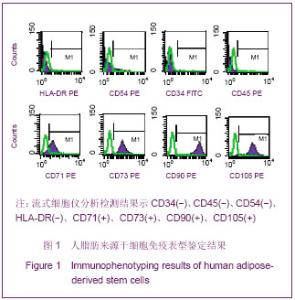
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Influence of different oxygen partial pressures on cytokines secreted from human adipose-derived stem cells
Jiang Yi-yao1, Liu Xiao-cheng1, Pei Yu2, Zhu De-lin1
- 1Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, TEDA International Cardiovascular Hospital, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300457, China; 2Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, TEDA International Cardiovascular Hospital, Peking Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Tianjin 300457, China
-
Revised:2013-08-02Online:2013-11-05Published:2013-11-05 -
Contact:Liu Xiao-cheng, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, TEDA International Cardiovascular Hospital, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300457, China TEDA_LXC@163.com -
About author:Jiang Yi-yao☆, Studying for doctorate, Physician, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, TEDA International Cardiovascular Hospital, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300457, China Jiangyiyao0309@sina.com -
Supported by:the Health Bureau of Tianjin Economic and Development Area Foundation, No. 2012BWKZ009*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Yi-yao, Liu Xiao-cheng, Pei Yu, Zhu De-lin. Influence of different oxygen partial pressures on cytokines secreted from human adipose-derived stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.45.007.
share this article
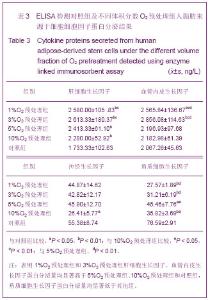
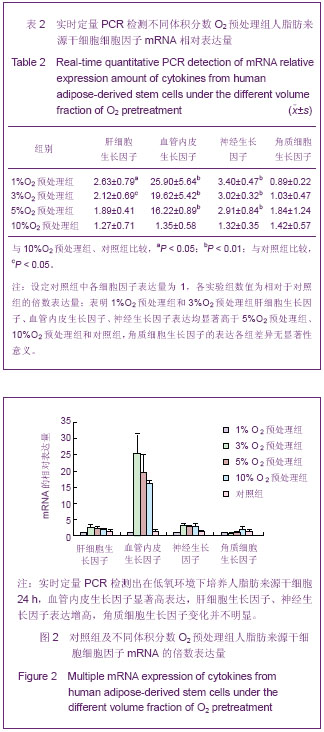
结果示各实验组中肝细胞生长因子的表达量差异有显著性意义(F=3.62,P < 0.05),肝细胞生长因子的表达在1%O2预处理组中显著多于10%O2预处理组、对照组,在3%O2预处理组中显著多于对照组(P < 0.05)。各实验组中血管内皮生长因子的表达量差异有非常显著性意义(F=8.19,P < 0.01),血管内皮生长因子的表达在1%O2预处理组、3%O2预处理组、5%O2预处理组中均高度显著多于10%O2预处理组、对照组;神经生长因子的表达量差异有非常显著性意义(F=15.46,P < 0.01),神经生长因子的表达在1%O2预处理组、3%O2预处理组、5%O2预处理组中均显著多于10%O2预处理组、对照组。角质细胞生长因子的表达无显著差异性意义(F=1.10,P > 0.05)。 2.3 肝细胞生长因子、血管内皮生长因子、神经生长因子、角质细胞生长因子蛋白分泌 收集各实验组细胞上清液,ELISA试剂盒测定各组蛋白浓度,见表3。"
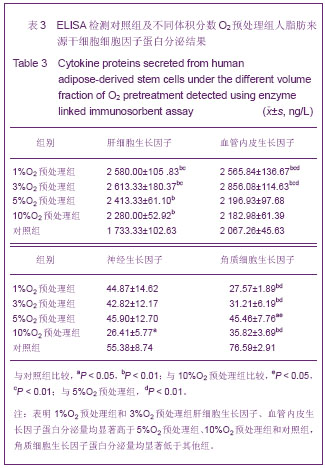

各实验组肝细胞生长因子蛋白分泌差异有非常显著性意义(F =31.34,P < 0.01),其中1%O2预处理组、3%O2预处理组肝细胞生长因子蛋白分泌量显著多于10%O2预处理组、对照组,5%O2预处理组、10%O2预处理组肝细胞生长因子蛋白分泌量显著多于对照组。各实验组血管内皮生长因子蛋白分泌量差异有显著性意义(F =34.25,P < 0.01),其中1%O2预处理组、3%O2预处理组血管内皮生长因子蛋白分泌量显著高于其他组,5%O2预处理组血管内皮生长因子蛋白分泌量与10%O2预处理组、对照组差异无显著性意义。各实验组角质细胞生长因子蛋白分泌量差异有显著性意义 (F =47.12,P < 0.01),1%O2预处理组、3%O2预处理组角质细胞生长因子蛋白分泌量显著低于5%O2预处理组和对照组,10%O2预处理组角质细胞生长因子蛋白分泌量显著低于5%O2预处理组和对照组,5%O2预处理组角质细胞生长因子蛋白分泌量显著低于对照组。10%O2预处理组神经生长因子蛋白的分泌量显著低于对照组(P < 0.05),见图3,4。"

| [1] Yamada Y, Wang XD, Yokoyama S, et al. Cardiac progentior cells in brown adipose tissue repaired damaged myocardium. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2006; 342(2):662-667. [2] Saltzman DJ, Toth A, Tsai AG, et al. Oxygen tension distribution in postcapillary venules in resting skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2003;285(5):H1980-1985. [3] Mckinley BA, Butler BD.Comparison of skeletal muscle PO2, PCO2 and pH with gastric tonometric PCO2 and pH in hemorrhagic shock. Crit Care Med 1999; 27(9):1869-1877 [4] Kim JH, Park SH, Park SG, et al. The pivotal role of reactive oxygen species generation in the hypoxia-induced stimulation of adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Dev, 2011; 20(10): 1753-1761 [5] Zhang XL, Wang HB, Ma X, et al. Preservation of the cardiac function in infarcted rat hearts by the transplantation of adipose-derived stem cells with injectable fibrin scaffolds. Experimental Biology and Medicine.2010; 235(12): 1505- 1515. [6] Chung HM, Won CH, Sung JH.Responses of adipose-derived stem cells during hypoxia:enhanced skin-regenerative potential. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2009; 9(12): 1499-1508. [7] 袁小刚,吕农华.