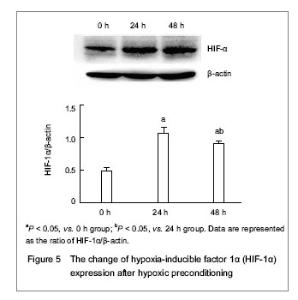
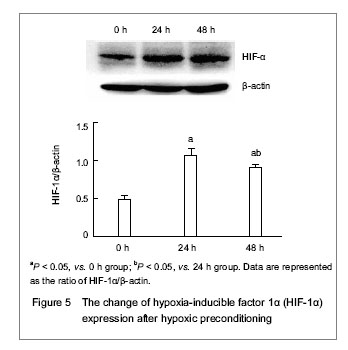
| [1] Malgieri A, Kantzari E, Patrizi MP, et al. Bone marrow and umbilical cord blood human mesenchymal stem cells: state of the art. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2010;3(4):248-269. [2] Tse WT, Pendleton JD, Beyer WM, et al. Suppression of allogeneic T-cell proliferation by human marrow stromal cells: implications in transplantation. Transplantation. 2003;75(3):389-397. [3] Li Y, McIntosh K, Chen J, et al. Allogeneic bone marrow stromal cells promote glial–axonal remodeling without immunologic sensitization after stroke in rats. Exp Neurol. 2006;198(2):313-25. [4] Hamou C, Callaghan MJ, Thangarajah H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells can participate in ischemic neovascularization. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;123(2 Suppl):45S-55S. [5] Abdollahi H, Harris LJ, Zhang P, et al.The role of hypoxia in stem cell differentiation and therapeutics. J Surg Res. 2011; 165(1):112-117. [6] Zhang M, Methot D, Poppa V, et al. Cardiomyocyte grafting for cardiac repair graft cell death and anti-death strategies. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001;33(5):907-921. [7] Toma C, Pittenger MF, Cahill KS, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells differentiate to a cardiomyocyte phenotype in the adult murine heart. Circulation. 2002;105(1):93-98. [8] Jin C, Zhang PJ, Wu XM, et al. Impact of hypoxic preconditioning on apoptosis and its possible mechanism in orthotopic liver autotransplantation in rats. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2009;8(1):40-45. [9] Leroux L, Descamps B, Tojais NF, et al. Hypoxia preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells improve vascular and skeletal muscle fiber regeneration after ischemia through a Wnt4-dependent pathway. Mol Ther. 2010; 18(8):1545-1552. [10] Hu X, Yu SP, Fraser JL, et al. Transplantation of hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells improves infarcted heart function via enhanced survival of implanted cells and angiogenesis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008; 135:799-808. [11] Yu X, Lu C, Liu H, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning with cobalt of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves cell migration and enhances therapy for treatment of ischemic acute kidney injury. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e62703. [12] Wang JC, Xia L, Song XB, et al. Transplantation of hypoxia preconditioned bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves survival of ultra-long random skin flap. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011;124(16):2507-2511.[13] Chang CP, Chio CC, Cheong CU, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning enhances the therapeutic potential of the secretome from cultured human mesenchymal stem cells in experimental traumatic brain injury. Clin Sci (Lond). 2013; 124(3):165-176. [14] Ohnishi S, Yasuda T, Kitamura S, et al. Effect of hypoxia on gene expression of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and mononuclear cells. Stem Cells. 2007;25(5): 1166-1177.[15] Tsai CC, Yew TL, Yang DC, et al. Benefits of hypoxic culture on bone marrow multipotent stromal cells. Am J Blood Res. 2012;2(3):148-159. [16] Abdollahi H, Harris LJ, Zhang P, et al. The role of hypoxia in stem cell differentiation and therapeutics. J Surg Res. 2011; 165:112-117. [17] Yu X, Lu C, Liu H, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning with cobalt of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves cell migration and enhances therapy for treatment of ischemic acute kidney injury. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e62703. [18] Hu X, Wei L, Taylor TM, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning enhances bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell migration via Kv2.1 channel and FAK activation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011;301(2):C362-372. [19] Liu H, Yu XF, Teng J, et al. Effects of hypoxic preconditioning on the migration of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012;92(10):709-713. [20] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30. [21] Ma XH, Gao CQ, Guo W, et al. Study of MSCs transplantation in therapy of myocardial infarction. Int J Phys Sci. 2011;6(9):2315-2320.[22] Yao X, Miao W, Li M, et al. Protective effect of albumin on VEGF and brain edema in acute ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2010;472(3):179-183. [23] Csete M. Oxygen in the cultivation of stem cells. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2005;1049:1-8. |