Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (17): 3732-3740.doi: 10.12307/2025.644
Causal relationship between 91 inflammatory proteins and cervical disc degeneration
Liu Shuaiyi1, Zhao Xiaoxuan1, Li Qi2, Xing Zheng2, Li Qingwen1, Chu Xiaolei2
- 1Tianjin Key Laboratory of Exercise Physiology and Sports Medicine, School of Sport, Exercise & Health, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 300381, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300000, China
-
Received:2024-07-09Accepted:2024-08-08Online:2025-06-18Published:2024-11-07 -
Contact:Li Qingwen, PhD, Professor, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Exercise Physiology and Sports Medicine, School of Sport, Exercise & Health, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 300381, China -
About author:Liu Shuaiyi, Master candidate, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Exercise Physiology and Sports Medicine, School of Sport, Exercise & Health, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 300381, China -
Supported by:the National Key R&D Program - “Biology and Information Convergence (BT and IT Convergence)” Key Special Project, No. 2023YFF1205200 (to XZ [project participant]); Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin City (General Program), Nos. 22JCYBJC00210 (to LQ) and 22JCYBJC00220 (to CXL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Shuaiyi, Zhao Xiaoxuan, Li Qi, Xing Zheng, Li Qingwen, Chu Xiaolei. Causal relationship between 91 inflammatory proteins and cervical disc degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3732-3740.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
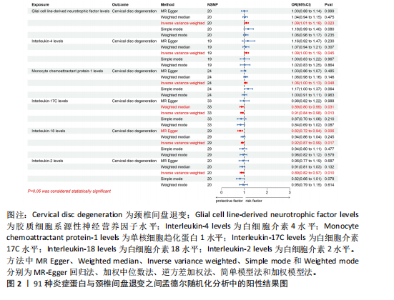
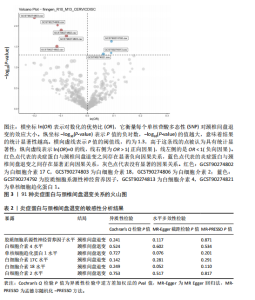
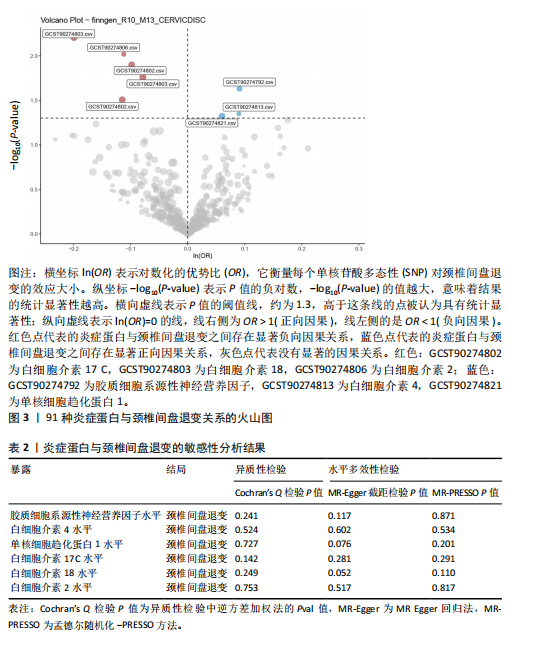
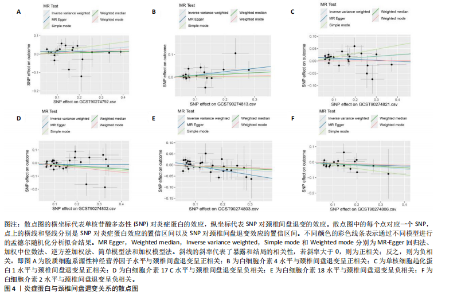
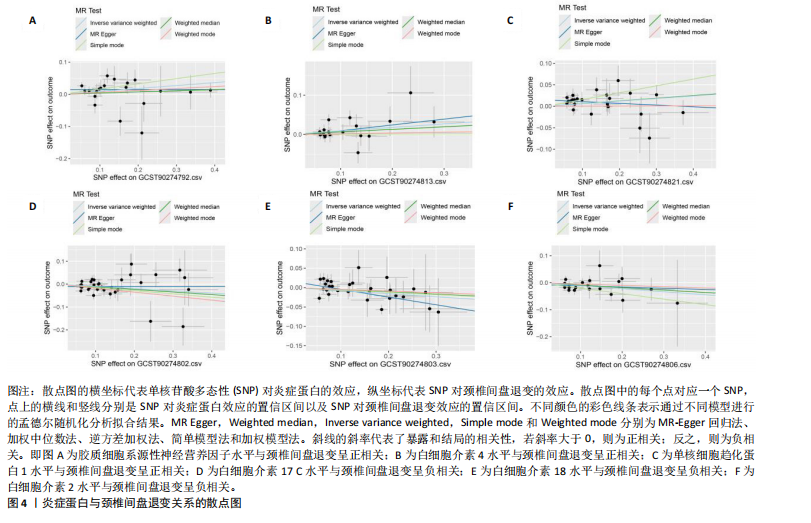
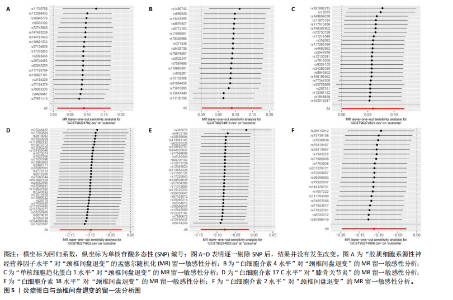
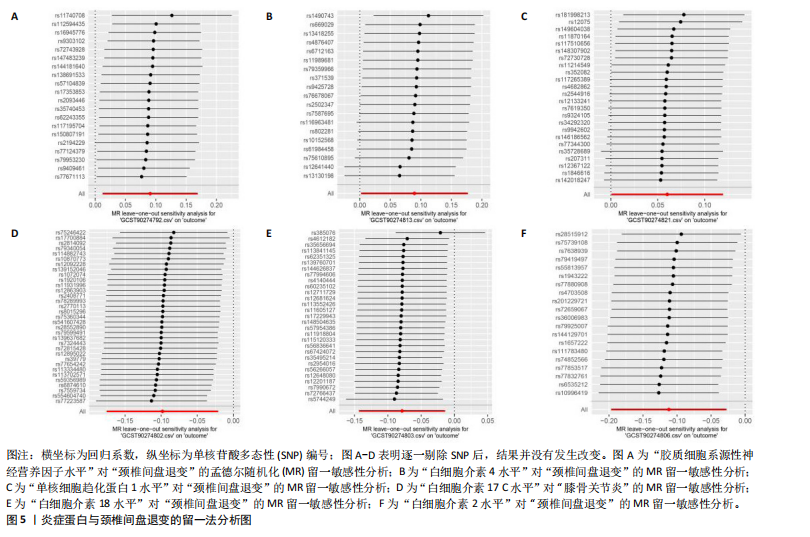
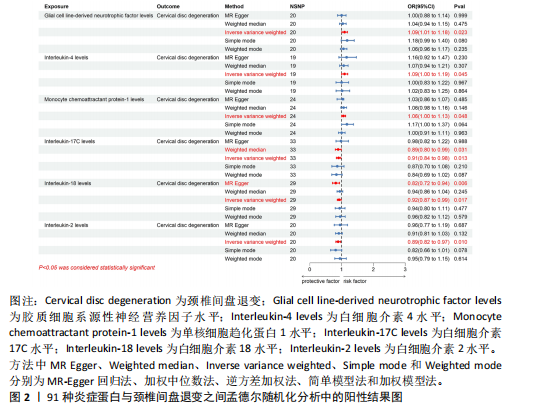
2.1 工具变量的选取结果 91个炎症蛋白共纳入2 337个SNPs,F值范围为19.513-3 469.481,均符合F > 10,说明文章具有弱工具变量偏倚的可能性较小。将过滤后的相关工具变量,与结局数据进行孟德尔随机化分析。 2.2 炎症蛋白对颈椎间盘退变的因果效应 文章以IVW方法为主要分析方法,发现3种炎症蛋白与颈椎间盘退变呈正相关,另外3种炎症蛋白与颈椎间盘退变呈负相关,见图2,3。IVW方法分析结果显示,胶质细胞系源性神经营养因子水平(glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor levels,GDNF)(OR=1.095,95%CI:1.012-1.184,P=0.023)、白细胞介素4水平(OR= 1.094,95%CI:1.002-1.194,P=0.045)、单核细胞趋化蛋白1水平(monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 levels,MCP-1)(OR=1.062,95%CI:1.001-1.127,P=0.048)与颈椎间盘退变之间存在正向因果效应;白细胞介素17 C水平(OR=0.906,95%CI:0.839-0.979,P=0.013)、白细胞介素18水平(OR=0.924,95%CI:0.866-0.986,P=0.017)、白细胞介素2水平(OR=0.894,95%CI:0.821-0.973,P=0.010)与颈椎间盘退变之间存在负向因果效应。此外,文章还使用了MR-Egger回归、加权中位数法、简单模型法、加权模型法对IVW方法的结果进行补充验证,结果显示其他4种方法结果的方向与IVW方法一致,见图4。 文章进行了一系列敏感性分析,以检验结果是否存在异质性和水平多效性,见表2。根据Cochran’s Q检验结果,没有观察到显著的异质性(P > 0.05)。同时MR-Egger回归的截距均接近于0且检验P值均> 0.05,MR-PRESSO方法结果未检测到离群值,表示结果不存在水平多效性。此外,留一法检验分析显示,在逐个剔除单核苷酸多态性后结果相对稳定,无单核苷酸多态性对因果关系具有较大影响,见图5。 2.3 颈椎间盘退变对炎症蛋白的因果效应 文章对颈椎间盘退变与91种炎症蛋白进行反向孟德尔随机化分析,分析结果的P值均> 0.05,表明颈椎间盘退变与91种炎症蛋白均不具有反向因果关系,进一步验证了正向孟德尔随机化分析得出的结果。"