骨髓间充质干细胞的诱导分化及其恶性转化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(14):2615-2618. [8] Røsland GV, Svendsen A, Torsvik A, et al. Long-term cultures of bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells frequently undergo spontaneous malignant transformation. Cancer Res.2009; 69(13):5331-5339. [9] Golfinopoulos V, Pentheroudakis G, Kamakari S,et al. Donor- derived breast cancer in a bone marrow transplantation recipient. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009; 113(2):211-213. [10] Stummann TC, Bremer S. Embryonic stem cells in safety pharmacology and toxicology. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology.2012;745:14-25. [11] Andrew D, Leavitt MD, Isla H D. Homologous recombination in human embryonic stem cells: a tool for advancing cell therapy and understanding and treating human disease. CTS. 2011;(4):298-305. [12] Pineda ET, Nerem RM, Ahsan T. Differentiation Patterns of Embryonic Stem Cells in Two- versus Three-Dimensional Culture. Cells Tissues Organs. 2013 Feb 9. [13] Swijnenburg RJ, Schrepfer S, Cao F, et al. In vivo imaging of embryonic stem cells reveals patterns of survival and immune rejection following transplantation. Stem Cells Dev. 2008; 17(6):1023-1029. [14] 王延光.论干细胞研究中胚胎的道德地位[J].中国医学伦理学, 2006,19(2):6-10. [15] 朱希山,赵春华.胚胎干细胞研究的伦理之争[J].中国医学伦理学, 2006,19(6):57-59. [16] Gimble JM. Adipose tissue-derived therapeutics. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2003; 3(5):705-713. [17] Hsu VM, Stransky CA, Bucky LP,et al. Fat grafting's past, present, and future: why adipose tissue is emerging as a critical link to the advancement of regenerative medicine. Aesthet Surg J. 2012; 32(7):892-899. [18] Choi J,Minn KW,Chang H.The efficacy and safety of platelet-rich plasma and adipose-derived stem cells: an update. Arch Plast Surg.2012; 39(6):585-592. [19] Ren ML,Peng W,Yang ZL,et al.Allogeneic adipose-derived stem cells with low immunogenicity constructing tissue-engineered bone for repairing bone defects in pigs. Cell Transplant. 2012; 21(12):2711-2721. [20] Strauß S, Dudziak S, Hagemann R,et al.Induction of osteogenic differentiation of adipose derived stem cells by microstructured nitinol actuator-mediated mechanical stress. PLoS One. 2012; 7(12):e51264. [21] Lee JH, Lee KH, Kim MH,et al.Possibility of undifferentiated human thigh adipose stem cells differentiating into functional hepatocytes. Arch Plast Surg.2012; 39(6):593-599. [22] Razavi S,Ahmadi N,Kazemi M,et al. Efficient transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into Schwann-like cells: A promise for treatment of demyelinating diseases. Adv Biomed Res.2012; 1:12 [23] 胡丽,刘加荣,陈莉莉.组织工程化口腔黏膜构建的研究现状[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康,2011,15(42):7902-7906. [24] 陈阳,高建华,察鹏飞,等. 5 μg/L碱性成纤维细胞生长因子促脂肪来源干细胞的增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(45): 8481-8485. [25] Uysal CA, Tobita M, Hyakusoku H,et al. Adipose-derived stem cells enhance primary tendon repair: biomechanical and immunohistochemical evaluation. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012; 65(12):1712-1719. [26] Locke M,Feisst V,Dunbar PR.Concise review: human adipose-derived stem cells: separating promise from clinical need. Stem Cells. 2011; 29(3):404-411. [27] Wilson A,Butler PE,Seifalian AM. Adipose-derived stem cells for clinical applications: a review. Cell Prolif. 2011; 44(1):86-98. [28] Locke M, Windsor J, Dunbar PR.Human adipose-derived stem cells: isolation, characterization and applications in surgery.ANZ J Surg.2009; 79: 235-244. [29] Gronthos S, Franklin DM, Leddy HA,et al. Surface protein characterization of human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. J Cell Physiol. 2001;189: 54-63. [30] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P,et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell.2002; 13: 4279-4295. [31] Abraham MR,Gerstenblith G. Preconditioning stem cells for cardiovascular disease:an important step forword. Circ Res.2007;100(4): 447-449. [32] 高景红,孙传波,张竞文,等.