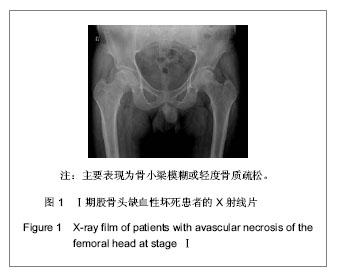
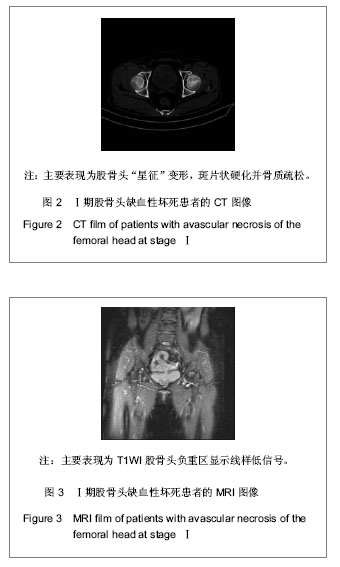
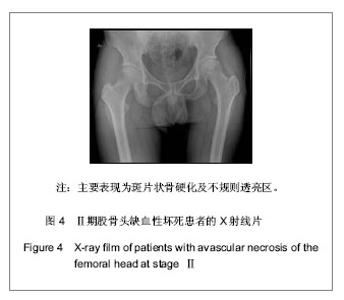
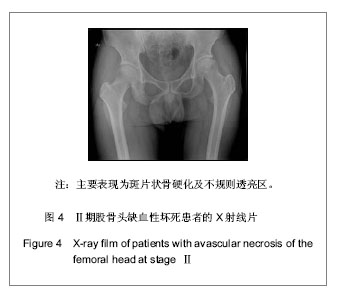
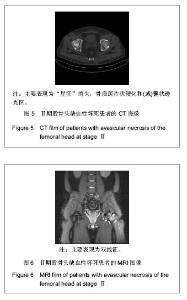
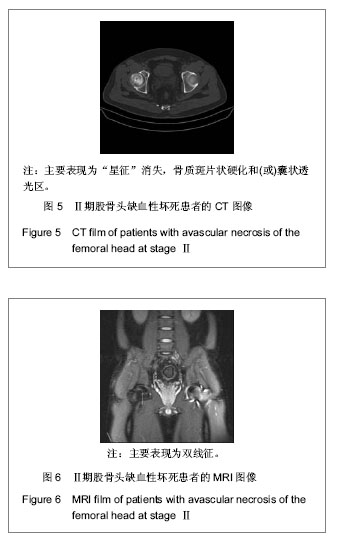
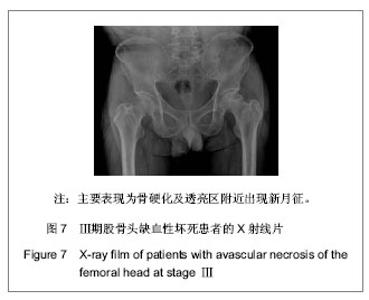
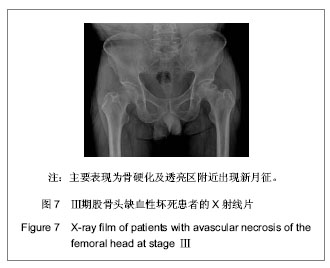
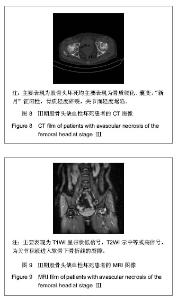
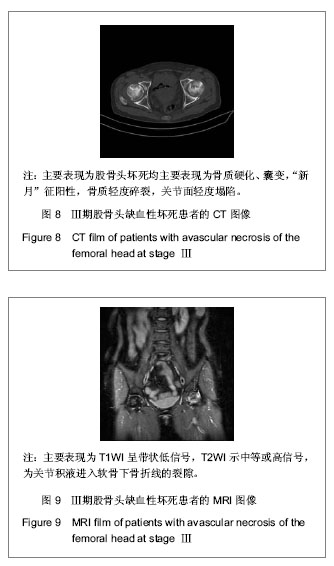
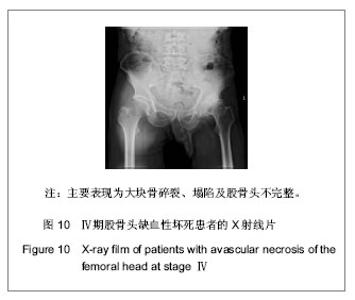
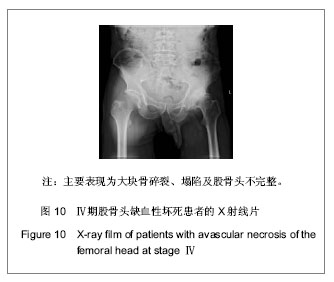
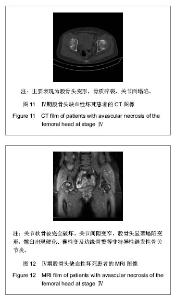
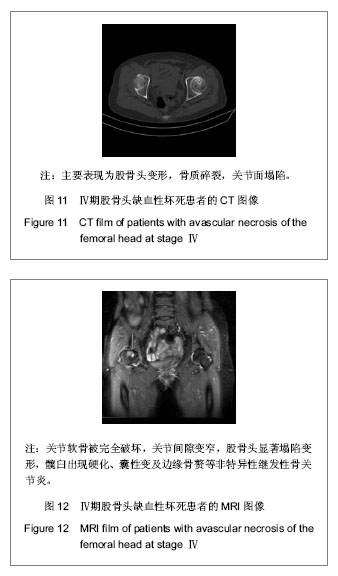
| [1] 任安,张雪哲.股骨头缺血性坏死研究简况[J].中华放射学杂志, 1997,31(3):199-202.
