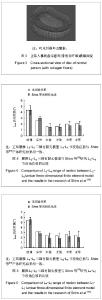
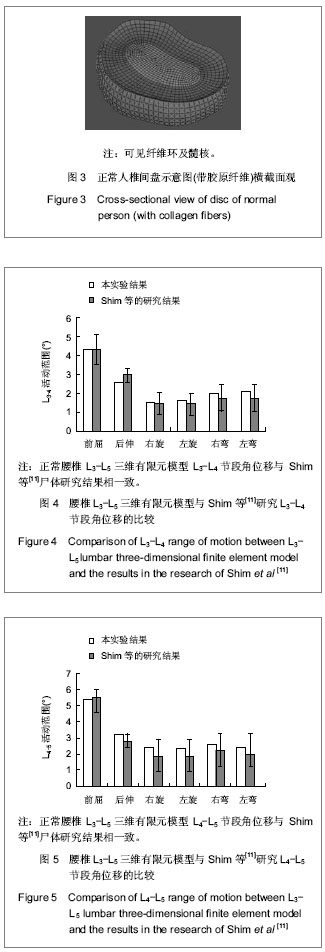
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (35): 6261-6266.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.35.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Validation and verification of L3-L5 lumbar three-dimensional finite element model
Xu Hao1, Zhang Qiu-lin2, Tang Hao2, Chen Bo3
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the First Hospital of Wujiang, Wujiang 215000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Changhai Hospital, Shanghai 200433, China; 3Traumatology and Orthopedics Institute of Shanghai, Shanghai 200025, China
-
Received:2013-02-22Revised:2013-04-20Online:2013-08-27Published:2013-08-27 -
Contact:Tang Hao, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Changhai Hospital, Shanghai 200433, China xuhaomouse2004@yahoo.com.cn -
About author:Xu Hao☆, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, the First Hospital of Wujiang, Wujiang 215000, Jiangsu Province, China Xuhaomouse2004@sina.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Hao, Zhang Qiu-lin, Tang Hao, Chen Bo. Validation and verification of L3-L5 lumbar three-dimensional finite element model[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(35): 6261-6266.
share this article
| [1] Belytschko T, Kulak RF, Schultz AB,et al.Finite element stress analysis of an intervertebral disc. J Biomech. 1974;7(3): 277-285.[2] Chen SH, Lin SC, Tsai WC,et al. Biomechanical comparison of unilateral and bilateral pedicle screws fixation for transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion after decompressive surgery -- a finite element analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13:72.[3] Lo CC, Tsai KJ, Chen SH,et al. Biomechanical effect after Coflex and Coflex rivet implantation for segmental instability at surgical and adjacent segments: a finite element analysis.Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2011;14(11):969-978.[4] Lee KK, Teo EC, Fuss FK,et al. Finite-element analysis for lumbar interbody fusion under axial loading.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2004;51(3):393-400.[5] Schmidt H, Heuer F, Simon U,et al.Application of a new calibration method for a three-dimensional finite element model of a human lumbar annulus fibrosus.Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2006;21(4):337-344.[6] Shirazi-Adl A, Ahmed AM, Shrivastava SC. Mechanical response of a lumbar motion segment in axial torque alone and combined with compression.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1986;11(9):914-927.[7] White Ⅲ AA, Panjabi MM. Clinical Biomechanics of the Spine. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott, 1990.[8] Polikeit A, Ferguson SJ, Nolte LP,et al.Factors influencing stresses in the lumbar spine after the insertion of intervertebral cages: finite element analysis.Eur Spine J. 2003;12(4):413-420.[9] Goto K, Tajima N, Chosa E,et al.Effects of lumbar spinal fusion on the other lumbar intervertebral levels (three- dimensional finite element analysis).J Orthop Sci. 2003; 8(4):577-584.[10] Goel VK, Monroe BT, Gilbertson LG,et al.Interlaminar shear stresses and laminae separation in a disc. Finite element analysis of the L3-L4 motion segment subjected to axial compressive loads.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(6):689-698.[11] Shim CS, Park SW, Lee SH,et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an interspinous stabilizing device, Locker.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(22):E820-E827.[12] Goel VK, Gilbertson LG. Applications of the finite element method to thoracolumbar spinal research--past, present, and future.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(15):1719-1727.[13] Yoganandan N, Kumaresan SC, Voo L,et al. Finite element modeling of the C4-C6 cervical spine unit.Med Eng Phys. 1996;18(7):569-574.[14] Tang S, Meng X.Does disc space height of fused segment affect adjacent degeneration in ALIF? A finite element study.Turk Neurosurg. 2011;21(3):296-303.[15] 刘勇,田青,李国庆,等.骨质疏松腰椎三维有限元模型的建立[J].中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(1):161-162.[16] 黄菊英,李海云,菅凤增,等.腰椎间盘突出症有限元模型的建立与分析[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志,2012,12(4):394-398. [17] 朱立新,王健,曹延林,等.基于CT数据构建人体腰骶椎的有限元模型[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,6(30):5511-5515.[18] 付裕,阮狄克,霍洪军,等.基于CT扫描及CAD技术建立下腰椎三维有限元模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(9): 1557-1561.[19] Yoganandan N, Myklebust JB, Ray G,et al. Mathematical and finite element analysis of spine injuries.Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 1987;15(1):29-93.[20] Yoganandan N, Kumaresan S, Voo L,et al.Finite element model of the human lower cervical spine: parametric analysis of the C4-C6 unit.J Biomech Eng. 1997 ;119(1):87-92.[21] Yoganandan N, Kumaresan S, Voo L,et al.Finite element applications in human cervical spine modeling.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(15):1824-1834.[22] Yoganandan N, Kumaresan S, Pintar FA. Biomechanics of the cervical spine Part 2. Cervical spine soft tissue responses and biomechanical modeling.Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2001; 16(1):1-27.[23] Schultz AB, Warwick DN, Berkson MH, et al. Mechanical Properties of Human Lumbar Spine Motion Segments-Part I: Responses in Flexion, Extension, Lateral Bending, and Torsion. J Biomech Eng. 1979; 101:46-52. [24] Panjabi MM, Krag MH, Chung TQ. Effects of disc injury on mechanical behavior of the human spine.