血管紧张素II预处理提高间充质干细胞耐缺氧能力[J].南京医科大学学报:自然科学版,2011,31(8): 1092-1096. [33] 郭军,李自成.IGF-1预处理对骨髓间充质干细胞心肌再生及抗炎效果的影响[J].临床心血管病杂志, 2011,27(12):948-951. [34] Mckinley BA, Butler BD. Comparison of skeletal muscle PO2, PCO2, and pH with gastric tonometric PCO2 and pH in hemorrhagic shock. Crit Care Med.1999; 27(9):1869-1877. [35] Saltzman DJ,Toth A,Tsai AG,et al.Oxygen tension distribution in postcapillary venules in resting skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.2003;285(5): H1980-1985. [36] Simon MC, Keith B. The role of oxygen availability in embryonic development and stem cell function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.2008;9(4):285-296. [37] Wild JM, Fichele S, Woodhouse N,et al. 3D volume-localized PO2 measurement in the human lung with 3He MRI. Magn Reson Med.2005;53(5):1055-1064. [38] Buravkova LB,Anokhina EB.Mesenchymal stromal progenitor cells: general characteristics and functional state in low oxygen tension. Ross Fiziol Zh Im IM Sechenova.2008;94(7): 737-757. [39] He MC, Li J, Zhao CH. Effect of hypoxia on mesenchyma stem cells- review. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2007;15(2):433-436. [40] Ma T Grayson WL,Frohlich M,Vunjak-Novakovic G. Hypoxia and stem cell-based engineering of mesenchymal tissues. Biotechnol Prog.2009;25(1):32-42. [41] 陈亭,周燕,张治萍,等.间充质干细胞在低氧环境下的增殖、代谢与成骨分化:胎盘羊膜及骨髓来源间充质千细胞的对比[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(6):957-961. [42] 王立维,黄文,赵渝.低氧培养对间充质干细胞生物学的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(23):4329-4334. [43] Wagegg M, Gaber T, Lohanatha FL,et al. Hypoxia Promotes Osteogenesis but Suppresses Adipogenesis of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in a Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Dependent Manner. PLoS ONE.2012; 7(9): e46483. [44] Stubbs SL, Hsiao ST, Peshavariya HM, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning enhances survival of human adipose-derived stem cells and conditions endothelial cells in vitro. Stem Cells Dev, 2012. [45] Lavrentieva A, Majore I, Kasper C, et al.Effects of hypoxic culture conditions on umbilical cord-derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Commun Signal. 2010;8:18. [46] Stubbs SL, Hsiao ST, Peshavariya HM, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning enhances survival of human adipose-derived stem cells and conditions endothelial cells in vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(11):1887-1896. [47] 宋华培,黄跃生,党永明,等.PI3K/ Akt 信号途径抑制烧伤后大鼠缺血缺氧心肌细胞凋亡[J].第三军医大学学报,2009,31(1): 52-55 [48] Kim JH, Park SH, Park SG, et al. The pivotal role of reactive oxygen species generation in the hypoxia-induced stimulation of adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2011; 20(10): 1753-1761. [49] Park SG, Kim JH, Xia Y,et al. Generation of reactive oxygen species in adipose-derived stem cells: friend or foe? Epert Opin Ther Targets.2011; 15(11): 1297-1306. [50] Planat-Benard V, Menard C, Andre M et al. Spontaneous cardiomyocyte differentiation from adipose tissue stroma cells. Cir Res.2004; 94(2):223-229. [51] Hsiao ST, Lokmic Z, Peshavariya H,et al. Hypoxic conditioning enhances the angiogenic paracrine activity of human adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013 Jan 2. [52] Huang F, Zhu X, Hu XQ,et al. Mesenchymal stem cells modified with miR-126 release angiogenic factors and activate Notch ligand Delta-like-4, enhancing ischemic angiogenesis and cell survival. Int J Mol Med. 2013; 31(2): 484-492. [53] Sanz-Rosa D, García-Prieto J, Ibanez B. The future: therapy of myocardial protection. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012; 1254: 90-98. [54] Song SY, Chung HM, Sung JH.The pivotal role of VEGF in adipose-derived-stem-cell-mediated regeneration. Expert Opin Biol Ther.2010;10(11):1529-1537. [55] Przybyt E, Krenning G, Brinker MG,et al. Adipose stromal cells primed with hypoxia and inflammation enhance cardiomyocyte proliferation rate in vitro through STAT3 and Erk1/2. J Transl Med. 2013;11(1):39. |