[2] 程晓光,屈辉.严重急性呼吸综合征康复患者骨缺血性坏死患病率的MRI筛查研究[J].中华放射学杂志,2005,39(8):791-797.
[3] 王文泉,董公怡.创伤性和激素性股骨头坏死的病理学研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,1997,19(2):140-142.
[4] 归云荣,归俊,芦苇,等.早期股骨头缺血性坏死MRI的诊断价值[J]. 右江民族医学院学报,2008,30(3):460-462.
[5] 徐爱德,徐文坚,刘吉华.骨关节CT和MRI诊断学[M].济南:山东科学技术出版社,2003:319-326.
[6] Mont MA, Hungerford DS. Non-traumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77(3): 459-474.
[7] 董天华. 成人股骨头缺血性坏死的现代新概念[J].苏州医学院学报,2000,20(12):1078-1080.
[8] 刘春红,徐爱德,刘吉华,等.成人股骨头缺血性坏死MRI研究[J].中国医学影像技术,2003,19(1):79-81.
[9] 余开湖,冯敢生,郑传胜. DR、CT、MRI在股骨头缺血性坏死的诊断和分期中的价值[J].临床放射学杂志,2005,24(2):151-153.
[10] 陈志刚.关节病影像诊断学[M].西安:陕西科学技术出版社,1999: 346-348.
[11] 高元桂,蔡幼铨,蔡祖龙.磁共振成像诊断学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,1997:683-684.
[12] Mitchell DG, Rao VM, Dalinka MK, et al. Femoral head avascular necrosis; correlatlon of MR imaging, radiolographic staging, radionuclide imaging and clinical finding. Radiology. 1997;162(11):708-709.
[13] Doury P. Bone marrow edema, transient osteoporosis and algodystrophy. J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 1994;76(12):993-997.
[14] Froberg PK, Braunstein EM, Buckwalter KA. Osteopnerosis transien osteoporosis and transient bone marrow edema: current concepts.Radial clin North Am. 1996;34(2):273-292.
[15] 连国兴,王天玉.激素所致股骨头无菌性坏死病因及影像学诊断[J]. 河南职工医学院学报,2008,20(1):17-19.
[16] 黄振国,王存利,张雪哲,等.非创伤性股骨头坏死:不同病因间MRI及病理对比研究[J].实用放射学杂志,2006,24(3):339-342.
[17] 尹晓明,邓刚,李宝平,等.磁共振成像早期诊断激素诱导股骨头缺血性坏死[J].CT理论与应用研究,2006,15(1):29-32.
[18] 申炜,雷其理.成人股骨头缺血性坏死的X线平片与CT片对比分析[J].右江医学,2009,37(4):472-473.
[19] 何长林,张琼,张静,等. 成人股骨头缺血性坏死的X线及CT诊断分析[J].常州实用医学,2010,26(3):169-170.
[20] Chernetsky SG, Mont MA, Laporte DM, et al Pathologic feactrues insteroid and nonsteroid associated osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop. 1999;368(11):149-161.
[21] 陈大朝.股骨头缺血性坏死磁共振成像诊断进展[J].国外医学: 临床放射学分册, 2004,27(2):105-108.
[22] 徐洪.股骨头缺血性坏死的影像学诊断及其临床意义[J].中国社区医师:医学专业,2010,12(15):159. |