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1984;9(7):707-713.[25] Tencer AF, Ahmed AM, Burke DL.Some static mechanical properties of the lumbar intervertebral joint, intact and injured.J Biomech Eng. 1982;104(3):193-201.[26] Shirazi-Adl A, Ahmed AM, Shrivastava SC. A finite element study of a lumbar motion segment subjected to pure sagittal plane moments.J Biomech. 1986;19(4):331-350.[27] Goel VK, Kim YE, Lim TH,et al. An analytical investigation of the mechanics of spinal instrumentation.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1988;13(9):1003-1011.[28] Vadapalli S, Sairyo K, Goel VK,et al.Biomechanical rationale for using polyetheretherketone (PEEK) spacers for lumbar interbody fusion-A finite element study.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(26):E992-998.[29] Tsuang YH, Chiang YF, Hung CY,et al. Comparison of cage application modality in posterior lumbar interbody fusion with posterior instrumentation--a finite element study.Med Eng Phys. 2009;31(5):565-570.[30] Zhong ZC, Wei SH, Wang JP,et al.Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine with a new cage using a topology optimization method.Med Eng Phys. 2006;28(1):90-98.[31] Chen SH, Lin SC, Tsai WC,et al. Biomechanical comparison of unilateral and bilateral pedicle screws fixation for transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion after decompressive surgery -- a finite element analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13:72.[32] Adam C, Pearcy M, McCombe P.Stress analysis of interbody fusion--finite element modelling of intervertebral implant and vertebral body.Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2003;18(4): 265-272.[33] Xu H, Tang H, Guan X,et al.Biomechanical comparison of posterior lumbar interbody fusion and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion by finite element analysis.Neurosurgery. 2013;72(1 Suppl Operative):21-26.[34] 马金梁,李孝林,邓忠良.一种新型椎间融合器用于腰椎融合的有限元模型建立[J].上海医学,2012,35(11):960-963.[35] 马辉,赵杰,侯铁胜,等.腰椎滑脱后路融合术式有限元模型的建立[J].脊柱外科杂志,2008,6(3):132-136. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Jiang Xiaoyan, Zhu Haifei, Lin Haiqi, Lin Wentao. Cold therapy promotes self-limited recovery of delayed-onset muscle soreness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3609-3613. |
| [3] | Xie Jingshu, Zhang Xianglin, Liu Jinlei, Wen Jing. Application of High Resolution reconstruction algorithm in precision CT scans of the middle and inner ears [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3614-3618. |
| [4] | Liu Jinwei, Chen Yunzhen, Wan Chunyou. Changes of osteogenic growth factors in the broken end of bone nonunion under stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3619-3624. |
| [5] | Luo Anyu, Liu Hanlin, Xie Xiaofei, Huang Chen. Effect of antioxidant mixture on structural degeneration of an osteoarthritis rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3625-3629. |
| [6] | Zhou Wu, Wang Binping, Wang Yawen, Cheng Yanan, Huang Xieshan. Transforming growth factor beta combined with bone morphogenetic protein-2 induces the proliferation and differentiation of mouse MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3630-3635. |
| [7] | Gao Kun, Chen Dayu, Zhang Yong, Liu Weidong, Sun Shufen, Lai Wenqiang, Ma Dujun, Wu Yihong, Lin Zhanpeng, Jiang Yinglu, Yu Weiji. Achyranthes bidentata alcohol extract inhibits extracellular matrix degradation of the cartilage by regulating synovial fibroblast exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3636-3640. |
| [8] | Liang Meifu, Qu Shuhua. Optimal power load forecasting of the skeletal muscle based on back propagation neural network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3641-3647. |
| [9] | Bai Shengchao, Gao Yang, Wang Bo, Li Junping, Wang Ruiyuan. Dynamic changes of mitochondrial function of the skeletal muscle after acupuncture intervention in rats with heavy load exercise-induced injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3648-3653. |
| [10] | Yang Caihui, Liu Qicheng, Dong Ming, Wang Lina, Zuo Meina, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Serine/threonine protein kinases can promote bone destruction in mouse models of chronic periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3654-3659. |
| [11] | Fan Junchao, Chen Yong, Song Junjie. Sevoflurance combined with xenon pretreatment protects against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3660-3665. |
| [12] | Zuo Zhenkui, Han Jiarui, Ji Shuling, He Lulu. Pretreatment with ginkgo biloba extract 50 alleviates radiation-induced acute intestinal injury in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3666-3671. |
| [13] | Zhang Liang, Ma Xiaoyan, Wang Jiahong. Regulatory mechanism of Shenshuai Yin on cell apoptosis in the kidney of chronic renal failure rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3672-3677. |
| [14] | Cheng Yanan, Wu Yucong, Mao Qiuhua, Chen Ling, Lu Liying, Xu Pu. Restoration effect and stability of resin infiltration combined with bioactive glass on demineralized tooth enamel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3522-3526. |
| [15] | Bi Qingwei, Liu Chengpu, Li Yan, Zhao Wenwen, Han Mei. Structure analysis of platelet-rich fibrin derived from two centrifugation procedures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3534-3539. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||