| [1] TERAGUCHI M, YOSHIMURA N, HASHIZUME H, et al. Prevalence and distribution of intervertebral disc degeneration over the entire spine in a population-based cohort: the Wakayama Spine Study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(1):104-110. [2] WEGNER M, BACKHAUSS JC, MICHALSKY Y, et al. Prevalence of degenerative vertebral disc changes in elite female Crossfit athletes - a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):963. [3] BRINJIKJI W, LUETMER PH, COMSTOCK B, et al. Systematic literature review of imaging features of spinal degeneration in asymptomatic populations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015;36(4):811-816. [4] LV Y, TIAN W, CHEN D, et al. The prevalence and associated factors of symptomatic cervical Spondylosis in Chinese adults: a community-based cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):325. [5] KAZEMINASAB S, NEJADGHADERI S A, AMIRI P, et al. Neck pain: global epidemiology, trends and risk factors. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):26. [6] BAUCHER G, TASKOVIC J, TROUDE L, et al. Risk factors for the development of degenerative cervical myelopathy: a review of the literature. Neurosurg Rev. 2022; 45(2):1675-1689. [7] CHU X, LIU S, ZHAO X, et al. Case report: virtual reality-based arm and leg cycling combined with transcutaneous electrical spinal cord stimulation for early treatment of a cervical spinal cord injured patient. Front Neurosci. 2024;18:1380467. [8] LYU F J, CUI H, PAN H, et al. Painful intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation: from laboratory evidence to clinical interventions. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):7. [9] WUERTZ K, HAGLUND L. Inflammatory mediators in intervertebral disk degeneration and discogenic pain. Global Spine J. 2013;3(3):175-184. [10] RISBUD MV, SHAPIRO IM. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(1):44-56. [11] PENG B, DEPALMA MJ. Cervical disc degeneration and neck pain. J Pain Res. 2018;11:2853-2857. [12] SMITH GD, EBRAHIM S. Mendelian randomization: prospects, potentials, and limitations. Int J Epidemiol. 2004;33(1):30-42. [13] DAVIES NM, HOLMES MV, DAVEY SG. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: a guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ. 2018;362:k601. [14] WU GL, LIU YZ, ZHANG L. Editorial: Mendelian randomization: approach and applications. Front Genet. 2021;12:752146. [15] ZHENG J, BAIRD D, BORGES MC, et al. Recent developments in mendelian randomization studies. Curr Epidemiol Rep. 2017;4(4):330-345. [16] ZHAO JH, STACEY D, ERIKSSON N, et al. Genetics of circulating inflammatory proteins identifies drivers of immune-mediated disease risk and therapeutic targets. Nat Immunol. 2023;24(9):1540-1551. [17] 陈世崧,黄凯,徐泓杰,等.91种炎症蛋白与5种心血管疾病的因果关系:双向孟德尔随机化研究[J].