| [1] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(在线): 3-. |
| [2] | Tu Pengcheng, Guo Yang, Ma Yong, Pan Yalan, Zheng Suyang, Wang Lining, Wu Chengjie, Guo Junjie. Phenotypic maintenance of chondrocytes in vitro under tensile stress enhanced by the extract of Clematis chinensis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1182-1187. |
| [3] |
Zhan Long, Meng Nongqin, Nong Juan, Li Xiaofeng, Yang Yuan, Yu Xue.
Protocatechuic acid alleviates degeneration of chondrocytes |
| [4] | Chen Jinsong, Wang Zhonghan, Chang Fei, Liu He. Tissue engineering methods for repair of articular cartilage defect under special conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1272-1279. |
| [5] | Liu Chundong, Shen Xiaoqing, Zhang Yanli, Zhang Xiaogen, Wu Buling. Effects of strontium-modified titanium surfaces on adhesion, migration and proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and expression of bone formation-related genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1009-1015. |
| [6] | Lin Ming, Pan Jinyong, Zhang Huirong. Knockout of NIPBL gene down-regulates the abilities of proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1002-1008. |
| [7] | Zhang Wen, Lei Kun, Gao Lei, Li Kuanxin. Neuronal differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via lentivirus-mediated bone morphogenetic protein 7 transfection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 985-990. |
| [8] | Wu Zhifeng, Luo Min. Biomechanical analysis of chemical acellular nerve allograft combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for repairing sciatic nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 991-995. |
| [9] | Huang Yongming, Huang Qiming, Liu Yanjie, Wang Jun, Cao Zhenwu, Tian Zhenjiang, Chen Bojian, Mai Xiujun, Feng Enhui. Proliferation and apoptosis of chondrocytes co-cultured with TDP43 lentivirus transfected-human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1016-1022. |
| [10] | Qin Xinyu, Zhang Yan, Zhang Ningkun, Gao Lianru, Cheng Tao, Wang Ze, Tong Shanshan, Chen Yu. Elabela promotes differentiation of Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocyte-like cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1046-1051. |
| [11] | Liu Mengting, Rao Wei, Han Bing, Xiao Cuihong, Wu Dongcheng. Immunomodulatory characteristics of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1063-1068. |
| [12] |
Cen Yanhui, Xia Meng, Jia Wei, Luo Weisheng, Lin Jiang, Chen Songlin, Chen Wei, Liu Peng, Li Mingxing, Li Jingyun, Li Manli, Ai Dingding, Jiang Yunxia.
Baicalein inhibits the biological behavior of hepatocellular
carcinoma stem cells by downregulation of Decoy receptor 3 expression |
| [13] | Zhang Peigen, Heng Xiaolai, Xie Di, Wang Jin, Ma Jinglin, Kang Xuewen. Electrical stimulation combined with neurotrophin 3 promotes proliferation and differentiation of endogenous neural stem cells after spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1076-1082. |
| [14] | Huang Cheng, Liu Yuanbing, Dai Yongping, Wang Liangliang, Cui Yihua, Yang Jiandong. Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor gene for spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1037-1045. |
| [15] | Han Bo, Yang Zhe, Li Jing, Zhang Mingchang . Regulation of limbal stem cells via Wnt signaling in the treatment of limbal stem cell deficiency [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1057-1062. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||