海军军医大学学报,2024,45(5):558-568. [18] LI P, WANG H, GUO L, et al. Association between gut microbiota and preeclampsia-eclampsia: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med. 2022;20(1):443. [19] XIAO Z, WANG Z, ZHANG T, et al. Bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis of the genetic association between primary lung cancer and colorectal cancer. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):722. [20] PALMER TM, LAWLOR DA, HARBORD RM, et al. Using multiple genetic variants as instrumental variables for modifiable risk factors. Stat Methods Med Res. 2012;21(3): 223-242. [21] YUAN S, WANG L, SUN J, et al. Genetically predicted sex hormone levels and health outcomes: phenome-wide Mendelian randomization investigation. Int J Epidemiol. 2022;51(6):1931-1942.
[22] SLOB E, BURGESS S. A comparison of robust Mendelian randomization methods using summary data. Genet Epidemiol. 2020;44(4):313-329. [23] GRECO MF, MINELLI C, SHEEHAN NA, et al. Detecting pleiotropy in Mendelian randomisation studies with summary data and a continuous outcome. Stat Med. 2015; 34(21):2926-2940. [24] HEMANI G, ZHENG J, ELSWORTH B, et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife. 2018;7:e34408. [25] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017;32(5):377-389. [26] YUAN Z, ZHU H, ZENG P, et al. Testing and controlling for horizontal pleiotropy with probabilistic Mendelian randomization in transcriptome-wide association studies. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3861. [27] HEMANI G, BOWDEN J, DAVEY SG. Evaluating the potential role of pleiotropy in Mendelian randomization studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2018;27(R2):R195-R208. [28] 陈帅,金杰,韩化伟,等.两样本孟德尔随机化分析循环炎症细胞因子与骨密度的因果关联[J].中国组织工程研究,2025, 29(8):1556-1564. [29] 吴广涛,秦刚,何凯毅,等.免疫细胞与膝骨关节炎之间因果作用:一项两样本双向孟德尔随机化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(5):1081-1090. [30] BAI R, REN L, GUO J, et al. The causal relationship between pure hypercholesterolemia and psoriasis: a bidirectional, two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Skin Res Technol. 2023;29(12):e13533. [31] LIU G, ZHANG H, CHEN M, et al. Causal relationship between intervertebral disc degeneration and osteoporosis: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024;15:1298531. [32] TOMAR M, BHOWMIK NC, SINGH S, et al. Efficacy of individualized homeopathic medicines in the treatment of cervical spondylosis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Complement Med Res. 2023;30(1):26-36. [33] TAO Y, GALBUSERA F, NIEMEYER F, et al. Radiographic cervical spine degenerative findings: a study on a large population from age 18 to 97 years. Eur Spine J. 2021; 30(2):431-443. [34] CHEN X, WANG Z, DENG R, et al. Intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammatory microenvironment: expression, pathology, and therapeutic strategies. Inflamm Res. 2023;72(9):1811-1828. [35] ZHENG Q, LIN R, WANG D, et al. Effects of circulating inflammatory proteins on spinal degenerative diseases: Evidence from genetic correlations and Mendelian randomization study. JOR Spine. 2024; 7(2):e1346. [36] BIRNEY E. Mendelian randomization. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022;12(4): a041302. [37] IBANEZ CF, PARATCHA G, LEDDA F. RET-independent signaling by GDNF ligands and GFRalpha receptors. Cell Tissue Res. 2020; 382(1):71-82. [38] PEREZ-GARCIA MJ, CENA V, de PABLO Y, et al. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor increases intracellular calcium concentration. Role of calcium/calmodulin in the activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(7): 6132-6142. [39] LI T T, REN WH, XIAO X, et al. NMDA NR2A and NR2B receptors in the rostral anterior cingulate cortex contribute to pain-related aversion in male rats. Pain. 2009;146(1-2): 183-193. [40] CORTES D, CARBALLO-MOLINA OA, CASTELLANOS-MONTIEL MJ, et al. The non-survival effects of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor on neural cells. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017;10:258. [41] YAMADA J, AKEDA K, SANO T, et al. Expression of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in the human intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(13):E768-E775. [42] CHAKMA CR, GOOD-JACOBSON KL. Requirements of IL-4 during the generation of B cell memory. J Immunol. 2023;210(12): 1853-1860. [43] NELMS K, KEEGAN AD, ZAMORANO J, et al. The IL-4 receptor: signaling mechanisms and biologic functions. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:701-738. [44] HERSHEY GK. IL-13 receptors and signaling pathways: an evolving web. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111(4):677-690. [45] GAO F, DENG C, WANG Z, et al. Causal relationship of interferon-gamma and interleukin-18 upstream of intervertebral disc degeneration pathogenesis: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Neurol. 2024;15:1420942. [46] KEDONG H, WANG D, SAGARAM M, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of interleukin-4 on intervertebral disc cells. Spine J. 2020; 20(1):60-68. [47] SINGH S, ANSHITA D, RAVICHANDIRAN V. MCP-1: Function, regulation, and involvement in disease. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;101(Pt B):107598. [48] YOSHIMURA T, LI C, WANG Y, et al. The chemokine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1/CCL2 is a promoter of breast cancer metastasis. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023; 20(7):714-738. [49] KAWAI M, INOUE T, INATANI M, et al. Elevated levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in the aqueous humor after phacoemulsification. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(13):7951-7960. [50] SANTAELLA A, KUIPERIJ HB, van RUMUND A, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 correlates with progression of Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2020;6(1):21. [51] ZHANG XW, QIN X, QIN CY, et al. Expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and CC chemokine receptor 2 in non-small cell lung cancer and its significance. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013;62(3):563-570. [52] AKHTER S, TASNIM FM, ISLAM MN, et al. Role of Th17 and IL-17 cytokines on inflammatory and auto-immune diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2023;29(26):2078-2090. [53] SUN L, WANG L, MOORE BB, et al. IL-17: Balancing protective immunity and pathogenesis. J Immunol Res. 2023;2023: 3360310. [54] MILOVANOVIC J, ARSENIJEVIC A, STOJANOVIC B, et al. Interleukin-17 in chronic inflammatory neurological diseases. Front Immunol. 2020;11:947. [55] OU-YANG DC, KLECK CJ, ACKERT-BICKNELL CL. Genetics of intervertebral disc degeneration. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2023;21(1):56-64. [56] ZHANG K, GAO L, WANG HX, et al. Interleukin-18 inhibition protects against intervertebral disc degeneration via the inactivation of caspase-3/9 dependent apoptotic pathways. Immunol Invest. 2022; 51(6):1895-1907. [57] IHIM SA, ABUBAKAR SD, ZIAN Z, et al. Interleukin-18 cytokine in immunity, inflammation, and autoimmunity: biological role in induction, regulation, and treatment. Front Immunol. 2022;13:919973. [58] LYKHOPIY V, MALVIYA V, HUMBLET-BARON S, et al. “IL-2 immunotherapy for targeting regulatory T cells in autoimmunity”. Genes Immun. 2023;24(5):248-262. [59] HASHIMOTO M, ARAKI K, CARDENAS MA, et al. PD-1 combination therapy with IL-2 modifies CD8(+) T cell exhaustion program. Nature. 2022;610(7930):173-181. [60] NIEDERLOVA V, TSYKLAURI O, KOVAR M, et al. IL-2-driven CD8(+) T cell phenotypes: implications for immunotherapy. Trends Immunol. 2023;44(11):890-901. [61] WHYTE CE, SINGH K, BURTON OT, et al. Context-dependent effects of IL-2 rewire immunity into distinct cellular circuits. J Exp Med. 2022;219(7):e20212391. [62] SKRIVANKOVA VW, RICHMOND RC, WOOLF B, et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using mendelian randomization: the STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA. 2021;326(16):1614-1621. [63] Le MAITRE CL, HOYLAND JA, FREEMONT AJ. Catabolic cytokine expression in degenerate and herniated human intervertebral discs: IL-1beta and TNFalpha expression profile. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(4):R77. [64] XU J, NUNEZ G. The NLRP3 inflammasome: activation and regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 2023;48(4):331-344. [65] WANG J, MARKOVA D, ANDERSON DG, et al. TNF-alpha and IL-1beta promote a disintegrin-like and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type I motif-5-mediated aggrecan degradation through syndecan-4 inintervertebral disc. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286(46):39738-39749. [66] SHAN C, ZHANG C, ZHANG C. The role of IL-6 in neurodegenerative disorders. Neurochem Res. 2024;49(4):834-846. [67] CLARK DN, BEGG LR, FILIANO AJ. Unique aspects of IFN-gamma/STAT1 signaling in neurons. Immunol Rev. 2022;311(1):187-204. |
| [1] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei, Zhou Jiatan. Based on Mendelian randomization, the causal relationship between 1400 metabolites and sarcopenia and the correlation analysis of cardiovascular disease were investigated [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [3] | Dong Tingting, Chen Tianxin, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei. Causal relationship between modifiable factors and joint sports injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1953-1962. |
| [4] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [5] | Chen Yilin, Jiang Xiaobo, Qu Honglin, Liu Ruilian. General pattern of GSK3/Nrf2-regulated biological rhythms in organismal aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1257-1264. |
| [6] |
Zhao Wensheng, Li Xiaolin, Peng Changhua, Deng Jia, Sheng Hao, Chen Hongwei, Zhang Chaoju, He Chuan.
Gut microbiota and osteoporotic fractures #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1296-1304.
|
| [7] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [8] | Li Jiatong, Jin Yue, Liu Runjia, Song Bowen, Zhu Xiaoqian, Li Nianhu . Association between thyroid function levels and phenotypes associated with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1312-1320. |
| [9] | Wu Guangtao, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Fan Yidong, Li Weicai, Zhu Baogang, Cao Ying . Causal relationship between immune cells and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1081-1090. |
| [10] | Huang Haina, Yu Yanrong, Bi Jian, Huang Miao, Peng Weijie. Epigenetic characteristics of hepatogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional culture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7848-7855. |
| [11] | Wang Xuepeng, , He Yong, . Effect of insulin-like growth factor family member levels on inflammatory arthritis: a FinnGen biobank-based analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7656-7662. |
| [12] | Wang Tao, Wang Shunpu, Min Youjiang, Wang Min, Li Le, Zhang Chen, Xiao Weiping. Causal relationship between gut microbiota and rheumatoid arthritis: data analysis in European populations based on GWAS data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7663-7668. |
| [13] | Han Jie, Pan Chengzhen, Shang Yuzhi, Zhang Chi. Identification of immunodiagnostic biomarkers and drug screening for steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7690-7700. |
| [14] | Wu Zhenhua, Zhang Xiwei, Wang Yipin, Li Qianqian. Relationship between seven serum lipid traits and osteoarthritis: a large sample analysis of European population in IEU OPEN GWAS database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 7004-7014. |
| [15] | Liu Xiaowu, Liu Jinping, Wu Ting, He Xian, Cai Jianxiong. Antioxidants from different sources and osteoarthritis: a genome-wide association analysis in European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 7015-7027. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||